Abstract
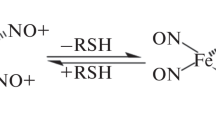
It has been shown that interaction of cysteine dinitrosyl iron complexes with methylglyoxal leads to the formation of a new type of dinitrosyl iron complexes, EPR spectrum of these complexes essentially differs from spectra of dinitrosyl iron complexes containing unmodified thiol. The products of the cysteine reaction with methylglyoxal are hemithioacetals, Schiff bases and thiazolidines, which most likely serve as ligands for the new type of dinitrosyl iron complexes. It has been shown that the new type of dinitrosyl iron complexes as cysteine dinitrosyl iron complexes, which are physiological donors of nitric oxide, exert a vasodilator effect. It has also been found that the oxidative destruction of the new type of dinitrosyl iron complexes occurs at normal oxygen partial pressure, but these dinitrosyl iron complexes remain rather stable under hypoxia modeling. An assumption that the destruction of the new type of dinitrosyl iron complexes is caused by the formation of a bound peroxynitrite-containing intermediate is made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Goldin, J. A. Beckman, A. M. Schmidt, and M. A. Creager, Circulation 114(6), 597 (2006).
A. Dhar, I. Dhar, K. M. Desai, and L. Wu, British J. Pharmacol. 161(8), 1843 (2010).
S. Vasdev and J. Stuckless, Int. J. Angiol. 19(2), e58 (2010).
R. Bucala, K. J. Tracey, and A. Cerami, J. Clin. Invest. 87(2), 432 (1991).
M. Hogan, A. Cerami, and R. J. Bucala, J. Clin. Invest. 90(3), 1110 (1992).
C. Napoli, L. O. Lerman, F. de Nigris, et al., J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 40(8), 1515 (2002).
T. W. C. Lo, M. E. Westwood, A. C. McLellan, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 269(51), 32299 (1994).
O. Brouwers, T. Teerlink, J. van Bezu, et al., Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1126, 231 (2008).
L. Wu and B. H. J. Juurlink, Hypertension 39(3), 809 (2002).
L. Wu, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 83(1), 63 (2005).
O. Brouwers, P. M. Niessen, G. Haenen, et al., Diabetologia 53(5), 989 (2010).
T. Chang, R. Wang, and L. Wu, Free Rad. Biol. Med. 38(2), 286 (2005).
M. G. Rosca, T. G. Mustada, M. T. Kinter, et al., Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 289(2), 420 (2005).
Z. Guo, Z. Xia, J. Jiang, and J. H. McNeill, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 92(4), H1728 (2007).
H.-S. Yim, S-O. Kang, Y-Ch. Hah, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 270(47), 28228 (1995).
K. B. Shumaev, S. A. Gubkina, E. M. Kumskova, et al., Biokhimiya 74(4), 568 (2009).
A. F. Vanin, V. P. Mokh, V. A. Serezhenkov, and E. I. Chazov, Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 16(2), 322 (2007).
A. F. Vanin, Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 21(1), 1 (2008).
K. B. Shumaev, A. A. Gubkin, S. A. Gubkina, et al., Biofizika 51(3), 472 (2006).
K. B. Shumaev, A. F. Vanin, V. L. Lakomkin, et al., Kardiol. Vestn. 2(2), 10 (2007).
K. L. Gudkov, K. B. Shumaev, E. I. Kalennikova, et al., Biofizika 52(3), 503 (2007).
K. B. Shumaev, A. A. Gubkin, V. A. Serezhenkov, et al., Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 18(1), 37 (2008).
J. M. Acimovic, B. D. Stanimirovic, N. Todorovic, et al., Chem. Biol. Interact. 188(1), 21 (2010).
P. B. L. Pun and M. P. Murphy, Int. J. Cell Biol. 843505, Epub. 2012 June 21 (2012).
L. Pripis-Nicolau, G. de Revel, A. Bertrand, and A. J. Maujean, Agric. Food Chem. 48(9) (2000).
D. Sh. Burbaev, A. F. Vanin, and L. A. Blumenfeld, Zh. Strukt. Khimii 2(1), 252 (1971).
A. F. Vanin and D. Sh. Burbaev, J. Biophys. 878236, Epub. 2011 Feb. 14 (2011).
J. Yang, X. Duan, A. P. Landry, and H. Ding, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 49(2), 268 (2010).
N. G. Tran, H. Kalyvas, K. M. Skodjet, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(5), 1184 (2011).
H, Ohshima, I. K. O’Neill, M. Friesen, et al., IARC Sci. Publ. 57, 77 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.B. Shumaev, S.A. Gubkina, A.F. Vanin, D.Sh. Burbaev, V.P. Mokh, A.F. Topunov, E.K. Ruuge, 2013, published in Biofizika, 2013, Vol. 58, No. 2, pp. 239–245.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shumaev, K.B., Gubkina, S.A., Vanin, A.F. et al. Formation of a new type of dinitrosyl iron complexes bound to cysteine modified with methylglyoxal. BIOPHYSICS 58, 172–177 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000635091302019X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000635091302019X