Abstract
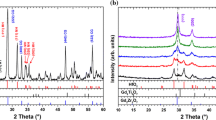
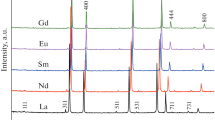
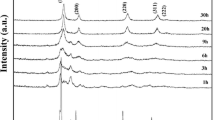
The effect of the addition of 11 mol % R2O3 (R = Sc, Y, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) on the phase and elemental composition, microstructure, and electroconductivity of hafnium oxide was studied. Samples of HfO2 doped with any of these elements, except for Sc, represent solid solutions with a cubic fluorite-like structure. The HfO2–Sc2O3 sample consists of the Hf7Sc2O17 phase with a fluorite-like structure with rhombohedral distortions that undergoes a reversible transformation into a cubic structure at a temperature of ~760°C. The dopant’s nature has almost no effect on the microstructure of HfO2–R2O3 ceramics; all synthesized samples are large-grain ceramics with a grain size as high as 10 μm. We show that the grain bulk conductivity is the limiting factor determining the conductivity of the HfO2–R2O3 samples. The HfO2–Tm2O3 and HfO2–Yb2O3 compositions, in which high conductivity is combined with structural stability, are the most promising materials as solid oxide electrolytes.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. K. Nahar, V. Singh, and A. Sharma, J. Mater. Sci. Electron. 18, 615 (2007).
G. D. Wilk, R. M. Wallace, and J. M. Anthony, J. Appl. Phys. 87, 484 (2000).
K. J. Hubbard and D. G. Schlom, J. Mater. Res. 11, 2757 (1996).
J. McPherson, J. Y. Kim, A. Shanware, and H. Mogul, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2121 (2003).
J. A. Valdez, I. O. Usov, J. Won, M. Tang, R. M. Dickerson, G. D. Jarvinen, and K. E. Sickafus, J. Nucl. Mater. 393, 126 (2009).
M. Yashima, H. Takahashi, K. Ohtake, T. Hirose, M. Kakihana, H. Arashi, Y. Ikuma, Y. Suzuki, and M. Yoshimura, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57, 289 (1996).
C. L. Platt, B. Dieny, and A. E. Berkowitz, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 2291 (1996).
M. J. Esplandiu, E. M. Patrito, and V. A. Macagno, Electrochim. Acta 42, 1315 (1997).
M. F. Trubelja and V. S. Stubican, Solid State Ionics 49, 89 (1991).
Y.-D. Kim, J.-Y. Yang, J.-I. Lee, M. Saqib, J.-S. Shin, M. Shin, J. H. Kim, H.-T. Lim, and J.-Y. Park, J. Alloys Compd. 779, 121 (2019).
N. Izu, T. Itoh, W. Shin, I. Matsubara, and N. Murayama, Sens. Actuators, B 123, 407 (2007).
M. Filipescu, N. Scarisoreanu, V. Craciun, B. Mitu, A. Purice, A. Moldovan, V. Ion, O. Toma, and M. Dinescu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 8184 (2007).
A. A. Demkov, O. Sharia, X. Luo, G. Bersuker, and J. Robertson, Microelectron. Eng. 86, 1763 (2009).
M. Kirm, J. Aarik, M. Jurgens, and I. Sildos, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 537, 251 (2005).
C. LeLuyer, M. Villanueva-Ibanez, A. Pillonnet, and C. Dujardin, J. Phys. Chem. A 122, 10152 (2008).
V. B. Glushkova and M. V. Kravchinskaya, Ceram. Int. 11, 56 (1985).
M. R. Winter and D. R. Clarke, Acta Mater. 54, 5051 (2006).
E. Wuchina, E. Opila, M. Opeka, W. Fahrenholtz, and I. Talmy, Electrochem. Soc. Interface 16, 30 (2007).
C. T. Lynch, High Temperature Oxides (Academic, New York, 1970), p. 193.
E. R. Andrievskaya, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 2363 (2008).
M. Mann and J. Kolis, J. Cryst. Growth 312, 461 (2010).
M. Yashima, K. Ohtake, M. Kakihana, H. Arashiand, and M. Yoshimura, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57, 17 (1996).
Y. Tabira, R. L. Withers, J. C. Barry, and L. Elcoro, J. Solid State Chem. 159, 121 (2001).
S. V. Zhidovinova, A. G. Kotlyar, V. N. Strekalovskii, and S. F. Pal’guev, Tr. Inst. Elektrokhim. UNTs AN SSSR 18, 148 (1972).
A. Chen, J. R. Smith, K. L. Duncan, R. T. DeHoff, K. S. Jones, and E. D. Wachsman, J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, B1624 (2010).
H. Iwahara, T. Yajima, T. Hibino, K. Ozaki, and H. Suzuki, Solid State Ionics 61, 65 (1993).
C. D. Savaniu, J. Canales-Vazquez, and J. T. S. Irvine, J. Mater. Chem. 15, 598 (2005).
K. D. Kreuer, S. Adams, W. Munch, A. Fuchs, U. Klock, and J. Maier, Solid State Ionics 145, 295 (2001).
T. H. Wan, M. Saccoccio, C. Chen, and F. Ciucci, Electrochim. Acta 184, 483 (2015).
V. Vashook, E. Girdauskaite, J. Zosel, T.-L. Wen, H. Ullmann, and U. Guth, Solid State Ionics 177, 1163 (2006).
Z. S. Volchenkova and D. S. Zubankova, Study of Molten Salt and Oxide Systems (Akad. Nauk SSSR UNTs, Sverdlovsk, 1975) [in Russian].
P. Simoncic and A. Navrotsky, J. Mater. Sci. 22, 876 (2007).
A. L. Gavrilyuk, D. A. Osinkin, and D. I. Bronin, Russ. J. Electrochem. 53, 575 (2017).
A. N. Vlasov, Elektrokhimiya 25, 699 (1989).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
SEM and XRD measurements were performed using the facilities of the Shared Access Centre “Composition of Compounds” Institute of High-Temperature Electrochemistry, Ural Branch Russian Academy of Sciences. We are grateful to A.A. Pankratov for SEM investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Kukharuk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meshcherskikh, A.N., Kolchugin, A.A., Antonov, B.D. et al. Phase Composition, Microstructure, and Electroconductivity of HfO2–R2O3 Solid Electrolytes (R = Sc, Y, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, and Lu). Phys. Solid State 62, 188–195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783420010229
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783420010229