Abstract
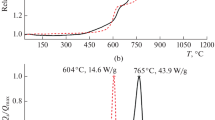
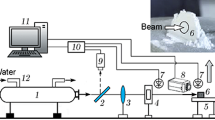
This paper presents the results of an experimental study of the processes of thermal decomposition and ignition of high-energy materials (HEMs) containing an oxidizer, a combustible binder, and dispersed additives of aluminum, aluminum borides (AlB2 and AlB12), and amorphous boron. A Netzsch STA 449 F3 Jupiter thermal analyzer and an experimental testbed, which includes a continuous-wave CO2 laser, are used to investigate the response and ignition characteristics of two basic HEM compositions based on AP/SKDM/Me and AP/AN/MPVT/Me at different heating rates. It is revealed that ammonium nitrate at low heat flux densities (\(q< 130\) W/cm2) decomposes and melts, forming a liquid layer on the reaction surface and increasing the delay time of the emergence of a HEM flame containing Al, AlB2, and AlB12. As the heat flux density becomes higher, the effect of the liquid layer on the reaction surface of the sample decreases due to an increase in the surface temperature, the outflow rate of gaseous decomposition products, and the layer evaporation.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
L. T. DeLuca, “Overview of Al-based Nanoenergetic Ingredients for Solid Rocket Propulsion," Defence Technol. 14 (5), 357–365 (2018); DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2018.06.005.
M. S. McClain, I. E. Gunduz, and S. F. Son, “Additive Manufacturing of Ammonium Perchlorate Composite Propellant with High Solids Loadings," Proc. Combust. Inst. 37 (3), 3135–3142 (2019); DOI: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.05.052.
M. Anniyappan, M. B. Talawara, R. K. Sinhaa, and K. P. S. Murthya, “Review on Advanced Energetic Materials for Insensitive Munition Formulations," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 56 (5), 3–31 (2020) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 56 (5), 495–519 (2020); DOI: 10.1134/S0010508220050019].
S. Park, S. Choi, K. Kim, et al., “Effects of Ammonium Perchlorate Particle Size, Ratio, and Total Contents on the Properties of a Composite Solid Propellant," Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 45 (9), 1376–1381 (2020); DOI: 10.1002/prep.202000055.
V. A. Arkhipov, S. S. Bondarchuk, A. G. Korotkikh, et al., “Influence of Aluminum Particle Size on Ignition and Nonstationary Combustion of Heterogeneous Condensed Systems," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 48 (5), 148–159 (2012) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 48 (5), 625–635 (2012)].
W.-Q. Pang, L. T. DeLuca, X.-Z. Fan, et al., “Combustion Behavior of AP/HTPB/Al Composite Propellant Containing Hydroborate Iron Compound," Combust. Flame 220, 157–167 (2020); DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.06.037.
A. G. Korotkikh, O. G. Glotov, V. A. Arkhipov, et al., “Effect of Iron and Boron Ultrafine Powders on Combustion of Aluminized Solid Propellants," Combust. Flame 178, 195–204 (2017); DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.01.004.
A. Okniński, P. Nowakowski, and A. Kasztankiewicz, “Survey of Low-Burn-Rate Solid Rocket Propellants," Innovative Energ. Mater.: Properties, Combust. Performance Application, 313–349 (2020); DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-4831-4_11.
A. G. Korotkikh, I. V. Sorokin, E. A. Selikhova, and V. A. Arkhipov, “Ignition and Combustion of Composite Solid Propellants Based on Double Oxidizer and Boron-Based Additives," Khim. Fiz. 39 (7), 32–40 (2020) [Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 14 (4), 592–600 (2020)].
N. Kubota and T. Kuwahara, “Combustion of GAP/HMX and GAP/TAGN Energetic Composite Materials," Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 25 (2), 86–91 (2000).
J. P. Agrawal, “Some New High Energy Materials and Their Formulations for Specialized Applications," Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 30 (5), 316–328 (2005); DOI: 10.1002/prep.200500021.
L. S. Yanovskii, D. B. Lempert, V. V. Raznoschikova, et al., “Evaluation of the Performance of Some Metals and Nonmetals in Solid Propellants for Rocket-Ramjet Engines," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 56 (1), 81–94 (2020) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 56 (1), 71–82 (2020); DOI: 10.1134/S0010508220010098].
A. G. Korotkikh and I. V. Sorokin, “Effect of Boron on the Combustion Parameters of HEM and Oxidation of Al/B and Ti/B Nanopowders," Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz. 64 (4), 3–8 (2021).
D. Sundaram, V. Yang, and R. Yetter, “Metal-Based Nanoenergetic Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications," Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 61, 293–365 (2017); DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2017.02.002.
T. R. Sippel, S. F. Son, L. J. Groven, et al., “Exploring Mechanisms for Agglomerate Reduction in Composite Solid Propellants with Polyethylene Inclusion Modified Aluminum," Combust. Flame 162 (3), 846–854 (2015); DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.08.013.
L. S. Yanovskii, Energy-Consuming Fuels for Aircraft and Rocket Engines (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2009) [in Russian].
W. Ao, Y. Wang, and S. Wu, “Ignition Kinetics of Boron in Primary Combustion Products of Propellant Based on Its Unique Characteristics," Acta Astronaut. 136, 450–458 (2017); DOI: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2017.03.002.
A. N. Pivkina, D. B. Meerov, K. A. Monogarov, et al., “Prospects of Using Boron Powders as Fuel. II. Influence of Aluminum and Magnesium Additives and Their Compounds on the Thermal Behavior of Boron Oxide," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 56 (2), 28–36 (2020) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 56 (2), 148–155 (2020); DOI: 10.1134/S0010508220010098].
Sh. Adil and B. S. Murty, “Effect of Milling on the Oxidation Kinetics of Aluminium + Boron Mixture and Nanocrystalline Aluminium Boride (AlB12)," Thermochim. Acta. 678, 178306 (2019); DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2019.178306.
A. G. Korotkikh, V. A. Arkhipov, K. V. Slyusarskya, and I. V. Sorokin, “Study of Ignition of High-Energy Materials with Boron and Aluminum and Titanium Diborides," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 54 (3), 109–115 (2018) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 54 (3), 350–356 (2018); DOI: 10.1134/S0010508220020057].
D. Liang, R. Xiao, J. Liu, and Y. Wang, “Ignition and Heterogeneous Combustion of Aluminum Boride and Boron–Aluminum Blend," Aerospace Sci. Technol. 84, 1081–1091 (2019); DOI: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.11.046.
D. A. Yagodnikov, Sh. L. Guseinov, P. A. Storozhenko, et al., “Morphologic, Chemical, and Spectral Analyses of Combustion Products of Micro- and Nanodispersed Particles of Aluminum Borides," Dokl. Akad. Nauk 484 (1), 44–47 (2019).
A. G. Korotkikh and I. V. Sorokin, “Effect of Me/B-Powder on the Ignition of High-Energy Materials," Propell., Explos., Pyrotech. 46 (11), 1709–1716 (2021); DOI: 10.1002/prep.202100180.
A. G. Korotkikh and I. V. Sorokin, “Study of the Chemical Activity of Metal Powders Based on Aluminum, Boron, and Titanium," AIP Conf. Proc. 2212 (1), 020029 (2020); DOI: 10.1063/5.0000838.
A. G. Korotkikh, I. V. Sorokin, K. V. Slyusarskiy, and V. A. Arkhipov, “Ignition of Boron-Containing High-Energy Materials Based on an Oxidizer and Polymer Binder," Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 91 (6), 928–934 (2021); [Tech. Phys. 66 (7), 895–901 (2021)]; DOI: 10.21883/JTF.2021.06.50861.329-20.
A. G. Korotkikh, I. V. Sorokin, and V. A. Arkhipov, “Laser Ignition of Aluminum and Boron Based Powder Systems," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 54 (4), 32–40 (2022) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 54 (4), 422–429 (2022); DOI: 10.1134/S0010508222040049].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, 2022, Vol. 58, No. 5, pp. 96-105.https://doi.org/10.15372/FGV20220512.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korotkikh, A.G., Sorokin, I.V. & Arkhipov, V.A. Effect of Ammonium Nitrate and Combustible Binder on the Ignition Characteristics of High-Energy Materials Containing Aluminum Borides. Combust Explos Shock Waves 58, 593–601 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508222050124
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508222050124