Abstract
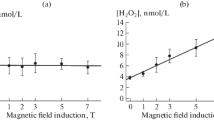
It is (theoretically) shown by an example of the reaction of a radical with an oxygen molecule that the alternating component of a combined weak magnetic field affects the rate constants of chemical reactions. The mechanism of transduction of a weak magnetic perturbation from the primary receptor of the field to experimentally observed biological effects is followed. It is stated that the external magnetic field alters the initial population of energy levels. The magnitude of these changes depends on the field parameters. The exposure to an alternating field with proper parameters can substantially increase the concentration of reactive oxygen species in biological systems. By controlling their concentration by means of weak magnetic field, it is possible to affect the key links of metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Berman, L. Chacon, D. House, et al., Bioelectromagnetics 11(2), 169 (1990).
C. F. Blackman, S. G. Benane, and D. E. House, Bioelectromagnetics 22(2), 122 (2001).
N. A. Belova and V. V. Lednev, Biofizika 46(1), 122 (2001).
J. Juutilainen, E. Laara, and K. Saali, Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relative Studies Phys. Chem. Med. 52(5), 787 (1987).
R. P. Liburdy, T. R. Sloma, R. Sokolic, and P. Yaswen, J. Pineal Res. 14, 89 (1993).
M. A. Persinger, L. L. Cook, and S. A. Koren, Int. J. Neurosci. 100(1/4), 107 (1999).
V. V. Novikov, Biophysics 49(Suppl. 1), S43 (2004).
N. V. Bobkova, V. V. Novikov, N. I. Medvinskaya, et al., Biophysics 50(Suppl. 1), S2 (2005).
V. V. Novikov, V. O. Ponomarev, and E. E. Fesenko, Biophysics 50(Suppl. 1), S110 (2005).
V. V. Novikov, N. I. Novikova, and A. K. Kachan, Biofizika 41(4), 934 (1996).
V. V. Novikov, I. M. Sheiman, and E. E. Fesenko, Bioelectromagnetics (in press).
V. V. Novikov and M. N. Zhadin, Biofizika 39(1), 41 (1994).
A. Pazur, Biomagnetic Res. Technol. 2, 8 (2004).
N. Comisso, E. Del Giudice, A. De Ninno, et al., Bioelectromagnetics 27(1), 16 (2006).
M. N. Zhadin, V. V. Novikov, F. S. Barnes, and N. F. Pergola, Bioelectromagnetics 19(1), 41 (1998).
A. L. Buchachenko, D. A. Kuznetsov, and V. L. Berdinskii, Biofizika 51(3), 545 (2006).
V. V. Lednev, A. K. Srebnitskaya, E. N. Il’yasova, et al., Dokl. Akad. Nauk 348(6), 830 (1996).
N. A. Belova, O. N. Ermakova, A. M. Ermakov, et al., Environmentalist 27, 411 (2007).
V. V. Novikov and A. V. Karnaukhov, Bioelectromagnetics 18(1), 25 (1997).
V. O. Ponomarev, V. V. Novikov, A. V. Karnaukhov, and O. A. Ponomarev, Biofizika 53(2), 197 (2008).
A. L. Buchachenko, Chemical Polarization of Electrons and Nuclei (Nauka, Moscow, 1974) [in Russian].
G. M. Zhidomirov, P. V. Schastnev, and N. D. Chuvylkin, Quantum-Chemical Calculations of Magnetic Resonance Parameters. Free Radicals (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1978) [in Russian].
V. F. Mikhailov, V. K. Mazurik, and E. B. Burlakova, Radiats. Biol. Radioekol. 43(1), 5 (2003).
Yu. A. Vladimirov, Soros. Obraz. Zh. 6(9), 2 (2000).
M. M. Potselueva, A. V. Pustovidko, Yu. V. Evtodienko, et al., Dokl. Akad. Nauk 359(3), 415 (1998).
V. V. Novikov and E. E. Fesenko, Biofizika 46(2), 235 (2001).
V. N. Kazachenko, O. N. Deryugina, K. V. Kochetkov, and E. E. Fesenko, Biofizika 44(5), 796 (1999).
L. M. Apasheva, A. V. Lobanov, and G. G. Komisarov, Dokl. RAN 406(1), 108 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.O. Ponomarev, V.V. Novikov, 2009, published in Biofizika, 2009, Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. 235–241.
Editor’s Note: This text meticulously reproduces the original Russian publication, so that the reader may more clearly recognize the major problems with this line of scholarly activity. A.G.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponomarev, V.O., Novikov, V.V. Effect of low-frequency alternating magnetic fields on the rate of biochemical reactions proceeding with formation of reactive oxygen species. BIOPHYSICS 54, 163–168 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350909020079
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350909020079