Abstract
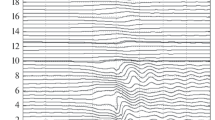
Within the framework of a two-dimensional, inviscid, stationary model, the problem of an unbounded (in height) two-layer quasi-static airflow over mesoscale mountains is considered. The airflow is characterized by a constant velocity and a discontinuity of temperature stratification at the inner interface (tropopause). The conjugation conditions for the flow fields at the boundary between the layers are formulated exactly, without the standard assumption of small perturbations. According to calculations, partial reflection of wave energy from the tropopause is substantially controlled by nonlinear effects associated with a finite height and shape of terrain. The tropopause’s displacement from the initial (equilibrium) level has a stabilizing effect on the flow, thus interfering with the development of anomalously strong disturbances. As a result, the flow field remains statically stable within a considerably wider range of flow parameters and for a larger mountain heights than predicted in the context of the conventional linear theory. The results obtained in this study are indicative of the importance of a correct consideration of the dynamic interaction between the troposphere and the overlying layers during both simulation of the process of flow and analysis of real atmospheric situations over mountains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Queney, G. A. Corby, N. Gerbier, et al., The Airflow over Mountains, Ed. by M. A. Alaka (WMO, Geneva, 1960).
V. N. Kozhevnikov, Disturbances of the Atmosphere during Flow over Mountains (Nauchnyi Mir, Moscow, 1999) [in Russian].
A. Eliassen and E. Palm, “On the Transfer of Energy in Stationary Mountain Waves,” Geophys. Publ 22(3), 1–23 (1961).
W. Blumen, “A Random Model of Momentum Flux by Mountain Waves,” Geophys. Publ. 26(2), 1–33 (1965).
J. Klemp, D. K. Lilly “The Dynamics of Wave-Induced Downslope Winds,” J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 320–339 (1975).
K. B. Moiseenko, “On the Role of the Stratosphere in the Process of Overflow of Mesoscale Mountains,” Ann. Geophys., No. 11, 3407–3417 (2005).
E. Gossard and W. Hooke, Waves in the Atmosphere (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1975; Mir, Moscow, 1978).
R. B. Smith, “The Influence of Mountains on the Atmosphere,” Adv. Geophys. 21(1), 81–230 (1979).
E. Palm and A. Foldvik, “Contribution to the Theory of Two-Dimensional Mountain Waves,” Geophys. Publ. 21(6), 1–30 (1960).
F. H. Berkshire and F. W. G. Warren, “Some Aspects of Linear Lee Wave Theory for the Stratosphere,” Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 96(407), 50–67 (1970).
F. H. Berkshire, “Two-Dimensional Linear Lee Wave Modes for Models Including a Stratosphere,” Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 101(428), 259–266 (1975).
D. R. Durran, “Another Look on Downslope Windstorms. Part I: The Development of Analogs to Super-Critical Flow in an Infinitely Deep, Continuously Stratified Flow,” J. Atmos. Sci. 43, 2527–2543 (1986).
D. R. Durran, “Mountain Waves and Downslope Winds,” in Atmospheric Processes over Complex Terrain, Ed. by W. D. Blumen (Am. Meteorol. Soc., Meteorol. Monograph, 1990), No. 45, pp. 59–81.
D. K. Lilly, “A Severe Downslope Windstorm and Aircraft Turbulence Event Induced by a Mountain Wave,” J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 59–77 (1978).
V. N. Kozhevnikov and M. K. Bedanokov, “Wave Disturbances over the Crimean Mountains: Theory and Observations,” Izv. Akad. Nauk, Fiz. Atmos. Okeana 34, 546–556 (1998) [Izv., Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 34, 491–500 (1998)].
R. B. Smith, “The Steeping of Hydrostatic Mountain Waves,” J. Atmos. Sci. 34, 1634–1654 (1977).
J. L. Attié, A. Druilhet, P. Durand, and B. Bénech, “Two-Dimensional Structure of Mountain Wave Observed by Aircraft during the PYREX Experiment,” Ann. Geophys. 15, 823–839 (1997).
D. K. Lilly and J. B. Klemp, “The Effects of Terrain Shape on Nonlinear Hydrostatic Mountain Waves,” J. Fluid Mech. 95, Part 2, 241–261 (1979).
V. N. Kozhevnikov and K. B. Moiseenko, “Simulation of the Flow over a Mountain Ridge with Height-Varying Free-Stream Characteristics,” Izv. Akad. Nauk, Fiz. Atmos. Okeana 40, 165–177 (2004) [Izv., Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 40, 142–152 (2004)].
R. R. Long, “Some Aspects of the Flow of Stratified Fluids. III. Continuous Density Gradients,” Tellus 7, 341–357 (1955).
A. J. Claus, “Large-Amplitude Motion of a Compressible Fluid in the Atmosphere,” J. Fluid Mech. 19, Part 2, 267–289 (1963).
V. N. Kozhevnikov and M. K. Bedanokov, “Nonlinear Multilayer Model of Flow over an Arbitrary Profile,” Izv. Akad. Nauk, Fiz. Atmos. Okeana 29, 780–792 (1993).
N. E. Kochin, I. A. Kibel’, and N. V. Roze, Theoretical Fluid Mechanics, Part 1 (Fizmatgiz, Moscow, 1963) [in Russian].
G. Lyra, “Theorie Der Stationaren Leewellenstromung in Freien Atmosphare,” Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 23(1), 1–28 (1943).
J. W. Miles and H. E. Huppert, “Lee Waves in Stratified Flow. 4. Perturbation Approximations,” J. Fluid Mech. 35 Part 3, 497–525 (1969).
L. N. Gutman, Introduction to the Theory of Mesometeorological Processes (Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad, 1969) [in Russian].
D. K. Lilly, J. M. Nicholls, R. M. Chervin, et al., “Aircraft Measurements of Wave Momentum Flux over the Colorado Rocky Mountains,” Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 108(457), 625–642 (1982).
D. K. Lilly and J. P. Kennedy, “Observations of a Stationary Mountain Wave and Its Associated Momentum Flux and Energy Dissipation,” J. Atmos. Sci. 30, 1135–1152 (1973).
N. I. Muskhelishvili, Singular Integral Equations (Fizmatgiz, Moscow, 1962) [in Russian].
M. Van Dyke, Perturbation Methods in Fluid Mechanics (Academic, New York, 1964).
V. N. Kozhevnikov, T. N. Bibikova, and E. V. Zhurba, “Orographic Disturbances of the Atmosphere over the Northern Ural,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Fiz. Atmos. Okeana 13, 451–461 (1977).
D. Lilly, Y. Pann, P. Kennedy, and W. Toutenhoofd, Data Catalog for the 1970 Colorado Lee Wave Observational Program (NCAR Tecnical Notes, Boulder, 1971), NCAR-TN/STR-72.
R. Scorer, Environmental Aerodynamics (Horwood, Chichester, 1978; Mir, Moscow, 1980).
N. E. Kochin, Effect of the Terrain Profile on Waves on the Interface between Two Masses of Fluids with Different Densities, Vol. 1 (Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow, 1949) [in Russian].
F. I. Frankl’ and L. N. Gutman, “Thermohydrodynamic Model of Bora,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 130(3) (1960).
A. A. Dorodnitsyn, “Effect of the Earth’s Surface Relief on Airflows,” Tr. TsIP, No. 21, 3–25 (1950).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.B. Moiseenko, 2007, published in Izvestiya AN. Fizika Atmosfery i Okeana, 2007, Vol. 43, No. 2, pp. 182–192.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moiseenko, K.B. Consideration for the tropopause’s displacements in the problem of flow over mountains. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 43, 158–167 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000143380702003X
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000143380702003X