Abstract
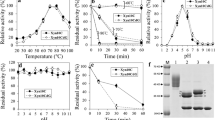
Based on the hyperthermostable family 11 xylanase (EvXyn11TS) gene sequence (EU591743), the gene Syxyn11 encoding a thermophilic xylanase SyXyn11 was synthesized with synonymous codons biasing towards Pichia pastoris. The homology alignment of primary structures among family 11 xylanases revealed that, at their N-termini, only SyXyn11 contains a disulfide bridge (Cys5–Cys32). This to some extent implied the significance of the disulfide bridge of SyXyn11 to its thermostability. To confirm the correlation between the N-terminal disulfide bridge and thermostability, a SyXyn11C5T-encoding gene, Syxyn11 C5T, was constructed by mutating the Cys5 codon of Syxyn11 to Thr5. Then, the genes for the recombinant xylanases, reSyXyn11 and reSyXyn11C5T, were expressed in P. pastoris GS115, yielding xylanase activity of about 35 U per ml cell culture. Both xylanases were purified to homogeneity with specific activities of 363 and 344 U/mg, respectively. The temperature optimum and stability of reSyXyn11C5T decreased to 70 and 50°C from 85 and 80°C of reSyXyn11, respectively. There was no obvious change in pH characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins, T., Gerday, C., and Feller, G. (2005) FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 29, 3–23.
Yin, X., Li, J. F., Wang, J. Q., Tang, C. D., and Wu, M. C. (2013) J. Sci. Food Agric., 93, 3016–3023.
Wang, Y., Fu, Z., Huang, H., Zhang, H., Yao, B., Xiong, H., and Turunen, O. (2012) Bioresour. Technol., 112, 275–279.
Paes, G., Berrin, J. G., and Beaugrand, J. (2012) Biotechnol. Adv., 30, 564–592.
Xiong, H., Fenel, F., Leisola, M., and Turunen, O. (2004) Extremophiles, 8, 393–400.
Zhang, S., Zhang, K., Chen, X. Z., Chu, X., Sun, F., and Dong, Z. (2010) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 395, 200–206.
Lee, J. H., Heo, S. Y., Lee, J. W., Yoon, K. H., Kim, Y. H., and Nam, S. W. (2009) Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 14, 639–644.
Hakulinen, N., Turunen, O., Janis, J., Leisola, M., and Rouvinen, J. (2003) Eur. J. Biochem., 270, 1399–1412.
Xue, H. P., Zhou, J. G., You, C., Huang, Q., and Lu, H. (2012) J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 39, 1279–1288.
Fenel, F., Leisola, M., Janis, J., and Turunen, O. (2004) J. Biotechnol., 108, 137–143.
Purmonen, M., Valjakka, J., Valjakka, K., Laitinen, T., and Rouvinen, J. (2007) Protein Eng. Des. Sel., 20, 551–559.
Janis, J., Rouvinen, J., Vainiotalo, P., Turunen, O., and Shnyrov, V. L. (2008) Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 42, 75–80.
Dumon, C., Varvak, A., Wall, M. A., Flint, J. E., Lewis, R. J., Lakey, J. H., Morland, C., Luginbuhl, P., Healey, S., and Todaro, T. (2008) J. Biol. Chem., 283, 22557–22564.
Verma, D., and Satyanarayana, T. (2012) Bioresour. Technol., 117, 360–367.
Badieyan, S., Bevan, D. R., and Zhang, C. (2012) Biotechnol. Bioeng., 109, 31–44.
Kabsch, W., and Sander, C. (1983) Biopolymers, 22, 2577–2637.
Li, J. F., Tang, C. D., Shi, H. L., and Wu, M. C. (2011) J. Biosci. Bioeng., 111, 537–540.
Wu, M. C., Fu, D. D., Zhu, J., and Xia, M. F. (2005) J. Food Sci. Biotechnol., 24, 29–33.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Nature, 227, 680–685.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., and Smith, F. (1956) Anal. Chem., 28, 350–356.
Radestock, S., and Gohlke, H. (2008) Eng. Life Sci., 8, 507–522.
Matthes, D., and de Groot, B. L. (2009) Biophys. J., 97, 599–608.
Zhang, H. M., Wu, M. C., Li, J. F., Gao, S. J., and Yang, Y. J. (2012) Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 167, 2198–2211.
Chen, X. L., Cao, Y. H., Ding, Y. H., Lu, W. Q., and Li, D. F. (2007) J. Biotechnol., 128, 452–461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2014, Vol. 79, No. 6, pp. 675–683.
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Yao, Y., Wu, M.C. et al. A unique disulfide bridge of the thermophilic xylanase syxyn11 plays a key role in its thermostability. Biochemistry Moscow 79, 531–537 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297914060066
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297914060066