Abstract
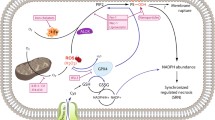
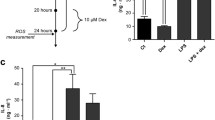
Previously, we have assembled a cellular model of pyelonephritis which contains a primary culture of renal tubular epithelial cells, mononuclear leukocytes, and bacterial lysate or lipopolysaccharide. After cocultivation of renal cells with leukocytes and bacterial lysate, proinflammatory changes were observed in the renal cells, followed by nitrosative and oxidative stress and cell death. The interaction of bacterial antigens not only with leukocytes, but also with epithelial cells of the renal tubules, was partially mediated by signaling pathways involving Toll-like receptors (TLR2 and TLR4). Activation of these receptors led to increased levels of oxidative stress and synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL-6, IL-1α) in the renal epithelium, while TLR4 blockade decreased the severity of these processes. Apart from the fact that activation of inflammatory signaling in response to bacterial antigens is observed directly in the renal cells, the presence of leukocytes significantly amplifies the inflammatory response as measured by the level of cytokines generated in the ensemble. In the presence of activated leukocytes, higher expression of TLR2 on the surface of renal cells was observed in response to exposure to bacterial components, which might explain the increased inflammatory response in the presence of leukocytes. The synthesis of IL-1α in the epithelial cells of the renal tubules in this inflammatory model leads to its accumulation in the nuclei, which has been reduced by the TLR4 antagonist polymyxin. TLR2 agonists also led to increased levels of IL-1α. The elevation in the content of IL-1α in nuclei was accompanied by increased acetylation of nuclear proteins, which has been reduced to control values after exposure to protective agents (Trolox, mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SkQR1 or LiCl). The high level of acetylation of histones is probably regulated by proinflammatory cytokines, and to some extent it is a marker of inflammation, which can indirectly be reduced by protective agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCF:
-
2,7-dihydrodichlorofluorescein
- IL:
-
interleukin
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- RTECs:
-
renal tubular epithelial cells
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
References
Prabhu, A., Taylor, P., Konecny, P., and Brown, M. A. (2013) Pyelonephritis: what are the present day causative organisms and antibiotic susceptibilities? Nephrology, 18, 463–467.
Meier, S., Weber, R., Zbinden, R., Ruef, C., and Haßse, B. (2011) Extended-spectrum ß-lactamase-producing Gramnegative pathogens in community-acquired urinary tract infections: an increasing challenge for antimicrobial therapy, Infection, 39, 333–340.
Shaikh, N., Ewing, A. L., Bhatnagar, S., and Hoberman, A. (2010) Risk of renal scarring in children with a first urinary tract infection: a systematic review, Pediatrics, 126, 10841091.
Smaill, F. M., and Vazquez, J. C. (2015) Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., 8, CD000490.
Plotnikov, E. Y., Morosanova, M. A., Pevzner, I. B., Zorova, L. D., Manskikh, V. N., Pulkova, N. V., Galkina, S. I., Skulachev, V. P., and Zorov, D. B. (2013) Protective effect of mitochondria-targeted antioxidants in an acute bacterial infection, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, e3100E3108.
Plotnikov, E. Y., Kazachenko, A. V., Vyssokikh, M. Y., Vasileva, A. K., Tcvirkun, D. V., Isaev, N. K., Kirpatovsky, V. I., and Zorov, D. B. (2007) The role of mitochondria in oxidative and nitrosative stress during ischemia/reperfusion in the rat kidney, Kidney Int., 72, 1493–1502.
Plotnikov, E. Y., Chupyrkina, A. A., Jankauskas, S. S., Pevzner, I. B., Silachev, D. N., Skulachev, V. P., and Zorov, D. B. (2011) Mechanisms of nephroprotective effect of mitochondria-targeted antioxidants under rhabdomyolysis and ischemia/reperfusion, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1812, 77–86.
Jankauskas, S. S., Plotnikov, E. Y., Morosanova, M. A., Pevzner, I. B., Zorova, L. D., Skulachev, V. P., and Zorov, D. B. (2012) Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SkQR1 ameliorates gentamycin-induced renal failure and hearing loss, Biochemistry (Moscow), 77, 666–670.
Kirpatovsky, V. I., Plotnikov, E. Y., Mudraya, I. S., Golovanov, S. A., Drozhzheva, V. V., Khromov, R. A., Chernikov, D. Y., Skulachev, V. P., and Zorov, D. B. (2013) Role of oxidative stress and mitochondria in onset of urinary bladder dysfunction under acute urine retention, Biochemistry (Moscow), 78, 542–548.
Plotnikov, E. Y., Silachev, D. N., Chupyrkina, A. A., Danshina, M. I., Jankauskas, S. S., Morosanova, M. A., Stelmashook, E. V., Vasileva, A. K., Goryacheva, E. S., Pirogov, Y. A., Isaev, N. K., and Zorov, D. B. (2010) Newgeneration Skulachev ions exhibiting nephroprotective and neuroprotective properties, Biochemistry (Moscow), 75, 145–150.
Skulachev, M. V., Antonenko, Y. N., Anisimov, V. N., Chernyak, B. V., Cherepanov, D. A., Chistyakov, V. A., Egorov, M. V., Kolosova, N. G., Korshunova, G. A., Lyamzaev, K. G., Plotnikov, E. Y., Roginsky, V. A., Savchenko, A. Y., Severina, I. I., Severin, F. F., Shkurat, T. P., Tashlitsky, V. N., Shidlovsky, K. M., Vyssokikh, M. Y., Zamyatnin, A. A., Jr., Zorov, D. B., and Skulachev, V. P. (2011) Mitochondrial-targeted plastoquinone derivatives. Effect on senescence and acute age-related pathologies, Curr. Drug Targets, 12, 800–826.
Zorov, D. B., Plotnikov, E. Y., Silachev, D. N., Zorova, L. D., Pevzner, I. B., Zorov, S. D., Babenko, V. A., Jankauskas, S. S., Popkov, V. A., and Savina, P. S. (2014) Microbiota and mitobiota. Putting an equal sign between mitochondria and bacteria, Biochemistry (Moscow), 79, 1017–1031.
Gupta, A., Sharma, S., Nain, C. K., Sharma, B. K., and Ganguly, N. K. (1996) Reactive oxygen species-mediated tissue injury in experimental ascending pyelonephritis, Kidney Int., 49, 26–33.
Mundi, H., Bjorksten, B., Svanborg, C., Ohman, L., and Dahlgren, C. (1991) Extracellular release of reactive oxygen species from human neutrophils upon interaction with Escherichia coli strains causing renal scarring, Infect. Immun., 59, 4168–4172.
Nassar, G. M., and Badr, K. F. (1998) Novel approaches to treatment of glomerulonephritis, J. Nephrol., 11, 177–184.
Gupta, A., Sharma, N., Sharma, B. K., Sharma, S., and Ganguly, N. K. (1996) Oxygen-dependent and -independent mechanisms of renal injury in experimental ascending pyelonephritis, FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol., 13, 35–42.
Badr, K. F. (1997) Glomerulonephritis, Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens., 6, 111–118.
Zorov, D. B., Filburn, C. R., Klotz, L.-O., Zweier, J. L., and Sollott, S. J. (2000) Reactive oxygen species (ROS)induced ROS release: a new phenomenon accompanying induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition in cardiac myocytes, J. Exp. Med., 192, 1001–1014.
Keston, A. S., and Brandt, R. (1965) The fluorometric analysis of ultramicro quantities of hydrogen peroxide, Anal. Biochem., 11, 1–5.
Janeway, C. A. (1989) Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology, Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., 54, 1–13.
Krysko, D. V., Agostinis, P., Krysko, O., Garg, A. D., Bachert, C., Lambrecht, B. N., and Vandenabeele, P. (2011) Emerging role of damage-associated molecular patterns derived from mitochondria in inflammation, Trends Immunol., 32, 157–164.
Vandewalle, A. (2008) Toll-like receptors and renal bacterial infections, Chang Gung Med. J., 31, 525–537.
Mingeot-Leclercq, M. P., Tulkens, P. M., Denamur, S., Vaara, T., and Vaara, M. (2012) Novel polymyxin derivatives are less cytotoxic than polymyxin B to renal proximal tubular cells, Peptides, 35, 248–252.
Satta, N., Kruithof, E. K. O., Reber, G., and De Moerloose, P. (2008) Induction of TLR2 expression by inflammatory stimuli is required for endothelial cell responses to lipopeptides, Mol. Immunol., 46, 145–157.
Fan, J., Frey, R. S., and Malik, A. B. (2003) TLR4 signaling induces TLR2 expression in endothelial cells via neutrophil NADPH oxidase, J. Clin. Invest., 112, 1234–1243.
Gribar, S. C., Anand, R. J., Sodhi, C. P., and Hackam, D. J. (2008) The role of epithelial Toll-like receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation, J. Leukoc. Biol., 83, 493–498.
Demirel, I., Vumma, R., Mohlin, C., Svensson, L., Save, S., and Persson, K. (2012) Nitric oxide activates IL-6 production and expression in human renal epithelial cells, Am. J. Nephrol., 36, 524–530.
Buryskova, M., Pospisek, M., Grothey, A., Simmet, T., and Burysek, L. (2004) Intracellular interleukin-1a functionally interacts with histone acetyltransferase complexes, J. Biol. Chem., 279, 4017–4026.
Cheng, W., Shivshankar, P., Zhong, Y., Chen, D., Li, Z., and Zhong, G. (2008) Intracellular interleukin-1a mediates interleukin-8 production induced by Chlamydia trachomatis infection via a mechanism independent of Type I interleukin-1 receptor, Infect. Immun., 76, 942951.
Rahman, I., Gilmour, P. S., Jimenez, L. A., and MacNee, W. (2002) Oxidative stress and TNF-alpha induce histone acetylation and NF-kappaB/AP-1 activation in alveolar epithelial cells: potential mechanism in gene transcription in lung inflammation, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 234-235, 239248.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M. A. Morosanova, E. Y. Plotnikov, L. D. Zorova, I. B. Pevzner, V. A. Popkov, D. N. Silachev, S. S. Jankauskas, V. A. Babenko, D. B. Zorov, 2016, published in Biokhimiya, 2016, Vol. 81, No. 11, pp. 1481–1493.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morosanova, M.A., Plotnikov, E.Y., Zorova, L.D. et al. Mechanisms of inflammatory injury of renal tubular cells in a cellular model of pyelonephritis. Biochemistry Moscow 81, 1240–1250 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791611002X
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791611002X