Abstract
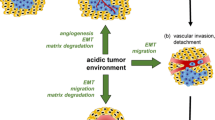
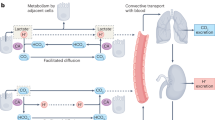
One of the differences between normal and cancer cells is lower pH of the extracellular space in tumors. Low pH in the extracellular space activates proteases and stimulates tumor invasion and metastasis. Tumor cells display higher level of the HIF1α transcription factor that promotes cell switch from mitochondrial respiration to glycolysis. The terminal product of glycolysis is lactate. Lactate formation from pyruvate is catalyzed by the specific HIF1α-dependent isoform of lactate dehydrogenase A. Because lactate accumulation is deleterious for the cell, it is actively exported by monocarboxylate transporters. Lactate is cotransported with proton, which acidifies the extracellular space. Another protein that contributes to proton concentration increase in the extracellular space is tumor-specific HIF1α-dependent carbonic anhydrase IX, which generates a proton in the reaction between carbon dioxide and water. The activity of Na+/H+ exchanger (another protein pump) is stimulated by stress factors (e.g. osmotic shock) and proliferation stimuli. This review describes the mechanisms of proton pump activation and reviews results of studies on effects of various proton pump inhibitors on tumor functioning and growth in cell culture and in vivo. The prospects of combined application of proton pump inhibitors and cytostatics in cancer therapy are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, K. A., Roth, R. A., and LaPres, J. J. (2007) Hypoxia, drug therapy and toxicity, Pharmacol. Ther., 13, 229–463.
Rankin, E. B., and Giaccia, A. J. (2016) Hypoxic control of metastasis, Science, 352, 175–180.
Lee, S. H., Lee, M. Y., and Han, H. J. (2008) Short-period hypoxia increases mouse embryonic stem cell proliferation through cooperation of arachidonic acid and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, Cell Prolif., 41, 230–247.
Zhao, T., Zhang, C. P., Liu, Z. H., Wu, L. Y., Huang, X., Wu, H. T., Xiong, L., Wang, X., Wang, X. M., Zhu, L. L., and Fan, M. (2008) Hypoxia-driven proliferation of embryonic neural stem/progenitor cells–role of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1alpha, FEBS J., 275, 1824–1834.
Di Carlo, A., De Mori, R., Martelli, F., Pompilio, G., Capogrossi, M. C., and Germani, A. (2004) Hypoxia inhibits myogenic differentiation through accelerated MyoD degradation, J. Biol. Chem., 279, 16332–16338.
Lin, Q., Lee, Y. J., and Yun, Z. (2006) Differentiation arrest by hypoxia, J. Biol. Chem., 281, 30678–30683.
Krishnamachary, B., Berg-Dixon, S., Kelly, B., Agani, F., Feldser, D., Ferreira, G., Iyer, N., LaRusch, J., Pak, B., Taghavi, P., and Semenza, G. (2003) Regulation of colon carcinoma cell invasion by hypoxia-inducible factor 1, Cancer Res., 63, 1138–1143.
Robertson, S. E., Weaver, V. M., and Simon, M. C. (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates avß3 integrin cell surface expression, Mol. Biol. Cell, 16, 1901–1912.
Piret, J. P., Minet, E., Cosse, J. P., Ninane, N., Debacq, C., Raes, M., and Michiels, C. (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent overexpression of myeloid cell factor-1 protects hypoxic cells against tert-butyl hydroperoxideinduced apoptosis, J. Biol. Chem., 280, 9336–9344.
Brahimi-Horn, M. C., and Pouyssegur, J. (2007) Oxygen, a source of life and stress, FEBS Lett., 581, 3582–3591.
Comerford, K. M., Wallace, T. J., Karhausen, J., Louis, N. A., Montalto, M. C., and Colgan, S. P. (2002) Hypoxiainducible factor-1-dependent regulation of the multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene, Cancer Res., 62, 3387–3394.
Li, D. W., Dong, P., Wang, F., Chen, X. W., Xu, C. Z., and Zhou, L. (2013) Hypoxia induced multidrug resistance of laryngeal cancer cells via hypoxia-inducible factor-1a, Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev., 14, 4853–4858.
Henegan, J. C., Jr., and Gomez, C. R. (2016) Heritable cancer syndromes related to the hypoxia pathway, Front. Oncol., doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00068.
Selak, M. A., Armour, S. M., MacKenzie, E. D., Boulahbel, H., Watson, D. G., Mansfield, K. D., Pan, Y., Simon, M. C., Thompson, C. B., and Gottlieb, E. (2005) Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting HIFalpha prolyl hydroxylase, Cancer Cell, 7, 77–85.
Nowicki, S., and Gottlieb, E. (2015) Oncometabolites: tailoring our genes, FEBS J., 282, 2796–2805.
Lai, F., Liu, Q., Liu, X., Ji, M., Xie, P., and Che, X. (2016) LXY6090–a novel manassantin A derivative–limits breast cancer growth through hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibition, Onco Targets Ther., 9, 3829–3840.
Tang, C. M., and Yu, J. (2013) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 as a therapeutic target in cancer, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 28, 401–405.
Kolobova, E., Tuganova, A., Boulatnikov, I., and Popov, K. M. (2001) Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity through phosphorylation at multiple sites, Biochem. J., 358, 69–77.
Hitosugi, T., Fan, J., Chung, T. W., Lythgoe, K., Wang, X., Xie, J., Ge, Q., Gu, T. L., Polakiewicz, R. D., Roesel, J. L., Chen, G. Z., Boggon, T. J., Lonial, S., Fu, H., Khuri, F. R., Kang, S., and Chen, J. (2011) Tyrosine phosphorylation of mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 is important for cancer metabolism, Mol. Cell, 44, 864–877.
Kim, J. W., Tchernyshyov, I., Semenza, G. L., and Dang, C. V. (2006) HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia, Cell. Metab., 3, 177–185.
Wigfield, S. M., Winter, S. C., Giatromanolaki, A., Taylor, J., Koukourakis, M. L., and Harris, A. L. (2008) PDK-1 regulates lactate production in hypoxia and is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cancer, Br. J. Cancer, 98, 1975–1984.
Kroemer, G., and Pouyssegur, J. (2008) Tumor cell metabolism: cancer’s Achilles’ heel, Cancer Cell, 13, 472–482.
Zhang, W., Zhang, S.-L., Hu, X., and Tam, K. Y. (2015) Targeting tumor metabolism for cancer treatment: is pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs) a viable anticancer target? Int. J. Biol. Sci., 11, 1390–1400.
Lu, H., Forbes, R. A., and Verma, A. (2002) Hypoxiainducible factor 1 activation by aerobic glycolysis implicates the Warburg effect in carcinogenesis, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 23111–23115.
Porporato, P. E., Dhup, S., Dadhich, R. K., Copetti, T., and Sonveaux, P. (2011) Anticancer targets in the glycolytic metabolism of tumors: a comprehensive review, Front. Pharmacol., 25, 1–18.
Valvona, C. J., Fillmore, H. L., Nunn, P. B., and Pilkington, G. J. (2016) The regulation and function of lactate dehydrogenase A: therapeutic potential in brain tumor, Brain Pathol., 26, 3–17.
Lu, H., Dalgard, C. L., Mohyeldin, A., McFate, T., Tait, A. S., and Verma, A. (2005) Reversible inactivation of HIF-1 prolyl hydroxylases allows cell metabolism to control basal HIF-1, J. Biol. Chem., 280, 41928–41939.
Koukourakis, M. I., Giatromanolaki, A., Simopoulos, C., Polychronidis, A., and Sivridis, E. (2005) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 (LDH5) relates to upregulated hypoxia inducible factor pathway and metastasis in colorectal cancer, Clin. Exp. Metastasis, 22, 25–30.
Koukourakis, M. I., Giatromanolaki, A., and Sivridis, E. (2003) Lactate dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) over expression in non-small-cell lung cancer tissues is linked to tumour hypoxia, angiogenic factor production and poor prognosis, Br. J. Cancer, 89, 877–885.
Leiblich, A., Cross, S. S., Catto, J. W., Phillips, J. T., Leung, H. Y., Hamdy, F. C., and Rehman, I. (2006) Lactate dehydrogenase-B is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in human prostate cancer, Oncogene, 25, 2953–2960.
Fantin, V. R., St-Pierre, J., and Leder, P. (2006) Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis, mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance, Cancer Cell, 9, 425–434.
Yao, F., Zhao, T., Zhong, C., Zhu, J., and Zhao, H. (2013) LDHA is necessary for the tumorigenicity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, Tumour Biol., 34, 25–31.
Merkle, S., Favor, J., Graw, J., Hornhardt, S., and Pretsch, W. (1992) Hereditary lactate dehydrogenase A-subunit deficiency as cause of early postimplantation death of homozygotes in Mus musculus, Genetics, 131, 413–421.
Gao, W., Zhang, H., Chang, G., Xie, Z., Wang, H., Ma, L., Han, Z., Li, Q., and Pang, T. (2014) Decreased intracellular pH induced by cariporide differentially contributes to human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 33, 185–194.
Maciolek, J. A., Pasternak, J. A., and Wilson, H. L. (2014) Metabolism of activated T lymphocytes, Curr. Opin. Immunol., 27, 7436–7438.
Frauwirth, K. A., and Thompson, C. B. (2004) Regulation of T lymphocyte metabolism, J. Immunol., 172, 4661–4665.
Fischer, K., Hoffmann, P., Voelkl, S., Meidenbauer, N., Ammer, J., Edinger, M., Gottfried, E., Schwarz, S., Rothe, G., Hoves, S., Renner, K., Timischl, B., Mackensen, A., Kunz-Schughart, L., Andreesen, R., Krause, S. W., and Kreutz, M. (2007) Inhibitory effect of tumor cell derived lactic acid on human T cells, Blood, 109, 3812–3819.
Pinheiro, C., Longatto-Filho, A., Azevedo-Silva, J., Casal, M., Schmitt, F. C., and Baltazar, F. (2012) Role of monocarboxylate transporters in human cancers: state of the art, J. Bioenerg. Biomembr., 44, 127–139.
Lambert, C. A., Colige, A. C., Mineur, P., Noël, A., Frankenne, F., Foidart, J. M., Baba, M., Hata, R., Miyazaki, K., and Tsukuda, M. (2005) Acidic extracellular pH induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in mouse metastatic melanoma cells through the phospholipase D-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, J. Biol. Chem., 280, 10938–10944.
Deryugina, E. L., and Quigley, J. P. (2012) Cell surface remodeling by plasmin: a new function for an old enzyme, J. Biomed. Biotechnol., Article ID564259.
Rofstad, E. K., Mathiesen, B., Kindem, K., and Galappathi, K. (2006) Acidic extracellular pH promotes experimental metastasis of human melanoma cells in athymic nude mice, Cancer Res., 66, 6699–6707.
Ben-Haim, S., and Ell, P. (2009) 18F-FDG PET and PET/CT in the evaluation of cancer treatment response, J. Nucl. Med., 50, 88–99.
Estrella, V., Chen, T., Lloyd, M., Wojtkowiak, J., Cornnell, H. H., Ibrahim-Hashim, A., Bailey, K., Balagurunathan, Y., Rothberg, J. M., Sloane, B. F., Johnson, J., Gatenby, R. A., and Gillies, R. J. (2013) Acidity generated by the tumor microenvironment drives local invasion, Cancer Res., 73, 1524–1535.
Brown, J. M., and Wilson, W. R. (2004) Exploiting tumor hypoxia in cancer treatment, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 4, 437–447.
Masoud, G. N., and Li, W. (2015) HIF-1a pathway: role, tregulation and intervention for cancer therapy, cta Pharm. Sin. B5, 378–389.
Rauch, C. (2009) Toward a mechanical control of drug delivery. On the relationship between Lipinski’s 2nd rule and cytosolic pH changes in doxorubicin resistance levels in cancer cells: a comparison to published data, Eur. Biophys. J., 38, 829–846.
Raghunand, N., He, X., Van Sluis, R., Mahoney, B., Baggett, B., Taylor, C. W., Paine-Murrieta, G., Roe, D., Bhujwalla, Z. M., and Gillies, R. J. (1999) Enhancement of chemotherapy by manipulation of tumour pH, Br. J. Cancer, 80, 1005–1011.
Masoud, G. N., Wang, J., Chen, J., Miller, D., and Li, W. (2015) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel HIF1a inhibitors, Anticancer Res., 35, 3849–3859.
Halestrap, A. P. (2012) The monocarboxylate transporter family–structure and functional characterization, IUBMB Life, 64, 1–9.
Halestrap, A. P., and Meredith, D. (2004) C16 gene family–from monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) to aromatic amino acid transporters and beyond, Pflug. Arch., 447, 619–628.
Brahimi-Horn, M. C., Bellot, G., and Pouyssegur, J. (2011) Hypoxia and energetic tumour metabolism, Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 21, 67–72.
Ullah, M. S., Davies, A. J., and Halestrap, A. P. (2006) The plasma membrane lactate transporter MCT4, but not MCT1, is up-regulated by hypoxia through a HIF-1alphadependent mechanism, J. Biol. Chem., 281, 9030–9037.
Halestrap, A. P. (2013) The SLC16 gene family–structure, role and regulation in health and disease, Mol. Asp. Med., 34, 337–349.
Draoui, N., and Feron, O. (2011) Lactate shuttles at a glance: from physiological paradigms to anti-cancer treatments, Dis. Model. Mech., 4, 727–732.
Kirk, P., Wilson, M. C., Heddle, C., Brown, M. H., Barclay, A. N., and Halestrap, A. P. (2000) CD147 is tightly associated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 and facilitates their cell surface expression, EMBO J., 19, 3896–3904.
Wilson, M. C., Meredith, D., Fox, J. E., Manoharan, C., Davies, A. J., and Halestrap, A. P. (2005) Basigin (CD147) is the target for organomercurial inhibition of monocarboxylate transporter isoforms 1 and 4, the ancillary protein for the insensitive MCT2 is EMBIGIN (gp70), J. Biol. Chem., 280, 27213–27221.
Nabeshima, K., Iwasaki, H., Koga, K., Hojo, H., Suzumiya, J., and Kikuchi, M. (2006) Emmprin (basigin/CD147): matrix metallo-proteinase modulator and multifunctional cell recognition molecule that plays a critical role in cancer progression, Pathol. Int., 56, 359–367.
Dimmer, K. S., Friedrich, B., Lang, F., Deitmer, J. W., and Broer, S. (2000) The low-affinity monocarboxylate transporter MCT4 is adapted to the export of lactate in highly glycolytic cells, Biochem. J., 350, 219–227.
Brooks, G. A. (2009) Cell–cell and intracellular lactate shuttles, J. Physiol., 587, 5591–5600.
Baltazar, F., Pinheiro, C., Morais-Santos, F., AzevedoSilva, J., Queiros, O., Preto, A., and Casal, M. (2014) Monocarboxylate transporters as targets and mediators in cancer therapy response, Histopathology, 29, 1511–1524.
Pertega-Gomes, N., and Baltazar, F. (2014) Lactate transporters in the context of prostate cancer metabolism: what do we know? Int. J. Mol. Sci., 15, 18333–18348.
Conde, V., Oliveira, P. F., Nunes, A. R., Rocha, C. S., Ramalhosa, E., Pereira, J. A., Alves, M. G., and Silva, B. M. (2015) The progression from a lower to a higher invasive stage of bladder cancer is associated with severe alterations in glucose and pyruvate metabolism, Exp. Cell. Res., 335, 91–98.
Pertega-Gomes, N., Felisbino, S., Massie, C. E., Vizcaino, J. R., Coelho, R., Sandi, C., Simoes-Sousa, S., Jurmeister, S., Ramos-Montoya, A., Asim, M., Tran, M., Oliveira, E., Lobo da Cunha, A., Maximo, V., Baltazar, F., Neal, D. E., and Fryer, L. G. (2015) A glycolytic phenotype is associated with prostate cancer progression and aggressiveness: a role for monocarboxylate transporters as metabolic targets for therapy, J. Pathol., 236, 517–530.
Choi, J. W., Kim, Y., Lee, J. H., and Kim, Y. S. (2014) Prognostic significance of lactate/proton symporters MCT1, MCT4, and their chaperone CD147 expressions in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, Urology, 84, e9–e15.
Pinheiro, C., Longatto-Filho, A., Scapulatempo, C., Ferreira, L., Martins, S., Pellerin, L., Rodrigues, M., Alves, V. A., Schmitt, F., and Baltazar, F. (2008) Increased expression of monocarboxylate transporters 1, 2, and 4 in colorectal carcinomas, Virch. Arch., 452, 139–146.
Pinheiro, C., Longatto-Filho, A., Ferreira, L., Pereira, S. M., Etlinger, D., Moreira, M. A., Jube, L. F., Queiroz, G. S., Schmitt, F., and Baltazar, F. (2008) Increasing expression of monocarboxylate transporters 1 and 4 along progression to invasive cervical carcinoma, Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol., 27, 568–574.
Doyen, J., Trastour, C., Ettore, F., Peyrottes, I., Toussant, N., Gal, J., Ilc, K., Roux, D., Parks, S. K., Ferrero, J. M., and Pouyssegur, J. (2014) Expression of the hypoxia-inducible monocarboxylate transporter MCT4 is increased in triple negative breast cancer and correlates independently with clinical outcome, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 451, 54–61.
Koukourakis, M. I., Giatromanolaki, A., Bougioukas, G., and Sivridis, E. (2007) Lung cancer: a comparative study of metabolism related protein expression in cancer cells and tumor-associated stroma, Cancer Biol. Ther., 6, 1476–1479.
Pinheiro, C., Reis, R. M., Ricardo, S., Longatto-Filho, A., Schmitt, F., and Baltazar, F. (2010) Expression of monocarboxylate transporters 1, 2, and 4 in human tumours and their association with CD147 and CD44, J. Biomed. Biotechnol., 427694.
Morais-Santos, F., Granja, S., Miranda-Goncalve, V., Moreira, A. H., Queiros, S., Vilaca, J. L., Schmitt, F. C., Longatto-Filho, A., Paredes, J., Baltazar, F., and Pinheiro, C. (2015) Targeting lactate transport suppresses in vivo breast tumour growth, Oncotarget, 6, 9177–9189.
Morais-Santos, F., Miranda-Goncalves, V., Pinheiro, S., Vieira, A. F., Paredes, J., Schmitt, F. C., Baltazar, F., and Pinheiro, C. (2013) Differential sensitivities to lactate transport inhibitors of breast cancer cell lines, Endocrin. Relat. Cancer, 21, 27–38.
Mathupala, S. P., Parajuli, P., and Sloan, A. E. (2004) Silencing of monocarboxylate transporters via small interfering ribonucleic acid inhibits glycolysis and induces cell death in malignant glioma: an in vitro study, Neurosurgery, 55, 1410–1419.
Colen, C. B., Shen, Y., Ghoddoussi, F., Yu, P., Francis, T. B., Koch, B. J., Monterey, M. D., Galloway, M. P., Sloan, A. E., and Mathupala, S. P. (2011) Metabolic targeting of lactate efflux by malignant glioma inhibits invasiveness and induces necrosis: an in vivo study, Neoplasia, 13, 620–632.
Sonveaux, P., Vegran, F., Schroeder, T., Wergin, M. C., Verrax, J., Rabbani, Z. N., De Saedeleer, C. J., Kennedy, K. M., Diepart, C., Jordan, B. F., Kelley, M. J., Gallez, B., Wahl, M. L., Feron, O., and Dewhirst, M. W. (2008) Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice, J. Clin. Invest., 118, 3930–3942.
Le Floch, R., Chiche, J., Marchiq, I., Naiken, T., Ilc, K., Murray, C. M., Critchlow, S. E., Roux, D., Simon, M. P., and Pouyssegur, J. (2011) CD147 subunit of lactate/H+ symporters MCT1 and hypoxia-inducible MCT4 is critical for energetics and growth of glycolytic tumors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 108, 16663–16668.
Marchiq, I., Le Floch, R., Roux, D., Simon, M. P., and Pouyssegur, J. (2015) Genetic disruption of lactate/H+ symporters (MCTs) and their subunit CD147/BASIGIN sensitizes glycolytic tumor cells to phenformin, Cancer Res., 75, 171–180.
Polanski, R., Hodgkinson, C. L., Fusi, A., Nonaka, D., Priest, L., Kelly, P., Trapani, F., Bishop, P. W., White, A., Critchlow, S. E., Smith, P. D., Blackhall, F., Dive, C., and Morrow, C. J. (2014) Activity of the monocarboxylate transporter 1 inhibitor AZD3965 in small cell lung cancer, Clin. Cancer Res., 20, 926–937.
Bola, B. M., Chadwick, A. L., Michopoulos, F., Blount, K. G., Telfer, B. A., Williams, K. J., Smith, P. D., Critchlow, S. E., and Stratford, I. J. (2014) Inhibition of monocarboxylate transporter-1 (MCT1) by AZD3965 enhances radiosensitivity by reducing lactate transport, Mol. Cancer Ther., 13, 2805–2816.
A phase I trial of AZD3965 in patients with advanced cancer; https://clinicaltrials.gov; Identifier: NCT01791595.
Draoui, N., Schicke, O., Seront, E., Bouzin, C., Sonveaux, P., Riant, O., and Feron, O. (2014) Antitumor activity of 7aminocarboxycoumarin derivatives, a new class of potent inhibitors of lactate influx but not efflux, Mol. Cancer Ther., 13, 1410–1418.
Mahon, B. P., Pinard, M. A., and McKenna, R. (2015) Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX activity and expression, Molecules, 20, 2323–2348.
Pastorekova, S., Parkkila, S., Parkkila, A. K., Opavsky, R., Zelnik, V., Saarnio, J., and Pastorek, J. (1997) Carbonic anhydrase IX, MN/CA IX: analysis of stomach complementary DNA sequence and expression in human and rat alimentary tracts, Gastroenterology, 112, 398–408.
Liao, S. Y., Lerman, M. I., and Stanbridge, E. J. (2009) Expression of transmembrane carbonic anhydrases, CAIX and CAXII, in human development, BMC Dev Biol., 9, 22.
Karhumaa, P., Parkkila, S., Tureci, O., Waheed, A., Grubb, J. H., Shah, G., Parkkila, A., Kaunisto, K., Tapanainen, J., Sly, W. S., and Rajaniemi, H. (2000) Identification of carbonic anhydrase XII as the membrane isozyme expressed in the normal human endometrial epithelium, Mol. Hum. Reprod., 6, 68–74.
Hynninen, P., Hamalainen, J. M., Pastorekova, S., Pastorek, J., Waheed, A., Sly, W. S., Tomas, E., Kirkinen, P., and Parkkila, S. (2004) Transmembrane carbonic anhydrase isozymes IX and XII in the female mouse reproductive organs, Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol., 2, 73.
Parkkila, S., Parkkila, A. K., Saarnio, J., Kivela, J., Karttunen, T. J., Kaunisto, K., Waheed, A., Sly, W. S., Tureci, O., Virtanen, I., and Rajaniemi, H. (2000) Expression of the membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase isozyme XII in the human kidney and renal tumors, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 48, 1601–1608.
Kivela, A. J., Parkkila, S., Saarnio, J., Karttunen, T. J., Kivela, J., Parkkila, A. K., Pastorekova, S., Pastorek, J., Waheed, A., Sly, W. S., and Rajaniemi, H. (2000) Expression of transmembrane carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes IX and XII in normal human pancreas and pancreatic tumours, Histochem. Cell. Biol., 114, 197–204.
Liao, S. Y., Ivanov, S., Ivanova, A., Ghosh, S., Cote, M. A., Keefe, K., Coca-Prados, M., Stanbridge, E. J., and Lerman, M. I. (2003) Expression of cell surface transmembrane carbonic anhydrase genes CA9 and CA12 in the human eye: overexpression of CA12 (CAXII) in glaucoma, J. Med. Genet., 40, 257–261.
Hilvo, M., Baranauskiene, L., Salzano, A. M., Scaloni, A., Matulis, D., Innocenti, A., Scozzafava, A., Monti, S. M., Di Fiore, A., De Simone, G., Lindfors, M., Janis, J., Valjakka, J., Pastorekova, S., Pastorek, J., Kulomaa, M. S., Nordlund, H. R., Supuran, C. T., and Parkkila, S. (2008) Biochemical characterization of CAIX, one of the most active carbonic anhydrase isozymes, J. Biol. Chem., 283, 27799–27809.
Gorbatenko, C. W., Olesen, E., Boedtkjer, S., and Pedersen, F. (2014) Regulation and roles of bicarbonate transporters in cancer, Front. Physiol., 5, doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00130.
Lou, Y., McDonald, P. C., Oloumi, A., Chia, S., Ostlund, C., Ahmadi, A., Kyle, A., Leung, S., Huntsman, D., Clarke, B., Sutherland, B. W., Waterhouse, D., Bally, M., Roskelley, C., Overall, C. M., Minchinton, A., Pacchiano, F., Carta, F., Scozzafava, A., Touisni, N., Winum, J. Y., Supuran, C. T., and Dedhar, S. (2011) Targeting tumor hypoxia: suppression of breast tumor growth and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors, Cancer Res., 71, 3364–3376.
Pacchiano, F., Carta, F., McDonald, P. C., Lou, Y., Vullo, D., Scozzafava, A., Dedhar, S., and Supuran, C. T. (2011) Ureidosubstituted benzenesulfonamides potently inhibit carbonic anhydrase IX and show antimetastatic activity in a model of breast cancer metastasis, J. Med. Chem., 54, 1896–1902.
Touisni, N., Maresca, A., McDonald, P. C., Lou, Y., Scozzafava, A., Dedhar, S., Winum, J. Y., and Supuran, C. T. (2011) Glycosyl coumarin carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors strongly attenuate the growth of primary breast tumors, J. Med. Chem., 54, 8271–8277.
Dubois, L., Peeters, S., Lieuwes, N. G., Geusens, N., Thiry, A., Wigfield, S., Carta, F., McIntyre, A., Scozzafava, A., Dogne, J. M., Supuran, C. T., Harris, A. L., Masereel, B., and Lambin, P. (2011) Specific inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX activity enhances the in vivo therapeutic effect of tumor irradiation, J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol., 99, 424–431.
Dubois, L. J., Niemans, R., Van Kuijk, S. J., Panth, K. M., Parvathaneni, N. K., Peeters, S. G., Zegers, C. M., Rekers, N. H., Van Gisbergen, M. W., Biemans, R., Lieuwes, N. G., Spiegelberg, L., Yaromina, A., Winum, J. Y., Vooijs, M., and Lambin, P. (2015) New ways to image and target tumour hypoxia and its molecular responses, Radiother. Oncol., 116, 352–357.
Baumgartner, M., Patel, H., and Barber, D. L. (2004) Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 as plasma membrane scaffold in the assembly of signaling complexes, Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol., 287, C844–850.
Meima, M. E., Mackley, J. R., and Barber, D. L. (2007) Beyond ion translocation: structural functions of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger isoform-1, Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens., 16, 365–372.
Slepkov, E. R., Rainey, J. K., Sykes, B. D., and Fliegel, L. (2007) Structural and functional analysis of the Na+/H+ exchanger, Biochem. J., 401, 623–633.
Boedtkjer, E., Bunch, L., and Pedersen, S. F. (2012) Physiology, pharmacology and pathophysiology of the pH regulatory transport proteins NHE1 and NBCn1: similarities, differences, and implications for cancer therapy, Curr. Pharmaceut. Des., 18, 1345–1371.
Hoffmann, E. K., Lambert, I., and Pedersen, S. F. (2009) Physiology of cell volume regulation in vertebrates, Physiol. Rev., 89, 193–277.
Pedersen, S. F. (2006) The Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 in stress-induced signal transduction: implications for cell proliferation and cell death, Pflugers’ Arch. Eur. J. Physiol., 452, 249–259.
Reshkin, S. J., Bellizzi, A., Caldeira, S., Albarani, V., Malanchi, I., Poignee, M., Alunni-Fabbroni, M., Casavola, V., and Tommasino, M. (2000) Na+/H+ exchanger-dependent intracellular alkalinization is an early event in malignant transformation and plays an essential role in the development of subsequent transformation-associated phenotypes, FASEB J., 14, 2185–2197.
Aravena, C., Beltran, A. R., Cornejo, M., Torres, V., Diaz, E. S., Guzman-Gutierrez, E., Pardo, F., Leiva, A., Sobrevia, L., and Ramirez, M. A. (2012) Potential role of sodium-proton exchangers in the low concentration arsenic trioxide-increased intracellular pH and cell proliferation, PLoS One, 7, e51451.
Reshkin, S. J., Greco, M. R., and Cardone, R. A. (2014) Role of pHi, and proton transporters in oncogene-driven neoplastic transformation, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci., 369, 20130100.
Reshkin, S. J., Cardone, R. A., and Harguindey, S. (2013) Na+-H+ exchanger, pH regulation and cancer, Rec. Pat. Anti Cancer Drug Discov., 8, 85–99.
Reshkin, S. J., Cardone, R. A., Zeeberg, K., Greco, M. R., and Harguindey, S. (2014) The Na+-H+ exchanger (NHE1) in pH regulation and cancer, Top. Anti Cancer Res., 3, 384–417.
Stylli, S. S., Kaye, A. H., and Lock, P. (2008) Invadopodia: at the cutting edge of tumour invasion, J. Clin. Neurosci., 15, 725–737.
Yamaguchi, H. (2012) Pathological roles of invadopodia in cancer invasion and metastasis, Eur. J. Cell. Biol., 91, 902–907.
Greco, M. R., Antelmi, E., Busco, G., Guerra, L., Rubino, R., Casavola, V., Reshkin, S. J., and Cardone, R. A. (2014) Protease activity at invadopodial focal digestive areas is dependent on NHE1-driven acidic pHe, Oncol. Rep., 31, 940–946.
Busco, G., Cardone, R. A., Greco, M. R., Bellizzi, A., Colella, M., Antelmi, E., Mancini, M. T., Dell’Aquila, M. E., Casavola, V., Paradiso, A., and Reshkin, S. J. (2010) NHE1 promotes invadopodial ECM proteolysis through acidification of the peri-invadopodial space, FASEB J., 24, 3903–3915.
Fujiwara, Y., Higuchi, K., Takashima, T., Hamaguchi, M., Hayakawa, T., Tominaga, K., Watanabe, T., Oshitani, N., Shimada, Y., and Arakawa, T. (2006) Roles of epidermal growth factor and Na+/H+ exchanger-1 in esophageal epithelial defense against acid-induced injury, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 290, G665–667.
Amith, S. R., and Fliegel, L. (2013) Regulation of the Na/H exchanger (NHE1) in breast cancer metastasis, Cancer Res., 73, 1259–1264.
Chiang, Y., Chou, C. Y., Hsu, K. F., Huang, Y. F., and Shen, M. R. (2008) EGF upregulates Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 by post-translational regulation that is important for cervical cancer cell invasiveness, J. Cell. Physiol., 214, 810–819.
Yang, X., Wang, D., and Dong, W. (2010) Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 by 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl) amiloride reduces hypoxia-induced hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and motility, Cancer Lett., 295, 198–204.
Guan, B., Hoque, A., and Xu, X. (2014) Amiloride and guggulsterone suppression of esophageal cancer cell growth in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts, Front. Biol. (Beijing), 9, 75–81.
Matthews, H., Ranson, M., and Kelso, M. J. (2011) Antitumour/metastasis effects of the potassium-sparing diuretic amiloride: an orally active anti-cancer drug waiting for its call-of-duty? Int. J. Cancer, 129, 2051–2061.
Tatsuta, M., Iishi, H., and Baba, M. (1997) Chemoprevention by amiloride against experimental hepatocarcinogenesis induced by N-nitrosomorpholine in Sprague–Dawley rats, Cancer Lett., 119, 109–113.
Sparfel, L., Huc, L., Le Vee, M., Desille, M., LagadicGossmann, D., and Fardel, O. (2004) Inhibition of carcinogen-bioactivating cytochrome P450 1 isoforms by amiloride derivatives, Biochem. Pharmacol., 67, 1711–1719.
Lyons, J. C., Ross, B. D., and Song, C. W. (1993) Enhancement of hyperthermia effect in vivo by amiloride and DIDS, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 25, 103.
Nagata, H., Che, X. F., Miyazawa, K., Tomoda, A., Konishi, M., Ubukata, H., and Tabuchi, T. (2011) Rapid decrease of intracellular pH associated with inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger precedes apoptotic events in the MNK45 and MNK74 gastric cancer cell lines treated with 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one, Oncol. Rep., 25, 341–346.
Nakachi, T., Tabuchi, T., Takasaki, A., Arai, S., Miyazawa, K., and Tomoda, A. (2010) Anticancer activity of phenoxazines produced by bovine erythrocytes on colon cancer cells, Oncol. Rep., 23, 1517–1522.
Zheng, C. L., Che, X. F., Akiyama, S., Miyazawa, K., and Tomoda, A. (2010) 2-Aminophenoxazine-3-one induces cellular apoptosis by causing rapid intracellular acidification and generating reactive oxygen species in human lung adenocarcinoma cells, Int. J. Oncol., 36, 641–650.
Harguindey, S., Arranz, J. L., Polo Orozco, J. D., Rauch, C., Fais, S., Cardone, R. A., and Reshkin, S. J. (2013) Cariporide and other new and powerful NHE1 inhibitors as potentially selective anticancer drugs–an integral molecular/biochemical/metabolic/clinical approach after one hundred years of cancer research, Transl. Med., 11, 282 doi: 10.1186/1479–5876–11–282.
Alfarouk, K. O., Verduzco, D., Rauch, C., Muddathir, A. K., Bashir, A. H., Elhassan, G. O., Ibrahim, M. E., Orozco, J. D., Cardone, R. A., Reshkin, S. J., and Harguindey, S. (2014) Glycolysis, tumor metabolism, cancer growth and dissemination. A new pH-based etiopathogenic perspective and therapeutic approach to an old cancer question, Oncoscience, 1, 777–802.
Osinsky, S., and Vaupel, M. (2009) Microphysiology of Tumors [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev.
McCarty, M. F., and Whitaker, J. (2010) Manipulating tumor acidification as a cancer treatment strategy, Altern. Med. Rev., 15, 264–272.
Trivedi, B., and Danforth, W. H. (1966) Effect of pH on the kinetics of frog muscle phosphofructokinase, J. Biol. Chem., 241, 4110–4112.
Guzy, R. D., and Schumacker, P. T. (2008) Oxygen sensing by mitochondria at complex III: the paradox of increased reactive oxygen species during hypoxia, Exp. Physiol., 91, 807–819.
Giang, A. H., Raymond, T., Brookes, P., De Mesy Bentley, K., Schwarz, E., O’ Keefe, R., and Eliseev, R. (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction and permeability transition in osteosarcoma cells showing the Warburg effect, J. Biol. Chem., 288, 33303–33311.
Gasparre, G., Romeo, G., Rugolo, M., and Porcelli, A. M. (2011) Learning from oncocytic tumors: why choose inefficient mitochondria? Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1807, 633–642.
Cordero-Espinoza, L., and Hagen, T. (2013) Increased concentrations of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate contribute to the Warburg effect in phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-deficient cells, J. Biol. Chem., 288, 36020–36028.
Harguindey, S., Arranz, J. L., Wahl, M. L., Orive, G., and Reshkin, S. J. (2009) Proton transport inhibitors as potentially selective anticancer drugs, Anticancer Res., 29, 2127–2136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V. A. Kobliakov, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 4, pp. 557-571.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobliakov, V.A. Role of proton pumps in tumorigenesis. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 401–412 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040010
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917040010