Abstract
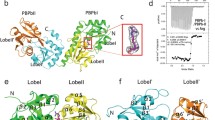
In this paper, kinetic properties of a soluble inorganic pyrophosphatase of family I from Vibrio cholerae (V-PPase), intestinal pathogen and causative agent of human cholera, are characterized in detail, and the crystal structure of a metal-free enzyme is reported. Hydrolytic activity of V-PPase has been studied as a function of pH, concentration of metal cofactors (Mg2+ or Mn2+), and ionic strength. It has been found that, despite the high conservation of amino acid sequences for the known bacterial PPases of family I, V-PPase differs from the other enzymes of the same family in a number of parameters. Dissociation constants of V-PPase complexed with Mg2+ or Mn2+ were essentially the same as for Escherichia coli PPase (E-PPase). However, the pH optimum of MgPPi hydrolysis by V-PPase was shifted to more alkaline pH due to higher values of the pK a of ionizable groups for both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex. The stability of a hexameric form of V-PPase has been studied as a function of pH. The corresponding pK a of a group that controls the stability of the hexamer at pH below 6 (pK a = 4.4) was significantly lower than in the other hexameric PPases. The crystal structure reported here is analyzed and compared with the structure of E-PPase. The location of amino acid residues that differ in V-PPase and E-PPase is discussed. Since V-PPase has been found to retain its hydrolytic activity in high ionic strength media, the observed structural and kinetic features are analyzed in view of the possible osmoadaptation of this protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E-PPase:
-
Escherichia coli inorganic pyrophosphatase
- V-PPase:
-
Vibrio cholerae inorganic pyrophosphatase
References
Pflughoeft, K. J., Kierek, K., and Watnick, P. I. (2003) Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69, 5919–5927.
Huq, A., West, P. A., Small, E. B., Huq, M. I., and Colwell, R. R. (1984) Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 48, 420–424.
Roesser, M., and Muller, V. (2001) Environ. Microbiol., 3, 743–754.
Dym, O., Mevarech, M., and Sussman, J. L. (1995) Science, 267, 1344–1346.
Tokunaga, H., Arakawa, T., and Tokunaga, M. (2008) Protein Sci., 17, 1603–1610.
Manikandan, K., Bhardwaj, A., Gupta, N., Lokanath, N. K., Ghosh, A., Reddy, V. S., and Ramakumar, S. (2006) Protein Sci., 15, 1951–1960.
Frolow, F., Harel, M., Sussman, J. L., Mevarech, M., and Shoham, M. (1996) Nat. Struct. Biol., 3, 452–458.
Heinonen, J. K. (2001) Biological Role of Inorganic Pyrophosphate, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Inc., Boston.
Heidelberg, J. F., Eisen, J. A., Nelson, W. C., Clayton, R. A., Gwinn, M. L., Dodson, R. J., Haft, D. H., Hickey, E. K., Peterson, J. D., Umayam, L. A., Gill, S. R., Nelson, K. E., Read, T. D., Tettelin, H., Richardson, D. L., Ermolaeva, M. D., Vamathevan, J. J., Bass, S., Qin, H., and Fraser, C. M. (2000) Nature, 406, 477–483.
Salminen, A., Ilias, M., Belogurov, G. A., Baykov, A. A., Lahti, R., and Young, T. (2006) Biochemistry (Moscow), 71, 978–982.
Rodina, E. V., Vainonen, L. P., Vorobyeva, N. N., Kurilova, S. A., Sitnik, T. S., and Nazarova, T. I. (2008) Biochemistry (Moscow), 73, 897–905.
Baykov, A. A., and Avaeva, S. M. (1981) Anal. Biochem., 116, 1–4.
Rodina, E. V., Vainonen, Y. P., Vorobyeva, N. N., Kurilova, S. A., Nazarova, T. I., and Avaeva, S. M. (2001) Eur. J. Biochem., 268, 3851–3857.
Otwinowski, Z., and Minor, W. (1997) Meth. Enzymol., 276, 307–326.
Vagin, A. A., and Teplyakov, A. (1997) J. Appl. Cryst., 30, 1022–1025.
Samygina, V. R., Moiseev, V. M., Rodina, E. V., Vorobyeva, N. N., Popov, A. N., Kurilova, S. A., Nazarova, T. I., Avaeva, S. M., and Bartunik, H. D. (2007) J. Mol. Biol., 366, 1305–1317.
Murshudov, G. N., Vagin, A. A., and Dodson, E. J. (1997) Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D, 53, 240–255.
Emsley, P., and Cowtan, K. (2004) Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D, 60, 2126–2132.
Gasteiger, E., Gattiker, A., Hoogland, C., Ivanyi, I., Appel, R. D., and Bairoch, A. (2003) Nucleic Acids Res., 31, 3784–3788.
Velichko, I. S., Mikalahti, K., Kasho, V. N., Dudarenkov, V. Y., Lahti, R., and Baykov, A. A. (1998) Biochemistry, 37, 734–740.
Vainonen, Ju. P., Rodina, E. V., Vorobyeva, N. N., Kurilova, S. A., Nazarova, T. I., and Avaeva, S. M. (2001) Rus. Chem. Bul., 50, 1877–1884.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2009, Vol. 74, No. 7, pp. 906–915.
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press as Manuscript BM08-392, June 7, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodina, E.V., Samygina, V.R., Vorobyeva, N.N. et al. Structural and kinetic features of family I inorganic pyrophosphatase from Vibrio cholerae . Biochemistry Moscow 74, 734–742 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297909070050
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297909070050