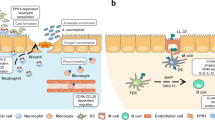
Abstract
Formyl peptide receptors (FPRs) expressed by mammalian myeloid cells are the important part of innate immunity. They belong to the seven-transmembrane domain class of receptors coupled to heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins. Binding of the receptor with a wide spectrum of exogenous and endogenous ligands triggers such defensive phagocyte reactions as chemotaxis, secretory degranulation, and respiratory burst, keeping a balance of inflammatory and antiinflammatory processes in the organism. The association between single nucleotide polymorphisms in the gene of FPR1 receptor resulting in disruption of the receptor structure and the development of certain pathologies accompanied with inflammation, such as aggressive periodontitis, macular degeneration, and even gastric cancer (Maney, P., and Walters, J. D. (2009) J. Periodontol., 80, 1498-1505; Liang, X. Y., et al. (2014) Eye, 28, 1502-1510; Otani, T., et al. (2011) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 405, 356-361) has been shown. In this review, we matched the missense mutation of formyl-peptide receptors with their known functional domains and classified them according to their potential significance in pathology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- fMLF:
-
N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine
- FPR:
-
formyl peptide receptor
- GPCR:
-
G-protein coupled receptor
- SNP:
-
single nucleotide polymorphism
References
Ye, R. D., Boulay, F., Wang, J. M., Dahlgren, C., Gerard, C., Parmentier, M., Sernan, C. N., and Murphy, P. M. (2009) International union of pharmacology LXXIII: nomenclature for the formyl peptide receptor (FPR) family, Pharmacol. Rev., 61, 119–161.
Le, Y., Oppenheim, J. J., and Wang, J. M. (2001) Pleiotropic roles of formyl peptide receptors, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 12, 91–105.
Dorward, D. A., Lucas, C. D., Chapman, G. B., Haslett, C., Dhaliwal, K., and Rossi, A. G. (2015) The role of formylated peptides and formyl peptide receptor 1 in governing neutrophil function during acute inflammation, Am. J. Pathol., 185, 1172–1184.
Rabiet, M. J., Macari, L., Dahlgren, C., and Boulay, F. (2011) N-Formyl peptide receptor 3 (FPR3) departs from the homologous FPR2/ALX receptor with regard to the major processes governing chemoattractant receptor regulation, expression at the cell surface, and phosphorylation, J. Biol. Chem., 286, 26718–26731.
Li, Y., and Ye, D. (2013) Molecular biology for formyl peptide receptors in human diseases, J. Mol. Med., 91, 781–789.
Maney, P., and Walters, J. D. (2009) Formyl peptide receptor single nucleotide polymorphism 348T>C and its relationship to polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis in aggressive periodontitis, J. Periodontol., 80, 1498–1505.
Otani, T., Ikeda, S., Lwin, H., Arai, T., Muramatsu, M., and Sawabe, M. (2011) Polymorphisms of the formyl peptide receptor gene (FPR1) and susceptibility to stomach cancer in 1531 consecutive autopsy cases, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 405, 356–361.
Zhang, D., Zhao, Q., and Wu, B. (2015) Structural studies of G protein-coupled receptors, Mol. Cells, 38, 836–842.
Bylund, J., Gabl, M., Winther, M., Onnheim, K., Dahlgren, C., and Forsman, H. (2014) Turning chemoattractant receptors on and off with conventional ligands and allosteric modulators: recent advances in formyl peptide receptor signaling and regulation, Inflamm. Cell Signal., 1, 73.
Ye, R. D., Cavanagh, S. L., Quehenberger, O., Prossnitz, E. R., and Cochrane, C. G. (1992) Isolation of a cDNA that encodes a novel granulocyte N-formyl peptide receptor, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 184, 582–589.
Quehenberger, O., Prossnitz, E. R., Cavanagh, S. L., Cochrane, C. G., and Ye, R. D. (1993) Multiple domains of the N-formyl peptide receptor are required for high-affinity ligand binding. Construction and analysis of chimeric Nformyl peptide receptors, J. Biol. Chem., 268, 18167–18175.
Perez, H. D., Holmes, R., Vilander, L. R., Adams, R. R., Manzana, W., Jolley, D., and Andrews, W. H. (1993) Formyl peptide receptor chimeras define domains involved in ligand binding, J. Biol. Chem., 268, 2292–2295.
Miettinen, H. M., Mills, J. S., Gripentrog, J. M., Dratz, E. A., Granger, B. L., and Jesaitis, A. J. (1997) The ligand binding site of the formyl peptide receptor maps in the transmembrane region, J. Immunol., 159, 4045–4054.
Quehenberger, O., Pan, Z. K., Prossnitz, E. R., Cavanagh, S. L., Cochrane, C. G., and Ye, R. D. (1997) Identification of an N-formyl peptide receptor ligand binding domain by a gain-of-function approach, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 238, 377–381.
Mills, J. S., Miettinen, H. M., Barnidge, D., Vlases, M. J., Wimer-Mackin, S., Dratz, E. A., Sunner, J., and Jesaitis, A. J. (1998) Identification of a ligand binding site in the human neutrophil formyl peptide receptor using a site-specific fluorescent photoaffinity label and mass spectrometry, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 10428–10435.
Mills, J. S., Miettinen, H. M., Cummings, D., and Jesaitis, A. J. (2000) Characterization of the binding site on the formyl peptide receptor using three receptor mutants and analogs of Met-Leu-Phe and Met-Met-Trp-Leu-Leu, J. Biol. Chem., 275, 39012–39017.
Khlebnikov, A. I., Schepetkin, I. A., Kirpotina, L. N., Brive, L., Dahlgren, C., Jutila, M. A., and Quinn, M. T. (2012) Molecular docking of 2-(benzimidazol-2-ylthio)N-phenylacetamide-derived small-molecule agonists of human formyl peptide receptor 1, J. Mol. Model., 18, 2831–2843.
Savarese, T. M., and Fraser, C. M. (1992) In vitro mutagenesis and the search for structure–function relationships among G-protein-coupled receptors, Biochem. J., 283, 1–19.
Bommakanti, R. K., Bokoch, G. M., Tolley, J. O., Schreiber, R. E., Siemsen, D. W., Klotz, K. N., and Jesaitis, A. J. (1992) Reconstitution of a physical complex between the N-formyl chemotactic peptide receptor and G protein. Inhibition by pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP ribosylation, J. Biol. Chem., 267, 7576–7581.
Bommakanti, R. K., Dratz, E. A., Siemsen, D. W., and Jesaitis, A. J. (1994) Characterization of complex formation between Gi2 and octyl glucoside solubilized neutrophil N-formyl peptide chemoattractant receptor by sedimentation velocity, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1209, 69–76.
Bommakanti, R. K., Dratz, E. A., Siemsen, D. W., and Jesaitis, A. J. (1995) Extensive contact between Gi2 and Nformyl peptide receptor of human neutrophils: mapping of binding sites using receptor-mimetic peptides, Biochemistry, 34, 6720–0728.
Amatruda, T. T., Dragas-Graonic, S., Holmes, R., and Perez, H. D. (1995) Signal transduction by the formyl peptide receptor. Studies using chimeric receptors and sitedirected mutagenesis define a novel domain for interaction with G-proteins, J. Biol. Chem., 270, 28010–28013.
Miettinen, H. M., Gripentrog, J. M., Mason, M. M., and Jesaitis, A. J. (1999) Identification of putative sites of interaction between the human formyl peptide receptor and G protein, J. Biol. Chem., 274, 27934–27942.
Prossnitz, E. R., Schreiber, R. E., Bokoch, G. M., and Ye, R. D. (1995) Binding of low affinity N-formyl peptide receptors to G protein. Characterization of a novel inactive receptor intermediate, J. Biol. Chem., 270, 10686–10694.
Gripentrog, J. M., and Miettinen, H. M. (2008) Formyl peptide receptor-mediated ERK1/2 activation occurs through G (i) and is not dependent on beta-arrestin1/2, Cell. Signal., 20, 424–431.
Ali, H., Richardson, R. M., Tomhave, E. D., Didsbury, J. R., and Snyderman, R. (1993) Differences in phosphorylation of formyl peptide and C5a chemoattractant receptors correlate with differences in desensitization, J. Biol. Chem., 268, 24247–24254.
Tardif, M., Mery, L., Brouchon, L., and Boulay, F. (1993) Agonist-dependent phosphorylation of N-formyl peptide and activation peptide from the fifth component of C (Cfa) chemoattractant receptors in differentiated HL60 cells, J. Immunol., 150, 3534–3545.
Han, M., Gurevich, V. V., Vishnivetskiy, S. A., Sigler, P. B., and Schubert, C. (2001) Crystal structure of beta-arrestin at 1.9 Å: possible mechanism of receptor binding and membrane translocation, Structure, 9, 869–880.
Milano, S. K., Pace, H. C., Kim, Y. M., Brenner, C., and Benovic, J. L. (2002) Scaffolding functions of arrestin-2 revealed by crystal structure and mutagenesis, Biochemistry, 41, 3321–3328.
Bennett, T. A., Foutz, T. D., Gurevich, V. V., Sklar, L. A., and Prossnitz, E. R. (2001) Partial phosphorylation of the N-formyl peptide receptor inhibits G protein association independent of arrestin binding, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 49195–49203.
Goodman, O. B., Jr., Krupnick, J. G., Santini, F., Gurevich, V. V., Penn, R. B., Gagnon, A. W., Keen, J. H., and Benovic, J. L. (1996) Beta-arrestin acts as a clathrin adaptor in endocytosis of the beta2-adrenergic receptor, Nature, 383, 447–450.
Laporte, S. A., Miller, W. E., Kim, K. M., and Caron, M. G. (2002) Beta-arrestin/AP-2 interaction in G proteincoupled receptor internalization: identification of a betaarrestin binging site in beta 2-adaptin, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 9247–9254.
Prossnitz, E. R., Kim, C. M., Benovic, J. L., and Ye, R. D. (1995) Phosphorylation of the N-formyl peptide receptor carboxyl terminus by the G protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK2, J. Biol. Chem., 270, 1130–1137.
Maestes, D. C., Potter, R. M., and Prossnitz, E. R. (1999) Differential phosphorylation paradigms dictate desensitization and internalization of the N-formyl peptide receptor, J. Biol. Chem., 274, 29791–29795.
Chiang, N., Fierro, I. M., Gronert, K., and Serhan, C. N. (2000) Activation of lipoxin A (4) receptors by aspirin-triggered lipoxins and select peptides evokes ligand-specific responses in inflammation, J. Exp. Med., 191, 1197–1208.
Bena, S., Brancaleone, V., Wang, J. M., Perretti, M., and Flower, R. J. (2012) Annexin A1 interaction with the FPR2/ALX receptor. Identification of distinct domains and downstream associated signaling, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 24690–24697.
Stepniewski, T., and Filipek, S. (2015) Non-peptide ligand binding to the formyl peptide receptor FPR2–a comparison to peptide ligand binding modes, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 23, 4072–4081.
Fujita, H., Kato, T., Watanabe, N., Takahashi, T., and Kitagawa, S. (2011) Stimulation of human formyl peptide receptors by calpain inhibitors: homology modeling of receptors and ligand docking simulation, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 516, 121–127.
He, H. Q., Troksa, E. L., Caltabiano, G., Pardo, L., and Ye, R. D. (2014) Structural determinants for the interaction of formyl peptide receptor 2 with peptide ligands, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 2295–306.
Lee, H. Y., Kim, S. D., Shim, J. W., Kim, H. J., Kwon, J. Y., Kim, J. M., Baek, S. H., Park, J. S., and Bae, Y. S. (2010) Activation of human monocytes by a formyl peptide receptor 2-derived pepducin, FEBS Lett., 584, 4102–4108.
Covic, L., Gresser, A. L., Talavera, J., Swift, S., and Kuliopulos, A. (2002) Activation and inhibition of G protein-coupled receptors by cell-penetrating membranetethered peptides, Biochemistry, 99, 643–648.
Forsman, H., Andreasson, E., Karlsson, J., Boulay, F., Rabiet, M. J., and Dahlgren, C. (2012) Selective peptides descending from a PIP2 profile of formyl peptide receptor 2 structural characterization and inhibitory-binding domain of gelsolin, J. Immunol., 189, 629–637.
Gehret, A. U., and Hinkle, P. M. (2010) Importance of regions outside the cytoplasmic tail of G-protein-coupled receptors for phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, Biochem. J., 428, 235–245.
Schreiber, R. E., Prossnitz, E. R., Ye, R. D., Cochrane, C. G., and Bokoch, G. M. (1994) Domains of the human neutrophil N-formyl peptide receptor involved in G protein coupling: mapping with receptor-derived peptides, J. Biol. Chem., 269, 326–331.
Kang, Y., Taddeo, B., Varai, G., Varga, J., and Fiore, S. (2000) Mutations of serine 236–237 and tyrosine 302 residues in the human lipoxin A4 receptor intracellular domains result in sustained signaling, Biochemistry, 39, 13551–13557.
Thompson, D., McArthur, S., Hislop, J. N., Flower, R. J., and Perretti, M. (2014) Identification of a novel recycling sequence in the C-tail of FPR2/ALX receptor. Association with cell protection from apoptosis, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 36166–36178.
Malech, H. L., Gardner, J. P., Heiman, D. F., and Rosenzweig, S. A. (1985) Asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on formyl peptide chemotactic receptors of human phagocytic cells, J. Biol. Chem., 260, 2509–2514.
Mery, L., and Boulay, F. (1994) The NH2-terminal region of C5aR but not that of FPR is critical for both protein transport and ligand binding, J. Biol. Chem., 269, 3457–3463.
Benachour, H., Zaiou, M., Herbeth, B., Lambert, D., Lamont, J. V., Pfister, M., Siest, G., Tiret, L., Blankenberg, S., Fitzgerald, P. S., and Visvikis-Siest, S. (2009) Human formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) c.32C>T SNP is associated with decreased soluble E-selectin levels, Fut. Med. Pharmacogenom., 10, 951–959.
Shamieh, S. E., Herbeth, B., Azimi-Nezhad, M., Benachour, H., Masson, C., and Visvikis-Siest, S. (2012) Human formyl peptide receptor 1 C32T SNP interacts with age and is associated with blood pressure levels, Clin. Chim. Acta, 413, 34–38.
Lala, A., Gwinn, M., and De Nardin, E. (1999) Human formyl peptide receptor function role of conserved and nonconserved charged residues, Eur. J. Biochem., 264, 495–499.
Liang, X. Y., Chen, L. J., Ng, T. K., Tuo, J., Gao, J. L., Tam, P. S., Lai, T. Y., Chan, C. C., and Pang, C. P. (2014) FPR1 interacts with CFH, HTRA1 and smoking in exudative age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy, Eye, 28, 1502–1510.
Zhang, Y., Syed, R., Uygar, C., Pallos, D., Gorry, M. C., Firatli, E., Cortelli, J. R., VanDyke, T. E., Hart, P. S., Feingold, E., and Hart, T. C. (2003) Evaluation of human leukocyte N-formyl peptide receptor (FPR1) SNPs in aggressive periodontitis patients, Genes Immun., 4, 22–29.
Jones, B. E., Miettinen, H. M., Jesaitis, A. J., and Mills, J. S. (2003) Mutations of F110 and C126 of the formyl peptide receptor interfere with G-protein coupling and chemotaxis, J. Periodontol., 74, 475–484.
Wenzel-Seifert, K., and Seifert, R. (2003) Functional differences between human formyl peptide receptor isoforms 26, 98, and G6, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol., 367, 509–515.
Gunji, T., Onouchi, Y., Nagasawa, T., Katagiri, S., Watanabe, H., Kobayashi, H., Arakawa, S., Noguchi, K., Hata, A., Izumi, Y., and Ishikawa, I. (2007) Functional polymorphisms of the FPR1 gene and aggressive periodontitis in Japanese, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 364, 7–13.
Zhou, C., Zhou, Y., Wang, J., Feng, Y., Wang, H., Xue, J., Chen, Y., Ye, R. D., and Wang, M. W. (2013) V101L of human formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) increases receptor affinity and augments the antagonism mediated by cyclosporins, Biochem. J., 451, 245–255.
Seifert, R., and Wenzel-Seifert, K. (2001) Defective Gi protein coupling in two formyl peptide receptor mutants associated with localized juvenile periodontitis, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 42043–42049.
Potter, R. M., Maestas, D. C., Cimino, D. F., and Prossnitz, E. R. (2006) Regulation of N-formyl peptide receptor signaling and trafficking by individual carboxylterminal serine and threonine residues, J. Immunol., 176, 5418–5425.
Sahagun-Ruiz, A., Colla, J. S., Juhn, J., Gao, J. L., Murphy, P. M., and McDermott, D. H. (2001) Contrasting evolution of the human leukocyte N-formyl peptide receptor subtypes FPR and FPRL1R, Genes Immun., 2, 335–342.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 4, pp. 587-600.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skvortsov, S.S., Gabdoulkhakova, A.G. Formyl peptide receptor polymorphisms: 27 most possible ways for phagocyte dysfunction. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 426–437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040034
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040034