Abstract
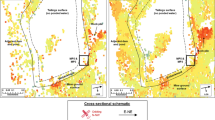
The possibilities of interferometric surveying using L-band PALSAR-1 and PALSAR-2 space radars on the ALOS-1 and ALOS-2 satellites for studying landslide processes are analyzed using the example of a catastrophic caving of ~18.5 million m3 on the Bureya River in December 2018. The motions of the landslide surface are revealed and their integral amplitude is estimated at time intervals of up to 2 years. It is found that summer images are less informative due to a dramatic loss of coherence due to heavy rainfall; almost all winter pairs of images taken at low negative temperatures have high coherence due to the stability of the dielectric properties of wood vegetation and underlying soils. Based on the analysis of the dynamics of the development of the landslide process over a 10-year time interval, it is shown that soil displacements along the slope were small in 2006–2010 (1.6–1.9 cm/month); in 2015–2016, the displacements increased significantly (4.7–4.9 cm/month), and the maximum measured velocity of displacements was reached in the summer of 2016 (10.7 cm/month). It has been suggested that intensification of the landslide process occurred at the time the filling of the reservoir basin was completed in 2006–2009; the process was triggered by both the initial rise and seasonal fluctuations in water levels.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akopian, S.Ts., Bondur, V.G., and Rogozhin, E.A., Technology for monitoring and forecasting strong earthquakes in Russia with the use of the seismic entropy method, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2017, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 32–51. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351317010025
Bamler, R. and Hartl, P., Synthetic aperture radar interferometry, Inverse Probl., 1998, vol. 14.
Berardino, P., Fornaro, G., Lanari, R., and Sansosti, E., A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2002, vol. 40, no. 11, pp. 2375–2383.
Bondur, V.G., Zakharova, L.N., Zakharov, A.I., Chimitdorzhiev, T.N., Dmitriev, A.V., and Dagurov, P.N., Long-term monitoring of the landslide process on Bureya riverbank based on interferometric L-band radar data, Sovr. Probl. Dist. Zond. Zemli Kosm., 2019a, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 113–119. https://doi.org/10.21046/2070-7401-2019-16-5-113-119
Bondur, V.G. and Starchenkov, S.A., Methods and programs for aerospace imagery processing and classification, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Geod. Aerofotos’emka, 2001, no. 3, pp. 118–143.
Bondur, V.G. and Smirnov, V.M., Method for monitoring seismically hazardous territories by ionospheric variations recorded by satellite navigation systems, Dokl., Earth Sci., 2005, vol. 403, no. 5, pp. 736–740.
Bondur, V.G. and Zverev, A.T., A method of earthquake forecast based on the lineament analysis of satellite images, Dokl., Earth Sci., 2005, vol. 402, no. 4, pp. 561–567.
Bondur, V.G., Garagash, I.A., Gokhberg, M.B., Lapshin, V.M., Nechaev, Yu.V., Steblov, G.M., and Shalimov, S.L., Geomechanical models and ionospheric variations related to strongest earthquakes and weak influence of atmospheric pressure gradients, Dokl., Earth Sci., 2007, vol. 414, no. 4, pp. 666–669.
Bondur, V.G. and Zverev, A.T., Lineament system formation mechanisms registered in space images during the monitoring of seismic danger areas, Issled. Zemli Kosmosa, 2007, no. 1, pp. 47–56.
Bondur, V.G., Pulinets, S.A., and Kim, G.A., Role of variations in galactic cosmic rays in tropical cyclogenesis: evidence of Hurricane Katrina, Dokl., Earth Sci., 2008a, vol. 422, no. 7, pp. 1124–1128. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X08070283
Bondur, V.G., Pulinets, S.A., and Uzunov, D., Ionospheric effect of large-scale atmospheric vortex by the example of hurricane Katrina, Issled. Zemli Kosmosa, 2008b, no. 6, pp. 3–11.
Bondur, V.G. and Chimitdorzhiev, T.N., Texture analysis of radar images of vegetation, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Geod. Aerofotos’emka, 2008a, no. 5, pp. 9–14.
Bondur, V.G. and Chimitdorzhiev, T.N., Remote sensing of vegetation by optical microwave methods, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Geod. Aerofotos’emka, 2008b, no. 6, pp. 64–73.
Bondur, V.G., Krapivin, V.F., and Savinykh, V.P., Monitoring i prognozirovanie prirodnykh katastrof (Monitoring and Forecasting of Natural Disasters), Moscow: Nauchnyi mir, 2009.
Bondur, V.G., Garagash, I.A., Gokhberg, M.B., Lapshin, V.M., and Nechaev, Yu.V., Connection between variations of the stress-strain state of the Earth’s crust and seismic activity: the example of Southern California, Dokl., Earth Sci., 2010, vol. 430, no. 1, pp. 147–150. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X10010320
Bondur, V.G., Aerospace methods and technologies for monitoring oil and gas areas and facilities, Izv., Atmos. Oceanic Phys., 2011, vol. 47, no. 9, pp. 1007–1018. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433811090039
Bondur, V.G., Krapivin, V.F., Potapov, I.I., and Soldatov, V.Ju., Natural disasters and the environment, Probl. Okr. Sredy Prir. Resur., 2012, no. 1, pp. 3–160.
Bondur, V.G., Garagash, I.A., and Gokhberg, M.B., Large scale interaction of seismically active tectonic provinces: the example of Southern California, Dokl., Earth Sci., 2016a, vol. 466, no. 2, pp. 183–186. .https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X16020100
Bondur, V.G., Garagash, I.A., Gokhberg, M.B., and Rodkin, M.V., The evolution of the stress state in Southern California based on the geomechanical model and current seismicity, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2016b, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 117–128. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351316010043
Bondur, V.G., Chimitdorzhiev, T.N., Dmitriev, A.V., Dagurov, P.N., Zakharov, A.I., and Zakharova, L.N., Application of radar polarimetry to monitor changes in backscattering mechanisms in landslide zones using the example of the collapse of the Bureya River bank, Izv., Atmos. Oceanic Phys., 2020, vol. 56, no. 9, pp. 916–926. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433820090054
Bondur, V.G., Chimitdorzhiev, T.N., Dmitriev, A.V., and Dagurov, P.N., Spatial anisotropy assessment of the forest vegetation heterogeneity at different azimuth angles of radar polarimetric sensing, Izv., Atmos. Oceanic Phys., 2019, vol. 55, no. 9, pp. 926–934. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433819090093
Chimitdorzhiev, T.N. Zakharov, A.I., Tat’kov, G.I., Khaptanov, V.B., Dmitriev, A.V., Budaev, R.Ts., and Tsybenov, Yu.B., Study of soils cryogenic deformation in Selenga River delta by means of SAR interferometry and georadar sounding, Issled. Zemli Kosmosa, 2011, no. 5, pp. 58–63.
Colesanti, C. and Wasowski, J., Investigating landslides with spaceborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) interferometry, Eng. Geol., 2006, vol. 88, pp. 173–199.
Epov, M.I., Mironov, V.L., Chymitdorzhiev, T.N., Zakharov, A.I., Zakharova, L.N., Seleznev, V.S., Emanov, A.F., Emanov, A.A., and Fateev, A.V., Observation of Earth’s surface subsidence in the area of Kuzbas underground coal mining with ALOS PALSAR radar interferometry, Issled. Zemli Kosmosa, 2012, no. 4, pp. 26–29.
Ferretti, A., Prati, C., and Rocca, F., Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2000, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 2202–2212.
Ferretti, A., Fumagalli, A., Novali, F., Prati, C., Rocca, F., and Rucci, A., A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2011, vol. 49, no. 9, pp. 3460–3470.
Hooper, A., Segall, P., and Zebker, H., Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcan Alcedo, Galapagos, J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth, 2007, vol. 112, no. B7, pp. B07407-1–B07407-21.
Kimura, H. and Yamaguchi, Y., Detection of landslide areas using satellite radar interferometry, Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens., 2000, vol. 66, pp. 337–344.
Korenyuk, I.Yu., Zhivaya Bureya (Alive Bureya), Khabarovsk, RusGidro, 2009.
Kramareva, L.S., Lupyan, E.A., Amel’chenko, Yu.A., Burtsev, M.A., Krasheninnikova, Yu.S., Sukhanova, V.V., and Shamilova, Yu.A., Observation of the hill collapse zone near the Bureya River on December 11, 2018, Sovr. Probl. Dist. Zond. Zemli Kosmosa, 2018, vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 266–271.
Kramareva, L.S., Lupyan, E.A., Amel’chenko, Yu.A., Burtsev, M.A., Krasheninnikova, Yu.S., Sukhanova, V.V., Shamilova, Yu.A., and Boroditskaya, A.V., Observing the progress of blasting operations and channeling in the area of the rock slide on the Bureya River, Sovr. Probl. Dist. Zond. Zemli Kosmosa, 2019, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 259–265.
Opolzen na r. Bureya (Landslide on Bureya River). http:// omdoki.nextgis.com/resource/103/display (Accessed on July 1, 2019).
Ostroukhov, A.V., Kim, V.I., and Makhinov, A.N., Estimation of the morphometric parameters of the landslide on the Bureya reservoir and its consequences on the basis of remote sensing data and field measurements, Sovr. Probl. Dist. Zond. Zemli Kosm., 2019, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 254–258.
Prirodnye opasnosti Rossii (Natural Hazards of Russia), vol. 2. Seismicheskie opasnosti (Seismic Hazards) Sobolev, G.A., Ed., Moscow: KRUK, 2000.
Strozzi, T., Wegmuller, U., Werner, C., Wiesmann, A., and Spreckels, V., JERS SAR interferometry for land subsidence monitoring, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2003, no. 41, pp. 1702–1708.
Strozzi, T., Teatini, P., Tosi, L., Wegmuller, U., and Werner, C., Land subsidence of natural transitional environments by satellite radar interferometry on artificial reflectors, J. Geophys. Res.: Earth Surface, 2013, vol. 118, pp. 1177–1191.
Xia, Y., Kaufmann, H., and Guo, X.F., Landslide monitoring in the Three Gorges area using D-INSAR and corner reflectors, Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens., 2004, no. 70 (10), pp. 1167–1172.
Zakharov, A.I. and Zakharova, L.N., Observation of snow cover dynamics on L-band SAR interferograms, Sovr. Probl. Dist. Zond. Zemli Kosm., 2017, vol. 14, no. 7, pp. 190–197.
Zakharova, L.N. and Zakharov, A.I., Interferometric observation of landslide area dynamics on the Bureya river by means of Sentinel-L radar data in 2017–2018, Sovr. Probl. Dist. Zond. Zemli Kosm., 2019, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 273–277.
Zakharova, L.N., Zakharov, A.I., and Mitnik, L.M., First results of the assessment of the landslide consequences on the Bureya River bank using Sentinel-1 radar data, Sovr. Probl. Dist. Zond. Zemli Kosm., 2019, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 69–74.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to JAXA for the ALOS PALSAR and ALOS‑2 PALSAR‑2 radar data provided as part of the RA-6 scientific projects and to the German Aerospace Center (DLR) for the TerraSAR X/TanDEM X data.
Funding
These studies were carried out as part of the state assignments of the AEROCOSMOS Research Institute for Aerospace Monitoring no. 075-00896-19-01 (theme no. ON58-2019-0030), the Kotelnikov Institute of Radioengineering and Electronics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Physical Materials Science, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Science, and with support in part from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grant no. 18-07-00816).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by E. Morozov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bondur, V.G., Zakharova, L.N., Zakharov, A.I. et al. Monitoring Landslide Processes by Means of L-Band Radar Interferometric Observations: Using the Example of the Bureya River Bank Caving. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 56, 1053–1061 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433820090078
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433820090078