Abstract
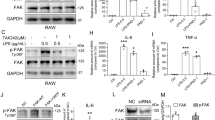
Overall analysis and understanding of mechanisms are of great importance for treatment of infantile pneumonia due to its high morbidity and mortality worldwide. In this study, we preliminarily explored the function and mechanism of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in regulation of inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharides in A549 cells. Flow cytometry, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and Western blot analysis were used to explore the correlation of FAK expression with cell apoptosis, viability, and the inflammatory cytokine activity in A549 cells. The results showed that knockdown of FAK enhanced cell viability, suppressed apoptosis, and decreased inflammatory cytokine activity. In addition, downregulation of FAK could activate the Wnt and nuclear factor κB signaling pathways. These findings suggest that FAK might be involved in progression of infantile pneumonia and could be a new therapeutic target for this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FAK:
-
focal adhesion kinase
- IP:
-
infantile pneumonia
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (assay)
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor κB
References
Wysocki, J., Sluzewski, W., Gutterman, E., Jouve, S., Moscariello, M., and Balter, I. (2016) Active hospitalbased surveillance of invasive pneumococcal disease and clinical pneumonia in infants and young children in two Polish counties, Arch. Med. Sci., 3, 629–638.
Shu, L. H., Jiang-Jiang, X. U., Wang, S., Zhong, H. Q., Dong, X. Y., Jiang, K., Zhang, H. Y., Xiong, Q., Wang, C., and Sun, T. (2015) Distribution of pathogenic microorganisms and its relationship with clinical features in children with community-acquired pneumonia, Chinese J. Contemp. Pediatr., 17, 1056–1061.
Chisti, M. J., Salam, M. A., Bardhan, P. K., Faruque, A. S., Shahid, A. S., Shahunja, K. M., Das, S. K., Hossain, M. I., and Ahmed, T. (2015) Treatment failure and mortality amongst children with severe acute malnutrition presenting with cough or respiratory difficulty and radiological pneumonia, PLoS One, 10.
Leung, D. T., Das, S. K., Malek, M. A., Qadri, F., Faruque, A. S., Chisti, M. J., and Ryan, E. T. (2015) Concurrent pneumonia in children under 5 years of age presenting to a diarrheal hospital in Dhaka, Bangladesh, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 93, 895–903.
Yu, Z. W., Qian, J., Gu, X. H., Zhang, X. J., Pan, J. R., and Ju, H. L. (2015) Changes in serum inflammatory factors in wheezing infants with community-acquired pneumonia, Chinese J. Contemp. Pediatr., 17, 815–818.
Zhang, X., Wu, J., Zhang, B., and Dong, L. (2015) Potassium dehydroandrographolide succinate injection for treatment of infantile pneumonia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis, J. Trad. Chinese Med., 35, 125–133.
Zhu, R., Lei, L., Zhao, L., Jie, D., Fang, W., Yu, S., Song, Q., Ding, Y., and Yuan, Q. (2015) Characteristics of the mosaic genome of a human parechovirus type 1 strain isolated from an infant with pneumonia in China, Infect. Genet. Evol., 29, 91–98.
Gomez Del Pulgar, T., Cebrian, A., Fernandez-Acenero, M. J., Borrero-Palacios, A., Puerto-Nevado, L. D., Martinez-Useros, J., Marin-Arango, J. P., Carames, C., Vega-Bravo, R., and Rodriguez-Remirez, M. (2016) Focal adhesion kinase: predictor of tumour response and risk factor for recurrence after neoadjuvant chemoradiation in rectal cancer, J. Cell. Mol. Med., 20, 1729–1736.
Uehara, K., and Uehara, A. (2016) Differentiated localizations of phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase in endothelial cells of rat splenic sinus, Cell Tissue Res., 83, 1–12.
Zheng, X., Bao, W., Yang, J., Zhang, T., Sun, D., Liang, Y., Li, S., Wang, Y., Feng, X., and Hao, H. (2016) Focal adhesion kinase directly interacts with TSC2 through its FAT domain and regulates cell proliferation in cashmere goat fetal fibroblasts, DNA Cell Biol., 9, 480–488.
Troutman, S., Moleirinho, S., Kota, S., Nettles, K., Fallahi, M., Johnson, G. L., and Kissil, J. L. (2016) Crizotinib inhibits NF2-associated schwannoma through inhibition of focal adhesion kinase 1, Oncotarget, doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10248.
Hao, Z., Shao, H., Golubovskaya, V. M., Chen, H., Cance, W., Adjei, A. A., and Dy, G. K. (2016) Efficacy of focal adhesion kinase inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with oncogenically activated MAPK pathways, Br. J. Cancer, 2, 203–211.
Heffler, M., Golubovskaya, V. M., Dunn, K. M. B., and Cance, W. (2013) Focal adhesion kinase autophosphorylation inhibition decreases colon cancer cell growth and enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy, Cancer Biol. Ther., 14, 761–772.
Woo, J. K., Jang, Y. S., Kang, J. H., Hwang, J. I., Seong, J. K., Lee, S. J., Jeon, S., Oh, G. T., Lee, H. Y., and Oh, S. H. (2016) Ninjurin1 inhibits colitis-mediated colon cancer development and growth by suppression of macrophage infiltration through repression of FAK signaling, Oncotarget, 20, 29592–29604.
Feng, R., and Yang, S. (2016) Effects of combining erlotinib and RNA-interfered downregulation of focal adhesion kinase expression on gastric cancer, J. Int. Med. Res., 44.
Shi, R., Wang, Q., Ouyang, Y., Wang, Q., and Xiong, X. (2016) Picfeltarraenin IA inhibits lipopolysaccharideinduced inflammatory cytokine production by the nuclear factor-κB pathway in human pulmonary epithelial A549 cells, Oncol. Lett., 11, 1195–1200.
Buck, C., Gallati, H., Pohlandt, F., and Bartmann, P. (1994) Increased levels of tumor necrosis factor a (TNF-a) and interleukin 1a (IL-1a) in tracheal aspirates of newborns with pneumonia, Infection, 22, 238–241.
Jodal, M., Fihn, B. M., and Sun, Y. (1990) Correlations and interactions in the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in human blood mononuclear cells: IL-6 suppresses IL-1 and TNF, Blood, 75, 40–47.
You, D., Xin, J., Volk, A., Wei, W., Schmidt, R., Scurti, G., Nand, S., Breuer, E. K., Kuo, P., and Breslin, P. (2015) FAK mediates a compensatory survival signal parallel to PI3K-AKT in PTEN-null T-ALL cells, Cell Rep., 10, 2055–2068.
Sun, C., Yuan, H., Wang, L., Wei, X., Williams, L., Krebsbach, P. H., Guan, J. L., and Liu, F. (2016) FAK promotes osteoblast progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation by enhancing Wnt signaling, J. Bone Min. Res., doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2908.
Harvey, R. D., Silberman, J., and Lonial, S. (2015) The PI3 kinase/Akt pathway as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma, Fut. Oncol., 3, 639–647.
Foster, K. A., Oster, C. G., Mayer, M. M., Avery, M. L., and Audus, K. L. (1998) Characterization of the A549 cell line as a type II pulmonary epithelial cell model for drug metabolism, Exp. Cell Res., 243, 359–366.
Uboldi, C., Bonacchi, D., Lorenzi, G., Hermanns, M. I., Pohl, C., Baldi, G., Unger, R. E., and Kirkpatrick, C. J. (2009) Gold nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity in the alveolar type-II cell lines A549 and NCIH441, Part. Fibre Toxicol., 6, 1–12.
Wu, J., Zhao, J., Yu, J., Zhang, W., and Huang, Y. (2015) Cylindromatosis (CYLD) inhibits Streptococcus pneumonia-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression via interacting with TRAF-6, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 463, 942–947.
Zhao, X., Li, H., Wang, J., Guo, Y., Liu, B., Deng, X., and Niu, X. (2015) Verbascoside alleviates pneumococcal pneumonia by reducing pneumolysin oligomers, Mol. Pharmacol., 89, 376–387.
Cantais, A., Mory, O., Pillet, S., Verhoeven, P. O., Bonneau, J., Patural, H., and Pozzetto, B. (2014) Epidemiology and microbiological investigations of community-acquired pneumonia in children admitted at the emergency department of a university hospital, J. Clin. Virol., 60, 402–407.
Li, Q., Liu, L., Zhang, Q., Liu, S., Ge, D., and You, Z. (2014) Interleukin-17 indirectly promotes M2 macrophage differentiation through stimulation of COX-2/PGE2 pathway in the cancer cells, Cancer Res. Treat. Offic. J. Korean Cancer Assoc., 46, 297–306.
Ali, A., Akhund, T., Warraich, G. J., Aziz, F., Rahman, N., Urmani, F. A., Qureshi, S., Petri, W. A., Bhutta, Z., Zaidi, A. K., and Hughes, M. A. (2016) Respiratory viruses associated with severe pneumonia in children under two years old in a rural community in Pakistan, J. Med. Virol., 88, 1882–1890.
Dop, D., Gheonea, C., Stanescu, G. L., Morosanu, A. E., Diaconu, R., Niculescu, E. C., Ognean, M. L., and Niculescu, D. (2015) Aspiration pneumonia in an infant with neurological sequelae–case report, Roman. J. Morphol. Embryol., 56, 1191–1194.
Wang, L. L., Zheng, S. Y., Ren, L., Xiao, Q. Y., Long, X. R., Luo, J., Qu-Bei, L. I., Deng, Y., Xie, X. H., and Liu, E. M. (2016) Levels of surfactant proteins A and D in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of children with pneumonia and their relationships with clinical characteristics, Chinese J. Contemp. Pediatr., 18.
Kessler, B. E., Sharma, V., Zhou, Q., Jing, X., Pike, L. A., Kerege, A. A., Sams, S. B., and Schweppe, R. E. (2016) FAK expression, not kinase activity, is a key mediator of thyroid tumorigenesis and pro-tumorigenic processes, Mol. Cancer Res., 14, 869–882.
Zaidi, A. (2015) FAK kinase activity is required for the progreßsion of c-Met/ß-catenin-driven HCC, Gene Express., 17, 79–88.
Serrels, A., and Frame, M. C. (2016) FAK goes nuclear to control anti-tumor immunity–a new target in cancer immunotherapy, Oncoimmunology, 5, e1119356.
Thiyagarajan, V., Lin, S. H., Chang, Y. C., and Weng, C. F. (2016) Identification of novel FAK and S6K1 dual inhibitors from natural compounds via ADMET screening and molecular docking, Biomed. Pharmacother., 80, 52–62.
Hutchinson, L. (2016) Ovarian cancer: FAK–new target for antiangiogenic therapy, Nature Rev. Clin. Oncol., 13, 328.
Ding, L., Wang, L., Sui, L., Zhao, H., Xu, X., Li, T., Wang, X., Li, W., Zhou, P., and Kong, L. (2016) Claudin-7 indirectly regulates the integrin/FAK signaling pathway in human colon cancer tissue, J. Human Genet., 61, 711–720.
Zhang, R., Li, L., Yuan, L., and Zhao, M. (2015) Hypoxic preconditioning protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell apoptosis via sphingosine kinase 2 and FAK/AKT pathway, Exp. Mol. Pathol., 100, 51–58.
Liu, F., Kohlmeier, S., and Wang, C. (2008) Wnt signaling and skeletal development, Cell. Signal., 20, 999–1009.
Topol, L., Jiang, X., Choi, H., Garrettbeal, L., Carolan, P. J., and Yang, Y. (2003) Wnt-5a inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting GSK-3-independent ß-catenin degradation, J. Cell Biol., 162, 899–908.
Oeckinghaus, A., Hayden, M. S., and Ghosh, S. (2011) Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways, Nature Immunol., 12, 695–708.
Mulero, M. C., Bigas, A., and Espinosa, L. (2013) I?Ba beyond the NF-κB dogma, Oncotarget, 4, 1550–1551.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 4, pp. 611-619.
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press, as Manuscript BM16-295, December 12, 2016.
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, D., Cong, S. & Zhu, L.P. Attenuation of focal adhesion kinase reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation injury through inactivation of the Wnt and NF-κB pathways in A549 cells. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 446–453 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040058
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040058