Abstract
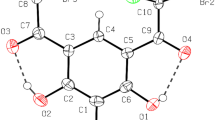
Ethyl esters of 3,4-dimethoxy-, 3,4,5-trimethoxy-, and 4-fluorobenzylidenecyanoacetic acids are investigated by X-ray diffraction analysis with the aim of elucidating the factors responsible for the formation of crystal structures of cyanovinylbenzene derivatives. The crystal data for other known derivatives of this series are analyzed. It is revealed that, in the absence of strong hydrogen bonding, the main structure-forming function in crystals is fulfilled by intermolecular contacts of two types, namely, staking contacts of parallel and antiparallel molecules. The staking contacts of antiparallel molecules are most frequently realized. It is assumed that their presence in the structure determines the prevailing formation of centrosymmetric packings in the compounds under consideration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nonlinear Optical Properties of Organic Molecules and Crystals, Ed. by D. S. Chemla and J. Zyss (Academic, New York, 1987), Vol. 1, p. 2.
Materials for Nonlinear Optics: Chemical Perspectives, Ed. by S. R. Marder, J. E. Sohn, and G. D. Stucky (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1991), ACS Symposium Series 455.
L. R. Dalton, A. W. Harper, R. Ghosn, et al., Chem. Mater. 7, 1060 (1995).
G. M. Sheldrick, SHELXTL97: An Integrated System for Solving, Refining, and Displaying Crystal Structures from Diffraction Data, Version 5.10 (Bruker AXS, Madison, 1997).
M. Yu. Antipin, R. D. Clark, V. N. Nesterov, et al., Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 313, 85 (1998).
M. Yu. Antipin, T. V. Timofeeva, R. D. Clark, et al., J. Phys. Chem. A 102, 7222 (1998).
Cambridge Structural Database (Univ. of Cambridge, Cambridge, 1999).
Ch. Serbutoviez, Ch. Bosshard, G. Knopfle, et al., Chem. Mater. 7, 1198 (1995).
L. N. Kuleshova and V. N. Khrustalev, Kristallografiya 45(1), 84 (2000) [Crystallogr. Rep. 45, 78 (2000)].
R. S. Rowland and R. Taylor, J. Phys. Chem. 100, 7384 (1996).
F. H. Allen, O. Kennard, D. G. Watson, et al., J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, S1 (1987).
A. G. Orpen, L. Brammer, F. H. Allen, et al., J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1, S1 (1989).
K. Nakatsu, H. Nyoshie, H. Yoshioka, et al., Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol., Sect. A 182, 59 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Kristallografiya, Vol. 46, No. 3, 2001, pp. 452–460.
Original Russian Text Copyright © 2001 by Nesterov, Kuleshova, Antipin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nesterov, V.N., Kuleshova, L.N. & Antipin, M.Y. Formation of crystal structure of cyanovinylbenzene derivatives: X-ray structure investigation of ethyl esters of 3,4-dimethoxy-, 3,4,5-trimethoxy-, and 4-fluorobenzylidenecyanoacetic acids. Crystallogr. Rep. 46, 402–410 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1376469
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1376469