Abstract
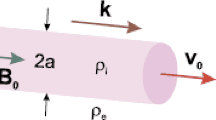
A quasi-linear prediction of the two-fluid dynamo effect is analyzed with the use of tearing eigenfunctions obtained for force-free equilibrium. In the range of parameters of practical interest, the basic shear Alfvén mode is decoupled from fast compressional Alfvén and slow magneto-acoustic modes. Kinetic Alfvén modification of the shear Alfvén wave drives an instability with a growth rate ∝δ1/3ρ 2/3s , where δ is the electron skin depth and ρs is the ion-sound gyroradius. A net dynamo effect parallel to the magnetic field is calculated at ρ s ≫δ for large values of the stability factor \(\Delta '\rho _s^{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 3}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} 3}} \delta ^{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 3}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} 3}} \gg 1\). The dynamo effect caused by the j×B Hall term dominates the contribution from the v×B term (the alpha effect) by a factor ∝(ρs/δ)2 in the narrow electron layer, while in the broader ion layer these contributions are comparable. The results are compared with the case of a strong guiding field where ρ s ≪δ and the tearing instability is described by resistive MHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Bhattacharjee and E. Hameiri, Phys. Rev. Lett. 57, 206 (1986).
S. Ortolani and D. Schnack, Magnetohydrodynamics of Plasma Relaxation (World Scientific, Singapore, 1993).
P. W. Fontana, D. J. Den Hartog, G. Fiksel, and S. C. Prager, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 566 (2000).
A. V. Gordeev, A. S. Kingsep, and L. I. Rudakov, Phys. Rep. 243, 215 (1994).
G. C. Lee, P. H. Diamond, and Z. C. An, Phys. Fluids B 1, 99 (1989).
H. Ji, S. C. Prager, A. F. Almagri, et al., Phys. Plasmas 3, 1935 (1996).
C. C. Hegna, Phys. Plasmas 5, 2257 (1998).
F. Porcelli, Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 425 (1991).
T. J. Schep, F. Pegoraro, and B. N. Kuvshinov, Phys. Plasmas 1, 2843 (1994).
B. N. Kuvshinov and B. N. Mikhailovskii, Fiz. Plazmy 22, 582 (1996) [Plasma Phys. Rep. 22, 529 (1996)].
P. D. Mininni, D. O. Gomez, and S. M. Mahajan, Astrophys. J. Lett. 567, L81 (2002).
J. B. Taylor, Phys. Rev. Lett. 33, 134 (1974).
R. G. Kleva, Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1509 (1994).
D. Biskamp, E. Schwarz, and J. F. Drake, Phys. Plasmas 4, 1002 (1997).
A. Y. Aydemir, Phys. Fluids B 3, 3025 (1991).
R. D. Hazeltine, C. T. Hsu, and P. J. Morrison, Phys. Fluids 30, 3204 (1987).
L. Zakharov and B. Rogers, Phys. Fluids B 4, 3285 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
From Fizika Plazmy, Vol. 29, No. 7, 2003, pp. 612–617.
Original English Text Copyright © 2003 by Mirnov, Hegna, Prager.
This article was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirnov, V.V., Hegna, C.C. & Prager, S.C. A hall dynamo effect driven by two-fluid tearing instability. Plasma Phys. Rep. 29, 566–570 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1592555
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1592555