Abstract
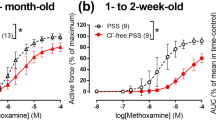
The age-related dynamics of the activity of signaling pathways coupled with α1-adrenoreceptors and their dependence on sympathetic innervation of arterial smooth muscle has been studied. For this purpose, the effects of protein kinase C inhibitor (GF 109203X, 10−6 M and Rho-kinase inhibitor (Y27632, 10−5 M) on isometric contraction of the rat saphenous artery in response to the α1-adrenoreceptor agonist methoxamine were determined. The rats in the age of two weeks (with partially developed sympathetic innervation) had the lower vascular sensitivity to methoxamine than adult rats, but the effects of both inhibitors were more prominent. The denervation induced by excision of sympathetic ganglia in adult rats increased the arterial sensitivity to methoxamine but the sensitivity to inhibitors was unchanged. Thus, the postnatal development of the arterial smooth muscle is accompanied by diminution of the role of protein kinase C and Rho-kinase in the regulation of contraction, but these changes do not correlate with the changes in arterial sensitivity to α1-adrenergic stimulation and development of sympathetic innervation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α-AR:
-
α-adrenoreceptors
- [Ca2+]i :
-
intracellular concentration of free Ca2+
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- RhoK:
-
Rho kinase (kinase activated by the Rho protein)
- MLC:
-
myosin light chains
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinases
References
G. K. Owens, M. S. Kumar, and B. R. Wamhoff, Physiol. Rev. 84, 767 (2004).
R. D. Bevan, Hypertension 6(Suppl. III), III–1 (1984).
D. H. Damon, Am. J. Physiol. 288, H2785 (2005).
M. E. Todd, J. Anat. 131, 121 (1980).
D. R. Varma and X. F. Deng, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 78, 267 (2000).
S. M. Yu, S. Y. Tsai, J. H. Guh, et al., Circulation 94, 547 (1996).
J. K. Phillips, M. Vidovic, and C. E. Hill, Mech. Ageing Dev. 92, 235 (1996).
J. K. Phillips and C. E. Hill, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 17, 377 (1999).
F. R. Stassen, R. G. Maas, P. M. Schiffers, et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 284, 399 (1998).
T. M. Seasholtz, M. Majumdar, and J. H. Brown, Mol. Pharmacol. 55, 949 (1999).
A. V. Vorotnikov, M. A. Krymskii, and V. P. Shirinskii, Biokhimiya 67(12), 1587 (2002).
A. P. Somlyo and A. V. Somlyo, Physiol. Rev. 83, 1325 (2003).
N. B. Standen and J. M. Quayle, Acta Physiol. Scand. 164, 549 (1998).
K. D. Luykenaar, S. E. Brett, B. N. Wu, et al., Am. J. Physiol. 286, H1088 (2004).
B. Y. Su, K. M. Reber, C. A. Nankervis, and P. T. Nowicki, Am. J. Physiol. 284, G445 (2003).
J. Belik, E. Kerc, and M. D. Pato, Am. J. Physiol. 290, L509 (2005).
M. Ekman, K. Fagher, M. Wede, et al., J. Gen. Physiol. 125, 187 (2005).
R. J. Sandoval, E. R. Injeti, W. T. Gerthoffer, and W. J. Pearce, Am. J. Physiol. 293, H2183 (2007).
M. C. Payne, H. Y. Zhang, T. Prosdocimo, et al., J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 40, 274 (2006).
I. Mueed, P. Bains, L. Zhang, and K. M. MacLeod, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 82, 895 (2004).
S. T. Abraham, M. Robinson, and P. J. Rice, Pharmacology 67, 32 (2003).
K. Kacem and R. Sercombe, Auton. Neurosci. 124, 38 (2006).
O. S. Tarasova, V. A. Puzdrova, V. U. Kalenchuk, and V. B. Koshelev, Biofizika 51(5), 912 (2006).
J. Q. Griffith, E. J. Farris, and J. B. Lippincott, in The Rat in Laboratory Investigation (Philadelphia-Montreal-London, 1942).
M. J. Mulvany and W. Halpern, Circ. Res. 41, 19 (1977).
M. Gollasch, H. Haase, C. Ried, et al., FASEB J. 12, 593 (1998).
J. F. Quignard, E. Grazzini, G. Guillon, et al., Pflugers Arch. 431, 791 (1996).
S. Dakshinamurti, L. Mellow, and N. L. Stephens, Pediatric Pulmonology 40, 398 (2005).
W. J. Pearce, J. M. Williams, M. M. Chang, and W. T. Gerthoffer, Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 111, 36 (2003).
W. W. Fleming, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 291, 925 (1999).
K. Ramos, W. T. Gerthoffer, and D. P. Westfall, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 236, 80 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.V. Mochalov, V.U. Kalenchuk, D.K. Gainullina, A.V. Vorotnikov, O.S. Tarasova, 2008, published in Biofizika, 2008, Vol. 53, No. 6, pp. 1102–1108.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochalov, S.V., Kalenchuk, V.U., Gainullina, D.K. et al. The contribution of protein kinase C and rho-kinase to the regulation of receptor-dependent contraction of arteries decreases with age independently of sympathetic innervation. BIOPHYSICS 53, 626–631 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350908060298
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350908060298