Abstract
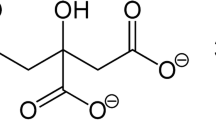
The possibility of increasing the effectiveness of antitumor drugs such as doxorubicin by preparing its complex with ultrafine magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles is considered. A method for binding doxorubicin molecules to magnetic nanoparticles via citric acid is proposed. The main magnetic properties of the obtained conjugates were studied by proton relaxometry and Mössbauer spectroscopy, while their cytotoxic activity was evaluated via spectrophotometric MTT assay in HeLa cells. It was shown that the conjugates of magnetite nanoparticles with doxorubicin are characterized by a high level of contrast in magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetic properties of doxorubicin-free and bound magnetite nanoparticles are mainly determined by the average size of nanoobjects and the phase composition and slightly depend on the composition of the stabilizing shell. The cytotoxic effect of the synthesized conjugates of magnetite nanoparticles with doxorubicin is higher than that of unbound doxorubicin. This makes it possible to increase the antitumor effect of doxorubicin and control the dynamics of its delivery in the form of a conjugate into the disease focus due to the magnetic contrast properties of nanoparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. A. Fedotcheva, A. Yu. Olenin, K. M. Starostin, et al., Khim.-Farm. Zh. 49 (4) 39 (2015).
K. Tomankova, K. Polakova, K. Pizova, et al., Int. J. Nanomedicine 10, 949 (2015).
A. G. Akopdzhanov, N. L. Shimanovski, V. Yu. Naumenko, Khim. Fizika 33 (7), 1 (2014).
N. L. Shimanovski, V. Yu. Naumenko, A. G. Akopdzhanov, et al., Nanotekhnika 20, 64 (2009).
A. G. Akopdzhanov, A. I. Sergeev, E. V. Manvelov, et al., Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. (6), 23 (2010).
T. A. Fedotcheva, A. G. Akopdzhanov, N. L. Shimanovski, et al., Biophysics (Moscow) 59 (5), 732 (2014).
K. Nawara, J. Romiszewski, K. Kijewska, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 116 (9), 5598 (2012).
N. L. Shimanovski, A. V. Semeikin, T. A. Fedotcheva, et al., Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 134 (4), 385 (2002).
A. Ganguly, S. Basu, P. Chakraborty, et al., PLoS One 55 (6), 11253 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.G. Akopdzhanov, N.L. Shimanovskii, T.A. Fedotcheva, V.K. Imshennik, Yu.V. Maksimov, S.V. Novichihin, 2016, published in Biofizika, 2016, Vol. 61, No. 6, pp. 1073–1078.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akopdzhanov, A.G., Shimanovskii, N.L., Fedotcheva, T.A. et al. The synthesis of doxorubicin-conjugated magnetite nanoparticles and their magnetic resonance and cytotoxic properties. BIOPHYSICS 61, 838–842 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350916060038
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350916060038