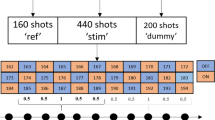
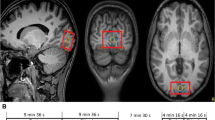
Abstract—Glutamate+glutamine (Glx) dynamics with 2s time resolution in the human occipital cortex in response to short visual stimulation was studied using functional magnetic resonance spectroscopy (fMRS) at 3 T. The dynamic changes in the Glx level and the BOLD signal were acquired in response to a 3 s flickering checkerboard in the occipital cortex of 25 volunteers. Glx concentration increased at 1 s and 15 s after the stimulus presentation. No correlation between the amplitude of the BOLD response and the change in Glx was found. The time course of changes in the total glutamate+glutamine level after the stimulus does not correspond to the turnover rate of the glutamine-glutamate cycle, but is consistent with the temporal characteristics of the vesicular cycle: the release of glutamate from vesicles and its reuptake. Thus, it can be assumed that the observed dynamics of glutamate and glutamine is not due to metabolic transformations in the neurotransmitter cycle, but due to a change in the mobility of glutamate upon exit from the vesicles and its re-entering back.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. Robinson and C. B. Williams, Clin. Chim. Acta 12, 311 (1965).
P. G. Mullins, H. Chen, J. Xu, et al., Magn. Reson. Med. 60, 964 (2008).
I. Tkač and R. Gruetter, Appl. Magn. Reson. 29, 139 (2005).
M. Garwood and L. DelaBarre, J. Magn. Reson. 153, 155 (2001).
E. Frias-Martinez et al., in Proc. 16th Scientific Meeting of Int. Soc. for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (Toronto, 2008), p. 691.
P. O. Wyss, C. Bianchini, M. Scheidegger, et al., Magn. Reson. Med. 80, 452 (2018).
P. Bednařik, I. Tkač, F. Giove, et al., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 35, 601 (2015).
R. Mekle, S. Kühn, H. Pfeiffer, et al., NMR Biomed. 30, e3672 (2017).
I. Betina Ip, U. E. Emir, A. J. Parker, et al., J. Neurosci. 39, 7968 (2019).
I. Betina Ip, A. Berrington, A. T. Hess, et al., NeuroImage 155, 113 (2017).
N. Lally, P. G. Mullins, M. V. Roberts, et al., Neuroimage 85, 823 (2014).
M. Cleve, A. Gussew, and J. R. Reichenbach, NeuroImage 105, 67 (2015).
A. Gussew, R. Rzanny, M. Erdtel, et al., NeuroImage 49, 1895 (2010).
D. Apšvalka, A. Gadie, M. Clemence, and P. G. Mullins, NeuroImage 118, 292 (2015).
K. Kurcyus, E. Annac, N. M. Hanning, et al., J. Neurosci. 38, 9967 (2018).
N. Lally, P. G. Mullins, M. V. Roberts, et al., NeuroImage 85, 823 (2014).
S. A. Huettel, A. W. Song, and G. McCarthy, Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 3rd ed. (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 2014).
A. Schousboe, S. Scafidi, L. K. Bak, et al., in Glutamate and ATP at the Interface of Metabolism and Signaling in the Brain (Springer, Cham, 2014), pp. 13–30.
L. K. Bak, A. Schousboe, and H. S. Waagepetersen, J. Neurochem. 98, 641 (2006).
S. Mangia, F. Giove, and M. DiNuzzo, Neurochem. Res. 37, 2554 (2012).
M. C. McKenna, J. Neurosci. Res. 85, 3347 (2007).
S. Mangia, I. Tkač, R. Gruetter, et al., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 27, 1055 (2007).
R. A. Kauppinen, T. R. M. Pirttila, S. O. K. Auriola, and S. R. Williams, Biochem. J. 298, 121 (1994).
P. G. Mullins, Scand. J. Psychol. 59, 91 (2018).
T. C. Sudhof, Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 509 (2004).
T. Hori and T. Takahashi, Neuron 76, 511 (2012).
D. L. Rothman, H. M. de Feyter, R. A. de Graaf, et al., NMR Biomed. 24, 943 (2011).
D. J. Heeger and D. Ress, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 142 (2002).
J. M. Chambers, in Statistical Models in S, Ed. by J. M. Chambers and T. J. Hastie (Chapman and Hall, Boca Raton, FL, 1992), pp. 95–144.
P. E. Menshchikov, N. A. Semenova, T. A. Akhadov, et al., Biophysics 62, 1009 (2017).
J. Near, R. Edden, C. J. Evans, et al., Magn. Reson. Med. 73, 44 (2015).
S. W. Provencher, Magn. Reson. Med. 30, 672 (1993).
M. Z. Goryawala, S. Sheriff, and A. A. Maudsley, NMR Biomed. 29, 1108 (2016).
J. Shen, K. F. Petersen, K. L. Behar, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 8235 (1999).
L. Hertz and Y. Chen, Front. Integr. Neurosci. 11, 18 (2017).
W. Chen, E. J. Novotny, X. H. Zhu, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90, 9896 (1993).
A. V. Tzingounis and J. I. Wadiche, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 935 (2007).
S. P. Gandhl and C. F. Stevens, Nature 423, 607 (2003).
J. Y. Sun, X. S. Wu, and L. G. Wu, Nature 417, 555 (2002).
B. Schaller, R. Mekle, L. Xin, et al., J. Neurosci. Res. 91, 1076 (2013).
Y. Boillat, L. Xin, W. van der Zwaag, and R. Gruetter, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 40, 488 (2020).
M. H. Baslow, J. Hrabe, and D. N. Guilfoyle, J. Mol. Neurosci. 32, 235 (2007).
A. V. Manzhurtsev, N. A. Semenova, M. V. Ublinskii, et al., Russ. Chem. Bull. 65, 1630 (2016).
D. Attwell, A. M. Buchan, S. Charpak, et al., Nature 468, 232 (2010).
Funding
The work was carried out with financial support of Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grant/Award no. 19-29-10040) and Russian Scientific Foundation (Grant/Award no. 18-1300030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. The study was approved by the Clinical and Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Trauma Ethics Committee. All participants were informed about the details of the study and provided written informed consent. All procedures were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Additional information
Abbreviations: fMRS, functional 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy; Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; Glx, sum of glutamate and glutamine; BOLD response, blood oxygenation level dependent response; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging; NAA, N-acetylaspartate; tNAA, the sum of N-acetylaspartate and N-acetylaspartylglutamate; Cr, the sum of creatine and osphocreatine; tCho, choline-containing compounds.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakovlev, A., Manzhurtsev, A., Menshchikov, P. et al. Functional Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study of Total Glutamate and Glutamine in the Human Visual Cortex Activated by a Short Stimulus. BIOPHYSICS 67, 265–273 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350922020245
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350922020245