Abstract
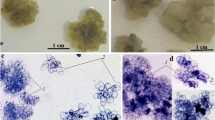
Callus and suspension plant cell cultures of Tribulus terrestris L., a valuable medicinal plant producing steroidal glycosides, were obtained. The seeds from an American population of T. terrestris were used as explants. Regulation of the production and growth of cell cultures, as well as the biosynthetic characteristics of the cell lines, were studied. The combination of phytohormones of 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L) and BAP (1.0 mg/L) was found to be optimal for callus induction and cultivation. Suspension cell culture obtained in liquid medium of the same composition showed such high growth characteristics during prolonged cultivation (more than 2 years) as a maximum accumulation of dry biomass of 13 g/L, specific growth rate at exponential phase of 0.24 day–1, and economical coefficient of 0.39. A semicontinuous mode of cultivation was used to grow the plant cell suspension in a lab-scale bioreactor. Screening of the steroidal glycosides in the obtained cell cultures was carried out. Steroidal glycosides were not found in the callus cultures. However, as was demonstrated by TLC and UPLC ESI MS methods, the suspension culture contained furostanol glycosides, and their amount increased during the cultivation process. These results support the hypothesis of the autoselection of cultivated cells containing compounds promoting their proliferation in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- 2,4-D-2:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- NAA:
-
α-naphthylacetic acid
- TLC:
-
thin layer chromatography
- UPLC ESI MS:
-
ultra performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry
References
Production of Biomass and Bioactive Compounds Using Bioreactor Technology, Paek, K.Y., Murthy, H.N., and Zhong, J.J., Eds., Dordrecht: Springer Science+Business Media, 2014.
Gama, C.R., Lasmar, R., Gama, G.F., Abreu, C.S., Nunes, C.P., Geller, M., Oliveira, L., and Santos, A., Clinical assessment of Tribulus terrestris extract in the treatment of female sexual dysfunction, Clin. Medicine Insights: Women’s Health, 2014, no. 7, pp. 45–50.
Singh, S., Nair, V., and Gupta, Y.K., Evaluation of the aphrodisiac activity of Tribulus terrestris Linn. in sexually sluggish male albino rats, J. Pharmacol. Pharmacotherapeutics, 2013, vol. 3, pp. 43–47.
Wesley, J.J., Christina, A.J.M., Chidambaranathan, N., and Ravikumar, K., Wound healing activity of the leaves of Tribulus terrestris (Linn.) aqueous extract in rats, J. Pharm. Res, 2009, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 841–843.
Wang, J., Zu, X., and Jiang, Y., Five furostanol saponins from fruits of Tribulus terrestris and their cytotoxic activities, Nat. Prod. Res, 2009, vol. 23, pp. 1436–1444.
Ivanova, A., Serly, J., Dinchev, D., Ocsovszki, I., Kostova, I., and Molnar, J., Screening of some saponins and phenolic components of Tribulus terrestris and Smilax excelsa as MDR modulators, In vivo, 2009, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 545–550.
Angelova, S., Gospodinova, Z., Krasteva, M., Antov, G., Lozanov, V., Markov, T., Bozhanov, S., Georgieva, E., and Mitev, V., Antitumor activity of Bulgarian herb Tribulus terrestris L. on human breast cancer cells, J. BioSci. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 25–32.
Kostova, I. and Dinchev, D., Saponins in Tribulus terrestris— chemistry and bioactivity, Phytochem. Rev., 2005, vol. 4, pp. 111–137.
Li, J.L. and Yang, S.S., Review of saponins in Tribulus terrestris—chemistry and bioactivity, Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med., 2006, vol. 24, pp. 1509–1510.
Sisto, M., Lisi, S., D’Amore, M., Lucro, R.D., Carati, D., Castellana, D., Pesa, V.L., Zuccarello, V., and Lofru Mento, D.D., Saponins from Tribulus terrestris L. protect human keratinocytes from UVB-induced damage, J. Photochem. Photobiol., Ser. B: Biol., 2012, vol. 117, pp. 193–201.
Xiao, J., Wang, N., Sun, B., and Cai, G., Estrogen receptor mediates the effects of pseudoprotodiocsin on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells, Amer. J. Physiol.: Cell Physiol., 2010, vol. 299, no. 1, pp. 128–138.
Dinchev, D., Janda, B., Evstatieva, L., Oleszek, W., Aslani, M.R., and Kostova, I., Distribution of steroidal saponins in Tribulus terrestris from different geographical regions, Phytochemistry, 2008, vol. 69, no. 1, pp. 176–186.
Sharifi, S., Sattari, T.N., Zebarjadi, A., Majd, A., and Ghasempour, H.R., Enhanced callus induction and high-efficiency plant regeneration in Tribulus terrestris L., an important medicinal plant, J. Med. Plants Res., 2012, vol. 6, no. 27, pp. 4401–4408.
Zafar, R. and Haque, J., Tissue culture studies on Tribulus terrestris Linn., Indian J. Pharmac. Sci., 1990, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 102–103.
Don Palmer, C. and Keller, W.A., Plant regeneration using immature zygotic embryos of Tribulus terrestris, Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2011, vol. 105, no. 1, pp. 121–127.
Mohan, J.S.S., Kumar, V.V., Aparna, V., and Vaidya, R.P., Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Tribulus terrestris L., Phytomorphology, 2000, vol. 50, nos. 3/4, pp. 307–311.
Murashige, T. and Skoog, F., A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue culture, Physiol. Plant., 1962, vol. 15, pp. 473–497.
Sukhanova, E.S., Chernyak, N.D., and Nosov, A.M., Obtaining and characteristics of callus and suspension cultures of Polyscias filicifolia and Polyscias fruticosa, Biotekhnologiya, 2010, no. 4, pp. 44–50.
Lipskii, A.Kh. and Chernyak, N.D., Effect of temperature on cell culture of Dioscorea deltoidea during submerged culturing, Fiziol. Rast., 1983, vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 437–447.
Samygin, G.A., Volkova, L.A., and Popov, A.S., Comparison of various methods for assessment of vitality of cells in suspension callus cultures, Fiziol. Rast., 1985, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 813–817.
Nosov, A.M., Metody otsenki i kharakteristiki rosta kul’tur kletok vysshikh rastenii: Molekulyarno-geneticheskie i biokhimicheskie metody v sovremennoi biologii rastenii (Methods for Assessment and Characteristics of Growth of Higher Plants Cell Cultures: Molecular Genetics and Biochemical Methods in Current Plant Biology), Moscow: Binom, 2011.
Titova, M.V., Shumilo, N.A., Kulichenko, I.E., Ivanov, I.M., Sukhanova, E.S., and Nosov, A.M., Features of respiration and formation of steroidal glycosides in suspension cell culture of Dioscorea deltoidea during culturing in flasks and bioreactors, Fiziol. Rast., 2015, no. 4, pp. 594–601.
Li, R., Zhou, Y., Wu, Z., and Ding, L., ESI-QqTOF-MS/MS and APCI-IT-MS/MS analysis of steroid saponins from the rhizomes of Dioscorea panthaica, Mass Spectrom., 2006, vol. 41, pp. 1–22.
Nosov, A.M., Popova, E.V., and Kochkin, D.V., Isoprenoid Production via Plant Cell Cultures: Biosynthesis, Accumulation and Scaling-up to Bioreactors: Production of Biomass and Bioactive Compounds Using Bioreactor Technology, Dordrecht: Springer Science + Business Media, 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.T. Khandy, D.V. Kochkin, S.V. Tomilova, B.A. Galishev, E.S. Sukhanova, A.G. Klyushin, I.M. Ivanov, A.M. Nosov, 2016, published in Biotekhnologiya, 2016, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 21–30.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khandy, M.T., Kochkin, D.V., Tomilova, S.V. et al. Obtaining and Study of Callus and Suspension Plant Cell Cultures of Tribulus terrestris L., a Producer of Steroidal Glycosides. Appl Biochem Microbiol 53, 800–806 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683817080038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683817080038