Abstract
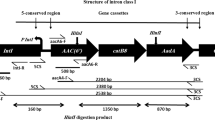
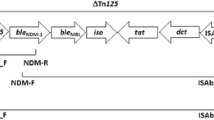
The drug resistance pattern of infectious A. baumannii isolates of Saudi Arabia was evaluated and the integrons in samples were characterized. The isolates were obtained from patients of King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between drug resistance and the presence of integrons in A. baumannii isolates. A total 84 A. baumannii isolates were collected from different sources. Identification of isolates was carried out by conventional methods as well as by VITEK 2 technology system. Antibiotic resistance of A. baumannii isolates was determined by disc diffusion method. PCR amplification was conducted to detect the presence of intI1, intI2, intI3 in isolates. Majority of the isolates (66.7%) were found resistant to 5 or more antibiotics while gentamicin was proved to be most inhibitory. All resistant A. baumannii isolates were also positive for class 1 integrons with gene cassettes of different sizes. On the other hand, all except one antibiotic sensitive isolate was devoid of any class 1 integrons. The DNA sequencing of PCR amplified class I integrons revealed the presence of different gene cassettes such as aac(3)-Ia, dfrA15, aac(6')-Ib, dfrA17, dfrA7, aadA5 etc. The obtained results are compelling for a strong association between antibiotic resistance and the presence of class 1 integrons in these A. baumannii isolates.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Roca, I., Espinal, P., Vila-Farrés, X., and Vila, J., Front. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 3, p. 148.
Visca, P., Seifert, H., and Towner, K. J., IUBMB Life, 2011, vol. 63 no. 12, pp. 1048–1054.
Yang, Q., Xu, Y.-C., Kiratisin, P., and Dowzicky, M.J., Diag. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., 2017, vol. 89, pp. 314–323.
Xie, R., Zhang, X.D., Zhao, Q., Peng, B., and Zheng, J., Emerg. Microbes Infect., 2018, vol. 7.
Gillings, M. R., Xuejun, D., Hardwick, S. A., Holley, M. P., and Stokes, H. W., ISME J., 2009, vol. 3 no. 2, pp. 209–215.
Nemergut, D. R., Martin, A. P., and Schmidt, S. K., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 70, no. 2, pp. 1160–1168.
Collis, C. M., Kim, M.-J., Partridge, S. R., Stokes, H. W., and Hall, R. M., J. Bacteriol., 2002, vol. 184, no. 11, pp. 3017–3026.
Juma, N.A., Manning, G., and Forsythe, S.J., Food Control, 2016, vol. 68, pp. 162–166.
Yang, M.-Y., Chang, K.-C., Chen, L.-Y., Wang, P.-C., Chou, C.-C., Wu, Z.-B., et al., J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol., 2018, vol. 180, pp. 235–242.
Huang, C., Long, Q., Qian, K., Fu, T., Zhang, Z., Lia-o, P., et al., New Microbes New Infect., 2015, vol. 8, pp. 103–108.
El-Shazly, S., Dashti, A., Vali, L., Bolaris, M., and Ibrahim, A. S., Int. J. Infect. Dis., 2015, vol. 41, pp. 42–49.
Yadav, S.K., Bhujel, R., Hamal, P., Mishra, S.K., Sharma, S., and Sherchand, J.B., Infect. Drug. Resist., 2020, vol. 13, pp. 725–732.
Rodríguez, C.H., Nastro, M., Fiorilli, G., Dabos, L., Calvo, J.L., Fariña, M.E., et al., J. Chemother., 2016, vol. 28, pp. 25–27.
Teerawattanapong, N., Panich, P., Kulpokin, D., Ranong, S.N., Kongpakwattana, K., Saksinanon, A., et al., Infect. Cont. Hosp. Epidemiol., 2018, vol. 39, pp. 525–533.
Cambray, G., Guerout, A.-M., and Mazel, D., Annu. Rev. Genet., 2010, vol. 44, pp. 141–166.
Rizk, D. E. and El-Mahdy, A. M., Microb. Pathol., 2017, vol. 112, pp. 50–56.
van Hoek, A.H.A.M., Mevius, D., Guerra, B., Mullany, P., Roberts, A.P., and Aarts, H.J.M., Front. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 2.
Lemay-St-Denis, C., Diwan, S.-S., and Pelletier, J.N., Antibiotics, 2021, vol. 10, p. 433.
Pereira, M.B., Österlund, T., Eriksson, K.M., Backhaus, T., Axelson-Fisk, M., and Kristiansson, E., BMC Genomics, 2020, vol. 21 no.1, p. 495.
Hunter, R. C., Asfour, F., Dingemans, J., Osuna, B. L., Samad, T., Malfroot, A., et al., mBio, 2013, vol. 4, no. 4.
Seyedmohammad, S., Fuentealba, N. A., Marriott, R. A. J., Goetze, T. A., Edwardson, J. M., Barrera, N. P., et al., Biosci. Rep., 2016, vol. 36, no. 2.
Domínguez, M., Miranda, C. D., Fuentes, O., de la Fuente, M., Godoy, F. A., Bello-Toledo, H., et al., Front. Microbiol., 2019, vol. 10.
Evangelopoulos, D., Gupta, A., Lack, N. A., Maitra, A., ten Bokum, A. M. C., Kendall, S., et al., Tuberculosis, 2014, vol. 94, no. 6, pp. 664–671.
Fluit, A. C. and Schmitz, F.-J., Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2004, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 272–288.
Rosser, S. J. and Young, H.-K., J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 1999, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 11–18.
Salimizand, H., Shahcheraghi, F., Kalantar, E., and Badmasti, F., Iran J. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 48–55.
Funding
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant no. (G-436-141-37). The author, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. Patients were informed about the study and verbal consents were obtained from all of them before taking samples. The samples were collected according to the guidelines of the Ethical Committee of King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, M.Z. Molecular Characterization of Integrons and Their Association with Antibiotic Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Hospitals in Jeddah. Appl Biochem Microbiol 57 (Suppl 1), S64–S70 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821100021
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821100021