Abstract
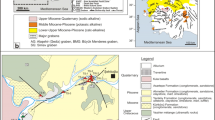
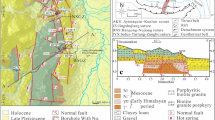
This article presents a comparative analysis of the isotope-geochemical characteristics of the products of activity of mud volcanoes (MVs) in the northwestern (Azerbaijan) and southeastern (Iran) parts of the South Caspian Basin (SCB). Gases of MVs in the studied regions are mainly of thermocatalytic origin, with the predominance of methane. High concentrations of nitrogen (up to 50%) are noted in the gases of some MVs in the Iranian sector. One distinctive feature of the MVs in the Azerbaijani part of the SCB is the presence of isotopically superheavy (>5‰) carbon dioxide, which is not typical for MVs in Iran. The waters of the MVs of Iran and most of the MVs of Azerbaijan are of the sodium chloride type. Isotopically heavy bicarbonate and carbonate ions, characteristic of the mud volcanic waters of Azerbaijan, are not typical for the volcanoes of the Iranian part of the SCB. Organic matter of rock ejecta of MVs in the Azerbaijani part of the SCB refers mainly to type II and type II–III kerogen, while in its Iranian part it is mainly type III kerogen. Mud volcanoes of Azerbaijan are characterized by a wide range of gas generation depths (10–16 km) and, accordingly, significant subvertical migration. The calculated maximum depth of the HC gas source in the Iranian part of the SCB does not exceed 12 km.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aliyev, A.A., Guliyev, I.S., and Rakhmanov, R.R., Katalog izverzhenii gryazevykh vulkanov Azerbaidzhana (1810–2007) (Catalog of Mud Volcano Eruptions in Azerbaijan (1810–2007)), Baku: Nafta-Press, 2009.
Arian, M. and Sistanipour, A., Mud diapirism on the Gorgan, North Iran, Open J. Geol., 2015, no. 5, pp. 442–450.
Artyushkov, E.V., Formation of the South Caspian Basin as a result of phase transitions in the lower continental crust, Dokl. Earth Sci., 2007, vol. 417, no. 8, pp. 1141–1146.
Axen, G.J., Lam, P.S., Grove, M., and Stockli, D.F., Exhumation of the West-Central Alborz mountains, Iran, Caspian subsidence, and collision-related tectonics, Geology, 2001, vol. 29, pp. 559–562.
Babadi, M.F., Mehrabi, B., Tassi, F., Cabassi, J., Vaselli, O., Shakeri, A., Pecchioni, E., Venturi, S., Zelenski, M., and Chaplygin, I., Origin of fluids discharged from mud volcanoes in SE Iran, Mar. Pet. Geol., 2019, vol. 106, pp. 190–205.
Babadi, M.F., Mehrabi, B., Tassi, F., Zelenski, M., Chaplygin, I., Shakeri, A., and Venturi, S., Geochemical and isotopic characteristic of emitted fluids from Pirgel mud volcano, SE Iran, Res. Earth Sci., 2020, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 159–174.
Babadi, M.F., Mehrabi, B., Tassi, F., Cabassi, J., Pecchioni, E., Shakeri, A., and Vaselli, O., Geochemistry of fluids discharged from mud volcanoes in SE Caspian Sea (Gorgan Plain, Iran), Int. Geol. Rev., 2021, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 1–16.
Bishanga, J.M. and Qiang, J., Origin and source characterization of methane in the shallow-water environment of Southern Lake Tanganyika Rift Basin, Tanzania, Curr. Sci., 2021, vol. 120, no. 6, pp. 1066–1073.
Brunet, M.F.O., Korotaev, M.V., Ershov, A.V., and Nikishin, A., The south Caspian basin: A review of its evolution from subsidence modeling, Sediment. Geol., 2003, vol. 156, pp. 119–148.
Dehghanian, M., Abedpour, Z., and Mirhosseini, S.M., Gatan mud volcanoes, Oman Sea coast in Southwestern Hormozgan, Iran, Iran. J. Earth Sci., 2015, no. 7, pp. 37–45.
Espitalié, J., Madec, M., Tissot, B., Mennig, J.J., and Leplat, P., Source rock characterization method for petroleum exploration, Proceedings of the 9th Annual Offshore Technology Conference, 1977, vol. 3, pp. 439–448.
Faber, E., Zur isotopengeochemie gasförmiger Kohlenwasserstoffe, Erdöl, Erdgas, Kohle, 1987, vol. 103, no. 5, pp. 210–218.
Feyzullayev, A.A., Mud volcanoes in the South Caspian basin: Nature and estimated depth of its products, Nat. Sci., 2012, vol. 4, no. 7, pp. 445–453.
Feyzullayev, A.A., Peculiarities of the rock–fluid system of the subduction zone in the South Caspian Basin, Izv., Atmos. Ocean. Phys., 2021, vol. 57, no. 11, pp. 1461–1478. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433821110025
Feyzullayev, A.A. and Kadirov, F.A., Spatial heterogeinity of petroleum content in south Caspian basin and its nature, in Third Int. Conf. on Geology of the Caspian Sea and Adjacent Areas; XI Azerbaijan Intern. Geophys. Conf, 2019, p. O11.
Feyzullayev, A.A. and Movsumova, U.A., The nature of the isotopically heavy carbon of carbon dioxide and bicarbonates in the waters of mud volcanoes in Azerbaijan, Geochem. Int., 2010, vol. 48, no. 5, pp. 517–522.
Feyzullayev, A.A. and Shykhaliev, Yu.A., Modern strategy of search for oil and gas in the Azerbaijani sector of the Caspian Sea, Geol. Nefti Gaza, 2016, no. 3, pp. 38–43.
Hensen, C., Wallmann, K., Schmidt, M., Ranero, C.R., and Suess, E., Fluid expulsion related to mud extrusion of Costa Rica: A window to the subducting slab, Geology, 2004, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 201–204.
Jackson, J., Priestley, K., Allen, M.B., and Berberian, M., Active tectonics of the South Caspian basin, Geophys. J. Int., 2002, vol. 148, pp. 214–245.
Jeffrey, A.W., Alimi, H.M., and Jenden, P.D., Geochemistry of Los-Angeles Basin oil and gas systems, AAPG Bull., 1988, pp. 197–219.
Kadirov, F., Floyd, M., Alizadeh, A., Guliyev, I., Reilinger, R., Kuleli, S., King, R., and Nafi Toksoz, M., Kinematics of the Eastern Caucasus near Baku, Azerbaijan, Nat. Hazards, 2012, no. 3, pp. 1–10.
Kharaka, Y.F. and Carothers, W.W., Stable carbon isotopes in oil field waters and origin of carbon dioxide, AAPG Bull., 1979, no. 63.
Knapp, C.C., Knapp, J.H., and Connor, J.A., Crustal-scale structure of the South Caspian basin revealed by deep seismic reflection profiling, Mar. Petrol. Geol., 2004, vol. 21, pp. 1073–1081.
Lafargue, E., Marquis, F., and Pillot, D., Rock-Eval 6 applications in hydrocarbon exploration, production, and soil contamination studies, Rev. Inst. Fr. Pet., 1998, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 421–437.
Lavrushin, V.Yu., Guliyev, I.S., Kikvadze, O.E., Aliyev, Ad.A., Pokrovskii, B.G., and Polyak, B.G., Mud volcano water in Azerbaijan: Isotope-chemical features and formation conditions, Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 2015, no. 1, pp. 3–29.
Mamedov, P.Z., Genesis and seismic stratigraphic model of the South Caspian megabasin architecture, in The South-Caspian Basin: Geology, Geophysics, Oil and Gas Content, Baku: Nafta-Press, 2004, pp. 150–164.
Mammadov, P.Z., The subsidence evolution of the South Caspian basin, in Book of Abstracts of the WAGE Conference “Petroleum Geology and Hydrocarbon Potential of Caspian and Black Sea Regions,” 2008, p. cp-91.
Mazzini, A., Etiope, G., and Svensen, H., A new hydrothermal scenario for the 2006 Lusi eruption, Indonesia: Insights from gas geochemistry, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2012, vol. 317, pp. 305–318.
Menapace, W., Mud volcanic episodicity: Subduction zone water budget, long-term monitoring and laboratory case studies, Doctoral (Nat. Sci.) Dissertation, Bremen: Bremen University, 2017.
Omrani, H. and Raghimi, M., Origin of the mud volcanoes in the South-East Caspian Basin, Iran, Mar. Pet. Geol., 2018, no. 96, pp. 615–626.
Philip, H., Cisternas, A., Gvishiani, A., and Gorshkov, A., The Caucasus: An actual example of the initial stages of continental collision, Tectonophysics, 1989, vol. 161, pp. 1–21.
Planke, S., Svensen, H., Hovland, M., Banks, D.A., and Jamtveit, B., Mud and fluid migration in active mud volcanoes in Azerbaijan, Geo-Mar. Lett., 2003, no. 23, pp. 258–268.
Schoell, M., The hydrogen and carbon isotopic composition of methane from natural gases of various origins, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1980, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 649–661.
Shamsi, A. and Kazemi, G.A., A review of research dealing with isotope hydrology in Iran and the first Iranian meteoric water line, Geopersia, 2014, no. 1, pp. 73–86.
Ulomov, V.I., A three-dimensional model of the lithosphere dynamics, seismicity structure, and variations in the Caspian Sea level, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2003, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 353–364.
Valyaev, B.M., Grinchenko, Yu.I., Erokhin, V.E., Prokhorov, V.S., and Titkov, G.A.,, Isotope profile of mud volcano gases, Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 1985, no. 1, pp. 72–87.
Zaputlyaeva, A., Mazzini, A., Caracausi, A., and Sciarra, A., Mantle-derived fluids in the East Java Sedimentary Basin, Indonesia, J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth, 2019, vol. 124, no. 8, pp. 7962–7977.
Zeinalzadeh, A., Sharafi, M., Mirshahani, M., and Shirzadi, A., Source rock evaluation and basin modelling in the Gorgan plain, the South Caspian Basin, Northern Iran, J. Pet. Geol., 2021, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 509–529.
Zonenshain, L.P., Kuzmin, M.I., and Natapov, L.M., Geology of the USSR: A Plate Tectonic Synthesis, Washington, DC: Am. Geophys. Union, 1990, pp. 169–198.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank our Iranian colleagues for the opportunity to use data on MVs in Iran.
Funding
This work was supported by ongoing institutional funding. No additional grants to carry out or direct this particular research were obtained.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feyzullayev, A.A., Movsumova, U.A. Isotope-Geochemical Characteristics of Fluids and Organic Matter of Rocks of Mud Volcanoes in the Northwestern (Azerbaijan) and Southeastern (Iran) Parts of the South Caspian Basin: A Comparative Analysis. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 59, 772–779 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433823070022
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433823070022