Abstract
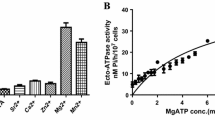
The activities of inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPase) and adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) were studied in the plasma membrane of Leishmania donovani promastigotes and amastigotes. It was shown that the specific activity of PPase was greater than that of ATPase in the promastigote plasma membrane. We characterized H+-PPase present in the plasma membrane of L. donovani and investigated its possible role in the survival of promastigote and amastigote. PPase activity was stimulated by K+ and sodium orthovanadate and inhibited by pyrophosphate analogs (imidodiphosphate and alendronate), KF, N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD), thiol reagents (p-chloromercuribenzenesulfonate (PCMBS), N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), and phenylarsine oxide (PAO)), the ABC superfamily transport modulator verapamil, and also by the F1Fo-ATPase inhibitor quercetin. ATPase activity was stimulated by K+ and verapamil, inhibited by DCCD, PCMBS, NEM, sodium azide, sodium orthovanadate, and quercetin, and was unaffected by PAO. We conclude that there are significant differences within promastigote, amastigote, and mammalian host in cytosolic pH homeostasis to merit the inclusion of PPase transporter as a putative target for rational drug design.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATPase:
-
adenosine triphosphatase
- DCCD:
-
N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
- IDP:
-
imidodiphosphate
- NEM:
-
N-ethylmaleimide
- PAO:
-
phenylarsine oxide
- PCMBS:
-
p-chloromercuribenzenesulfonate
- PPase:
-
pyrophosphatase
- PPi :
-
pyrophosphate
References
Perez-Victoria, J. M., di Pietro, A., Barron, D., Ravelo, A. G., Castanys, S., and Gamarro, F. (2002) Curr. Drug Target., 3, 311–333.
Pearson, R. D., and Wilson, M. E. (1989) in Parasite Infections in the Compromised Host (Welzeh, P. D., and Genta, R. M., eds.) Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp. 31–81.
Rea, P. A., and Poole, R. J. (1993) Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 44, 157–180.
Baltscheffsky, M., and Baltscheffsky, H. (1995) Photosynth. Res., 46, 87–91.
Baltscheffsky, M. (1969) Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 133, 46–53.
Baltcheffsky, M. (1969) Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 130, 646–652.
Keister, D. L., and Minton, N. J. (1971) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 42, 932–939.
Baltcheffsky, M., Nadanacera, S., and Schulter, A. (1998) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1364, 301–306.
Prerez-Castineira, J. R., Alvar, J., Ruiz-Perez, L. M., and Serrano, A. (2002) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 294, 567–573.
Mansurova, S. E. (1989) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 977, 237–247.
Desgeux, P. (2001) Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg., 95, 239–243.
Mukhopadhyay, S., Sen, P., Bhattacharya, S., Majumdar, S., and Roy, S. (1999) Vaccine, 17, 291–300.
Bera, T. (1987) Mol. Biochem. Parasitol., 23, 183–192.
Berredo-Pinho, M., Perus-Sampaio, C. E., Chrispim, P. P., Belmont-Firpo, R., Lemo, A. P., Martiny, A., Vannier-Santos, M. A., and Meyer-Fernandes, J. R. (2001) Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 391, 16–24.
Debrabant, A., Joshi, M. B., Pimenta, P. F., and Dwyer, D. M. (2004) Int. J. Parasitol., 34, 205–217.
Sereno, D., and Lemesre, J. L. (1997) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 41, 972–976.
Kar, K., Mukherji, K., Naskar, K., Bhattacharya, A., and Ghosh, D. K. (1990) J. Protozool., 37, 277–290.
Katewa, S. D., and Katyare, S. S. (2003) Anal. Biochem., 323, 180–187.
Biswas, S., Haque, R., Bhuyan, N. R., and Bera, T. (2008) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1780, 116–127.
Gornall, A. G., Bardawill, C. J., and David, M. M. (1949) J. Biol. Chem., 177, 751–766.
Markwell, M. K., Hass, S. M., Bieber, L. L., and Tolbert, N. E. (1978) Anal. Biochem., 87, 206–210.
Zilberstin, D., and Dwyer, D. M. (1988) Biochem. J., 256, 13–21.
Stiles, J. K., Kucerova, Z., Sarfo, B., Meade, C. A., Thompson, W., Shah, P., and Xue, L. (2003) Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol., 97, 351–366.
Jiang, S., Anderson, S. A., Winget, G. D., and Mukkada, A. J. (1994) J. Cell. Physiol., 15, 60–66.
Rodan, G. A. (1998) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 38, 375–388.
Stocken, L. A., and Thompson, R. H. S. (1946) Biochem. J., 40, 529–535.
VanderHeyden, N., Benaim, G., and Docampo, R. (1996) Biochem. J., 318, 103–109.
Linnett, P. E., and Beechey, R. B. (1979) Meth. Enzymol., 55, 472–518.
Ivey, D. M., and Ljungdahl, L. G. (1986) J. Bacteriol., 165, 252–257.
Sanchez, A., Castanys, S., and Gamarro, F. (1994) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 919, 855–861.
Orlowski, S., Mir, L. M., Belehradek, J., and Garrigos, M. (1996) Biochem. J., 317, 515–522.
Glaser, T. A., Baatz, J. E., Kreishman, G. P., and Mukkada, A. J. (1988) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 85, 7602–7606.
Rivas, L., and Chang, K. P. (1983) Biol. Bull., 165, 536–537.
Belogurov, G. A., Malinen, A. M., Turkina, M. V., Jalonen, U., Rytkonen, K., Baykov, A. A., and Lathi, R. (2005) Biochemistry, 44, 2088–2096.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2009, Vol. 74, No. 12, pp. 1695–1702.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, S.S., Bhuyan, N.R., Lakshman, K. et al. Membrane bound pyrophosphatase and P-Type adenosine triphosphatase of Leishmania donovani as possible chemotherapeutic targets: Similarities and differences in inhibitor sensitivities. Biochemistry Moscow 74, 1382–1387 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629790912013X
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629790912013X