Abstract
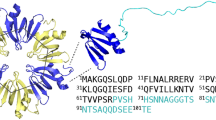
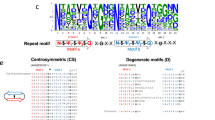
Bacterial Hfq proteins are structural homologs of archaeal and eukaryotic Sm/Lsm proteins, which are characterized by a 5-stranded β-sheet and an N-terminal α-helix. Previously, it was shown that archaeal Lsm proteins (SmAP) could produce long fibrils spontaneously, in contrast to the Hfq from Escherichia coli that could form similar fibrils only after special treatment. The organization of these fibrils is significantly different, but the reason for the dissimilarity has not been found. In the present work, we studied the process of fibril formation by bacterial protein Hfq from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and archaeal protein SmAP from Methanococcus jannaschii. Both proteins have high homology with E. coli Hfq. We found that Hfq from P. aeruginosa could form fibrils after substitutions in the conserved Sm2 motif only. SmAP from M. jannaschii, like other archaeal Lsm proteins, form fibrils spontaneously. Despite differences in the fibril formation conditions, the architecture of both was similar to that described for E. coli Hfq. Therefore, universal nature of fibril architecture formed by Hfq proteins is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vogel, J., and Luisi, B. F. (2011) Hfq and its constellation of RNA, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 9, 578–589.
Valentin-Hansen, P., and Eriksen, M. (2004) Micro-review: the bacterial Sm-like protein Hfq: a key player in RNA transactions, Mol. Microbiol., 51, 1525–1533.
Brennan, R. G., and Link, T. M. (2007) Hfq structure, function and ligand binding, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 10, 125–133.
Beggs, J. D. (2005) Lsm proteins and RNA processing, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 33, 433–438.
Spiller, M. P., Boon, K.-L., Reijns, M. M., and Beggs, J. D. (2007) The Lsm2–8 complex determines nuclear localization of the spliceosomal U6 snRNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 35, 923–929.
Mura, C., Randolph, P. S., Patterson, J., and Cozen, A. E. (2013) A structural and evolutionary perspective on Sm function archaeal and eukaryotic homologs of Hfq, RNA Biol., 10, 636–651.
Fischer, S., Benz, J., Spath, B., Maier, L.-K., Straub, J., Granzow, M., Raabe, M., Urlaub, H., Hoffmann, J., Brutschy, B., Allers, T., Soppa, J., and Marchfelder, A. (2010) The archaeal Lsm protein binds to small RNAs, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 34429–34438.
Murina, V. N., and Nikulin, A. D. (2011) RNA-binding Sm-like proteins of bacteria and archaea: similarity and difference in structure and function, Biochemistry (Moscow), 76, 1434–1449.
Khusial, P., Plaag, R., and Zieve, G. W. (2005) LSm proteins form heptameric rings that bind to RNA via repeating motifs, Trends Biochem. Sci., 30, 522–528.
Robinson, K. E., Orans, J., Kovach, A. R., Link, T. M., and Brennan, R. G. (2014) Mapping Hfq-RNA interaction surfaces using tryptophan fluorescence quenching, Nucleic Acids Res., 42, 2736–2749.
Sauter, C. (2003) Sm-like proteins in Eubacteria: the crystal structure of the Hfq protein from Escherichia coli, Nucleic Acids Res., 31, 4091–4098.
Salgado-Garrido, J., Bragado-Nilsson, E., Kandels-Lewis, S., and Seraphin, B. (1999) Sm and Sm-like proteins assemble in two related complexes of deep evolutionary origin, EMBO J., 18, 3451–3462.
Nikulin, A., Stolboushkina, E., Perederina, A., Vassilieva, I., Blaesi, U., Moll, I., Kachalova, G., Yokoyama, S., Vassylyev, D., Garber, M., and Nikonov, S. (2005) Structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hfq protein, Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr., 61, 141–146.
Moskaleva, O., Melnik, B., Gabdulkhakov, A., Garber, M., Nikonov, S., Stolboushkina, E., and Nikulin, A. (2010) The structures of mutant forms of Hfq from Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveal the importance of the conserved His57 for the protein hexamer organization, Acta Crystallogr. F, 66, 760–764.
Murina, V. N., Melnik, B. S., Filimonov, V. V., Uhlein, M., Weiss, M. S., Muller, U., and Nikulin, A. D. (2014) Effect of conserved intersubunit amino acid substitutions on Hfq protein structure and stability, Biochemistry (Moscow), 79, 469–477.
Mura, C., Kozhukhovsky, A., Gingery, M., and Phillips, M. (2003) The oligomerization and ligand-binding properties of Sm-like archaeal proteins (SmAPs), Protein Sci., 12, 832–847.
Arluison, V., Mura, C., Guzman, M. R., Liquier, J., Pellegrini, O., Gingery, M., Regnier, P., and Marco, S. (2006) Three-dimensional structures of fibrillar Sm proteins: Hfq and other Sm-like proteins, J. Mol. Biol., 356, 86–96.
Nielsen, J. S., Boggild, A., Andersen, C. B. F., Nielsen, G., Boysen, A., Brodersen, D. E., and Valentin-Hansen, P. (2007) An Hfq-like protein in archaea: crystal structure and functional characterization of the Sm protein from Methanococcus jannaschii, RNA, 13, 2213–2223.
Calderone, T. L., Stevens, R. D., and Oas, T. G. (1996) High-level misincorporation of lysine for arginine at AGA codons in a fusion protein expressed in Escherichia coli, J. Mol. Biol., 262, 407–412.
Brinkmann, U., Mattes, R. E., and Buckel, P. (1989) High-level expression of recombinant genes in Escherichia coli is dependent on the availability of the dnaY gene product, Gene, 85, 109–114.
Guryanov, S. G., Selivanova, O. M., Nikulin, A. D., Enin, G. A., Melnik, B. S., Kretov, D. A., Serdyuk, I. N., and Ovchinnikov, L. P. (2012) Formation of amyloid-like fibrils by Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) is mediated by its cold shock domain and modulated by disordered terminal domains, PLoS One, 7, e36969.
Beznosov, S. N., Pyatibratov, M. G., and Fedorov, O. V. (2009) Archaeal flagellas as new nanomaterial creation matrixes, Russ. Nanotechnol., 4, 94–98.
Beznosov, S. N., Pyatibratov, M. G., Fedorov, O. V., Kulova, T. L., and Skundin, A. M. (2011) Electrochemical characteristics of nanostructured material based on modified flagella of halophilic archaea Halobacterium salinarum for the negative electrode of lithium-ion battery, Russ. Nanotechnol., 6, 43–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2015, Vol. 80, No. 4, pp. 517–526.
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press, as Manuscript BM14-297, February 22, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murina, V.N., Selivanova, O.M., Mikhaylina, A.O. et al. Supramolecular organization of Hfq-like proteins. Biochemistry Moscow 80, 441–448 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915040070
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915040070