Abstract
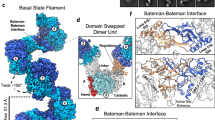
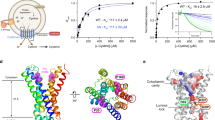
Cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) domains discovered 20 years ago can bind different adenosine derivatives (AMP, ADP, ATP, S-adenosylmethionine, NAD, diadenosine polyphosphates) and thus regulate the activities of numerous proteins. Mutations in CBS domains of enzymes and membrane transporters are associated with several hereditary diseases. The regulatory unit is a quartet of CBS domains that belong to one or two polypeptides and usually form a conserved disk-like structure. CBS domains function as “internal inhibitors” in enzymes, and their bound ligands either amplify or attenuate the inhibitory effect. Recent studies have opened a way to understanding the structural basis of enzyme regulation via CBS domains and widened the list of their bound ligands.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AdoMet:
-
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
- AID:
-
auto-inhibitory domain
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- CBS:
-
cystathionine β-synthase
- dCBS:
-
Drosophila melanogaster CBS
- hCBS:
-
human CBS
- yCBS:
-
yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS
- IMPDH:
-
inosine-5′-monophosphate dehydroge-nase
- MTA:
-
5′-methylthioadenosine
References
Bateman, A. (1997) The structure of a domain common to archaebacteria and the homocystinuria disease protein, Trends Biochem. Sci., 22, 12–13.
Scott, J. W., Hawley, S. A., Green, K. A., Anis, M., Stewart, G., Scullion, G. A., Norman, D. G., and Hardie, D. G. (2004) CBS domains form energy-sensing modules whose binding of adenosine ligands is disrupted by disease mutation, J. Clin. Invest., 113, 274–284.
Ereсo-Orbea, J., Oyenarte, I., and Martнnez-Cruz, L. A. (2013) CBS domains: ligand binding sites and conformational variability, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 540, 70–81.
Hedstrom, L. (2009) IMP dehydrogenase: structure, mechanism and inhibition, Chem. Rev., 109, 2903–2928.
Aguado-Llera, D., Oyenarte, I., Martнnez-Cruz, L. A., and Neira, J. L. (2010) The CBS domain protein MJ0729 of M. jannaschii binds DNA, FEBS Lett., 584, 4485–4489.
Baykov, A. A., Tuominen, H. K., and Lahti, R. (2011) The CBS domain: a protein module with an emerging prominent role in regulation, ACS Chem. Biol., 6, 1156–1163.
Huang, C. W., and Moore, P. K. (2015) H2S synthesizing enzymes: biochemistry and molecular aspects, in Chemistry, Biochemistry and Pharmacology of Hydrogen Sulfide (Moore, P. K., and Whiteman, M., eds.) Handb. Exp. Pharmacol., 230, 3–25.
Kery, V., Poneleit, L., and Kraus, J. P. (1998) Trypsin cleavage of human cystathionine β-synthase into an evolutionarily conserved active core: structural and functional consequences, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 355, 222–232.
Jhee, K. H., McPhie, P., and Miles, E. W. (2000) Domain architecture of the heme independent yeast cystathionine β-synthase provides insights into mechanisms of catalysis and regulation, Biochemistry, 39, 10548–10556.
Majtan, T., Pey, A. L., Fernandez, R., Fernandez, J. A., Martнnez-Cruz, L. A., and Kraus, J. P. (2014) Domain organization, catalysis and regulation of eukaryotic cystathionine beta-synthases, PLoS One, 14, e105290.
Ereсo-Orbea, J., Majtan, T., Oyenarte, I., Kraus, J. P., and Martнnez-Cruz, L. A. (2013) Structural basis of regulation and oligomerization of human cystathionine β-synthase, the central enzyme of transsulfuration, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 3790–3799.
Koutmos, M., Kabil, O., Smith, J. L., and Banerjee, R. (2010) Structural basis for substrate activation and regulation by cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) domains in cystathionine β-synthase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 20958–20963.
Oliveriusova, J., Kery, V., Maclean, K. N., and Kraus, J. P. (2002) Deletion mutagenesis of human cystathionine β-synthase. Impact on activity, oligomeric status, and S-adenosylmethionine regulation, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 48386–48394.
Maclean, K. N., Janosik, M., Oliveriusova, J., Kery, V., and Kraus, J. P. (2000) Transsulfuration in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is not dependent on heme: purification and characterization of recombinant yeast cystathionine β-synthase, J. Inorg. Biochem., 81, 161–171.
Su, Y., Majtan, T., Freeman, K. M., Linck, R., Ponter, S., Kraus, J. P., and Burstyn, J. N. (2013) Comparative study of enzyme activity and heme reactivity in Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens cystathionine β-synthases, Biochemistry, 52, 741–751.
Taoka, S., Widjaja, L., and Banerjee, R. (1999) Assignment of enzymatic functions to specific regions of the PLP-dependent heme protein cystathionine β-synthase, Biochemistry, 38, 13155–13161.
Pey, A. L., Majtan, T., Sanchez-Ruiz, J. M., and Kraus, J. P. (2013) Human cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) contains two classes of binding sites for S-adenosylmethionine (SAM): complex regulation of CBS activity and stability by SAM, Biochem. J., 449, 109–121.
Ereсo-Orbea, J., Majtan, T., Oyenarte, I., Kraus, J. P., and Martнnez-Cruz, L. A. (2014) Structural insight into the molecular mechanism of allosteric activation of human cystathionine β-synthase by S-adenosylmethionine, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 111, E3845–E3852.
Weber, G., Nakamura, H., Natsumeda, Y., Szekeres, T., and Nagai, M. (1992) Regulation of GTP biosynthesis, Adv. Enzyme Regul., 32, 57–69.
Labesse, G., Alexandre, T., Vaupre, L., Salard-Arnaud, I., Him, J. L., Raynal, B., Bron, P., and Munier-Lehmann, H. (2013) MgATP regulates allostery and fiber formation in IMPDHs, Structure, 21, 975–985.
Alexandre, T., Raynal, B., and Munier-Lehmann, H. (2015) Two classes of bacterial IMPDHs according to their quaternary structures and catalytic properties, PLoS One, 10, e0116578.
Buey, R. M., Ledesma-Amaro, R., Velazquez-Campoy, A., Balsera, M., Chagoyen, M., De Pereda, J. M., and Revuelta, J. L. (2015) Guanine nucleotide binding to the Bateman domain mediates the allosteric inhibition of eukaryotic IMP dehydrogenases, Nat. Commun., 6, 1–11.
Smith, S., Boitz, J., Chidambaram, E. S., Chatterjee, A., Ait-Tihyaty, M., Ullman, B., and Jardim, A. (2016) The cystathionine-β-synthase domains on the guanosine 5′-monophosphate reductase and inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase enzymes from Leishmania regulate enzymatic activity in response to guanylate and adenylate nucleotide levels, Mol. Microbiol., 100, 824–840.
Corton, J. M., Gillespie, J. G., and Hardie, D. G. (1994) Role of the AMP-activated protein kinase in the cellular stress response, Curr. Biol., 4, 315–324.
Kemp, B. E., Stapleton, D., Campbell, D. J., Chen, Z. P., Murthy, S., Walter, M., Gupta, A., Adams, J. J., Katsis, F., Van Denderen, B., Jennings, I. G., Iseli, T., Michell, B. J., and Witters, L. A. (2003) AMP-activated protein kinase, super metabolic regulator, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 31, 162–168.
Adams, J., Chen, Z. P., Van Denderen, B. J., Morton, C. J., Parker, M. W., Witters, L. A., Stapleton, D., and Kemp, B. E. (2004) Intrasteric control of AMPK via the γ1 subunit AMP allosteric regulatory site, Protein Sci., 13, 155–165.
Chen, L., Wang, J., Zhang, Y. Y., Yan, S. F., Neumann, D., Schlattner, U., Wang, Z. X., and Wu, J. W. (2012) AMP-activated protein kinase undergoes nucleotide-dependent conformational changes, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 19, 716–718.
Xiao, B., Heath, R., Saiu, P., Leiper, F. C., Leone, P., Jing, C., Walker, P. A., Haire, L., Eccleston, J. F., Davis, C. T., Martin, S. R., Carling, D., and Gamblin, S. J. (2007) Structural basis for AMP binding to mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase, Nature, 449, 496–500.
Xiao, B., Sanders, M. J., Underwood, E., Heath, R., Mayer, F. V., Carmena, D., Jing, C., Walker, P. A., Eccleston, J. F., Haire, L. F., Saiu, P., Howell, S. A., Aasland, R., Martin, S. R., Carling, D., and Gamblin, S. J. (2011) Structure of mammalian AMPK and its regulation by ADP, Nature, 472, 230–233.
Gowans, G. J., Hawley, S. A., Ross, F. A., and Hardie, D. G. (2013) AMP is a true physiological regulator of AMP-activated protein kinase by both allosteric activation and enhancing net phosphorylation, Cell Metab., 18, 556–566.
Witczak, C. A., Sharoff, C. G., and Goodyear, L. J. (2008) AMP-activated protein kinase in skeletal muscle: from structure and localization to its role as a master regulator of cellular metabolism, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 65, 3737–3755.
Xiao, B., Sanders, M. J., Carmena, D., Bright, N. J., Haire, L. F., Underwood, E., Patel, B. R., Heath, R. B., Walker, P. A., Hallen, S., Giordanetto, F., Martin, S. R., Carling, D., and Gamblin, S. J. (2013) Structural basis of AMPK regulation by small molecule activators, Nat. Commun., 4, 3017.
Calabrese, M. F., Rajamohan, F., Harris, M. S., Caspers, N. L., Magyar, R., Withka, J. M., Wang, H., Borzilleri, K. A., Sahasrabudhe, P. V., Hoth, L. R., Geoghegan, K. F., Han, S., Brown, J., Subashi, T. A., Reyes, A. R., Frisbie, R. K., Ward, J., Miller, R. A., Landro, J. A., Londregan, A. T., Carpino, P. A., Cabral, S., Smith, A. C., Conn, E. L., Cameron, K. O., Qiu, X., and Kurumbail, R. G. (2014) Structural basis for AMPK activation: natural and synthetic ligands regulate kinase activity from opposite poles by different molecular mechanisms, Structure, 22, 1161–1172.
Li, X., Wang, L., Zhou, X. E., Ke, J., De Waal, P. W., Gu, X., Tan, M. H., Wang, D., Wu, D., Xu, H. E., and Melcher, K. (2015) Structural basis of AMPK regulation by adenine nucleotides and glycogen, Cell Res., 25, 50–66.
Li, J., Li S., Wang, F., and Xin, F. (2017) Structural and biochemical insights into the allosteric activation mechanism of AMP-activated protein kinase, Chem. Biol. Drug Des., 89, 663–669.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V. A. Anashkin, A. A. Baykov, R. Lahti, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 10, pp. 1417-1426.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anashkin, V.A., Baykov, A.A. & Lahti, R. Enzymes regulated via cystathionine β-synthase domains. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 1079–1087 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917100017
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917100017