Abstract
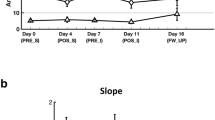
In this study we investigated a motor-neuronal functional state based on H- and M-responses from m. quadratus plantae in dogs before and after experimental spinal cord contusion with and without following local intraoperative hypothermia. H- and M-responses from m. quadratus plantae were recorded during stimulation of the tibial nerve and results were compared between the groups. Our results demonstrate that local hypothermia applied after spinal cord contusion reduces amplitude of both M- and H-responses and also H max/M max ratio that may indicate depression of motorneurons excitability. After spinal cord contusion with-out following hypothermia the excitability of the spinal motorneurons during post-traumatic period, in opposite, was significantly increased. These results support a conclusion that intraoperative hypothermia after spinal cord contusion can delay development of functional excitability of the motoneurons and protect from further changes in H- and M-responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Marion and M. R. Bullock. J. Neurotrauma 26(3), 455 (2009).
W. D. Dietrich, C. M. Atkins, and H. M. Bramlett, J. Neurotrauma 26(3), 301 (2009).
M. S. Albin, R. J. White, G. S. Locke, et al., Anesth. Analg. 46(1), 8 (1967).
C. H. Tator, Can. Med. Assoc. J. 107(2), 143 (1972).
J. D. Wells and R. R. Hansebout, Surg. Neurol. 10(3), 200 (1978).
C. E. Dixon, C. G. Markgraf, F. Angileri, et al., J. Neurotrauma 15(2), 95 (1998).
M. Yamamoto, C. R. Marmarou, M. F. Stiefel, et al., J. Neurotrauma 16(6), 487 (1999).
Y. Matsushita, H. M. Bramlett, O. Alonso, and W. D. Dietrich, Crit. Care. Med. 29(11), 2060 (2001).
F. U. Ahmad, M. Y. Wang, and A. D. Levi, World Neurosurgery, (5), ii: S1878-8750(13)00015-6 (2013).
W. D. Dietrich, A. D. Levi, M. Wang, and B. A. Green, Neurotherapeutics 8(2), 229 (2011).
C. H. Tator and L. Deecke, J. Neurosurg. 39(1), 52 (1973).
R. Morochovic, M. Chudá, J. Talánová, et al., Int. J. Neurosci. 118(4), 555 (2008).
T. E. Anderson, J. Neurosci. Methods 6(4), 327 (1982).
S. V. Lebedev, S. V. Timofeev, A. V. Zharkov, et al., Byul. Eksperim. Biol. Med. 146(10), 471 (2008).
R. F. Tumakaev, Zh. Vopr. Neirokhir. Im. N. N. Burdenko (2), 51 (2010).
R. R. Hunsebout, E. F. Kuchner, and C. Romero-Sierra, Surg. Neurol. 4(6), 531 (1975).
E. F. Kuchner and R. R. Hansebout, Surg. Neurol. 6(6), 371 (1976).
O. Kiehn, Trends Neurosci. 14(2), 68 (1991).
J. F. Miller, K. D. Paul, R. H. Lee, et al., J. Neurophysiol. 75(2), 620 (1996).
R. H. Lee and C. J. Heckman, J. Neurosci. 20(17), 6734 (2000).
J. C. Schadt and C. D. Barnes, Brain Res. 201(2), 373 (1980).
L. P. Hiersemenzel, A. Curt, and V. Dietz, Neurology 54(8), 1574 (2000).
F. J. Thompson, P. J. Reier, C. C. Lucas, and R. Parmer, J. Neurophysiol. 68(5), 1473 (1992).
A. 1. Valero-Cabré, J. Forés, and X. Navarro, J. Neurophysiol. 91(6), 2838 (2004).
R. J. Schwartzman, E. Eidelberg, and G. M. Alexander, J. Yu. Ann Neurol. 14(1), 33 (1983).
R. K. Simpson, Jr., C. S. Robertson, and J. C. Goodman, J. Spinal Cord. Med. 19(4), 215 (1996).
I. J. Llewellyn-Smith and L. C. Weaver, J. Comp. Neurol. 435(2), 226 (2001).
S. Taylor, P. Ashby, and M. Verrier, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 47(10), 1102 (1984).
J. Malmsten, Acta Physiol. Scand. 119(4), 435 (1983).
X. Y. Chen, K. C. Feng-Chen, L. Chen, et al., J. Neurotrauma 18(3), 313 (2001).
T. V. Baltina, G. G. Iafarova, and L. M. Abyazova, World Appl. Sci. J. 25(5), 822 (2013).
H. Hultborn and J. Malmsten, Acta Physiol. Scand. 119(4), 405 (1983).
A. A. Leis, H. H. Zhou, M. Mehta, et al., Muscle Nerve 19(11), 1373 (1996).
B. Calancie, J. G. Broton, K. J. Klose, et al., Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 89(3), 177 (1993).
M. Faist, M. Ertel, W. Berger, and V. Dietz, Brain 122(3), 567 (1999).
P. E. Batchelor, P. Skeers, A. Antonic, et al., PLoS One 8(8), e71317 (2013).
Y. Li, P. J. Harvey, X. Li, and D. J. Bennett, J. Neurophysiol. 91(5), 2236 (2004).
R. L. Harris, C. T. Putman, M. Rank, et al., J. Neurophysiol. 97(2), 1040 (2007).
A. S. Gorgey, A. E. Chiodo, E. D. Zemper, et al., J. Spinal Cord Med. 33(1), 6 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © G.G. Iafarova, R.F. Tumakaev, A.R. Hazieva, T.V. Baltina, 2014, published in Biofizika, 2014, Vol. 59, No. 5, pp. 1017–1022.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iafarova, G.G., Tumakaev, R.F., Hazieva, A.R. et al. Effect of local hypothermia on H- and M-responses after spinal cord contusion in dogs. BIOPHYSICS 59, 829–833 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350914050303
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350914050303