Abstract
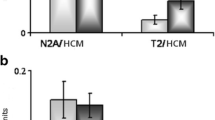
An electophoretic study of changes in composition of titin isoforms in human and rat skeletal and cardiac muscles is carried out. A more considerable decrease in the content of intact titin isoforms was observed than in the content of N2A-titin in the dorsal muscle of patients with the “stiff-person syndrome” and in m. soleus of humans and rats during development of “muscle hypogravity syndrome” and than in the content of N2BA- and N2B-titins in hypertrophic heart of spontaneously hypertensive rats. The relation between reduction of titin content in m. soleus and the increase of time the rats were in conditions of simulated microgravity is revealed. On electrophoregrams of left ventricle myocardium of patients with terminal stage of dilated cardiomyopathy the intact titin and N2BA-titin were absent and a considerable decrease in the content of N2B-titin was observed. This could be the consequence of the terminal stage of pathology. It follows that development of the diseases is accompanied by a greater destruction of intact titin than of its other forms which may be important for diagnostics of pathological processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCM:
-
dilated cardiomyopathy
References
N. Fukuda, H. L. Granzier, S. Ishiwata, and S. Kurihara, J. Physiol. Sci. 58(3), 151 (2008).
I. M. Vikhlyantsev and Z. A. Podlubnaya, Biofizika 52(6), 1020 (2007).
I. Makarenko, C. Opitz, M. Leake, et al., Curc. Res. 95, 708 (2004).
S. Nagueh, G. Shah, Y. Wu, et al., Circulation 110, 155 (2004).
Y. Wu, S. Bell, K. Trombitas, et al., Circulation 106, 1384 (2002).
C. Neagoe, M. Kulke, F. Del Monte, et al., Circulation 106, 1333 (2002).
C. M. Warren, M. C. Jordan, K. P. Roos, et al., Cardiovascular Research 59, 86 (2003).
I. Morano, K. Hadicke, S. Grom, et al., J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 26, 361 (1994).
I. V. Makarenko, M. D. Shpagina, Z. I. Vishnevskaya, and Z. A. Podlubnaya, Biofizika 47(4), 706 (2002).
K. S. Litvinova, I. M. Vikhlyantsev, I. B. Kozlovskaya, et al., J. Gravit. Physiol. 11(2), 131 (2004).
T. Toursel, L. Stevens, H. Granzier, and Y. Mounier, J. Appl. Physiol. 92, 1465 (2002).
B. S. Shenkman, T. L. Nemirovskaya, I. M. Vikhlyantsev, et al., J. Gravit. Physiol. 10(1), 53 (2003).
I. M. Vikhlyantsev and Z. A. Podlubnaya, Biofizika 51(5), 951 (2006).
Z. A. Podlubnaya, I. M. Vikhlyantsev, A. M. Mukhina, et al., Biofizika 49(3), 424 (2004).
B. S. Shekman, Z. A. Podlubnaya, and I. M. Vikhlyantsev, Biofizika 49(5), 881 (2004).
I. M. Vikhlyantsev, Z. A. Podlubnaya, and I. B. Kozlovskaya, Doklady RAN 395(6), 828 (2004).
K. Maruyama, S. Kimura, H. Yoshidomi, et al., J. Biochem. 95, 1423 (1984).
K. Wang, R. McCarter, and J. Wright, Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 7101 (1991).
H. Granzier and K. Wang, Electrophoresis 14, 56 (1993).
M. Kruger, J. Wright, and K. Wang, J. Cell Biol. 115(1), 97 (1991).
D. O. Furst, M. Osborn, R. Nave, and K. Weber, J. Cell Sci. 94, 119 (1988).
D. O. Furst, R. Nave, M. Osborn, and K. Weber, J. Cell Biol. 106, 1563 (1988).
A. Freiburg, K, Trombitas, W. Hell, et al., Curc. Res. 86, 1114 (2000).
M. L. Bang, T. Centner, F. Fornoff, et al., Circ. Res. 89, 1065 (2001).
M. L. Greaser, M. Berri, C. M. Warren, and P. E. Mozdziak, J. Musc. Res. Cell Motil. 23, 473 (2003).
M. L. Greaser, P. R. Krzesinski, C. M. Warren, et al., J. Musc. Res. Cell Motil. 26, 325 (2005).
O. Cazorla, A. Freiburg, M. Helmes, et al., Circ. Res. 86, 59 (2000).
S. Lahmers, Y. Wu, D. R. Call, et al., Circ. Res. 94, 505 (2004).
K. Maruyama, Int. Rev. Cytol. 104, 81 (1986).
I. M. Vikhlyantsev, Z. A. Podlubnaya, E. V. Karaduleva, et al., Doklady AN 417(3), 403 (2007).
S. Lange, F. Xiang, A. Yakovenko, et al., Science 308, 1599 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.M. Vikhlyantsev, Z.A. Podlubnaya, 2008, published in Biofizika, 2008, Vol. 53, No. 6, pp. 1058–1065.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vikhlyantsev, I.M., Podlubnaya, Z.A. Composition of titin isoforms of skeletal and cardiac muscles in pathologies. BIOPHYSICS 53, 592–597 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350908060237
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350908060237