Abstract
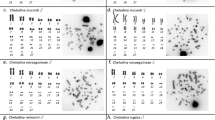
A striking example of the power of chromosome painting has been the resolution of the male platypus karyotype and the pairing relationships of the chain of ten sex chromosomes. We have extended our analysis to the nine sex chromosomes of the male echidna. Cross-species painting with platypus shows that the first five chromosomes in the chain are identical in both, but the order of the remainder are different and, in each species, a different autosome replaces one of the five X chromosomes. As the therian X is homologous mainly to platypus autosome 6 and echidna 16, and as SRY is absent in both, the sex determination mechanism in monotremes is currently unknown. Several of the X and Y chromosomes contain genes orthologous to those in the avian Z but the significance of this is also unknown. It seems likely that a novel testis determinant is carried by a Y chromosome common to platypus and echidna. We have searched for candidates for this determinant among the many genes known to be involved in vertebrate sex differentiation. So far fourteen such genes have been mapped, eleven are autosomal in platypus, two map to the differential regions of X chromosomes, and one maps to a pairing segment and is likewise excluded. Search for the platypus testis-determining gene continues, and the extension of comparative mapping between platypus and birds and reptiles may shed light on the ancestral origin of monotreme sex chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferguson-Smith, M.A. and Trifonov, V., Mammalian Karyotype Evolution, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2007, vol. 8, pp. 950–962.
Bick, Y.A. and Sharman, G.B., The Chromosomes of the Platypus, Cybios, 1975, vol. 14, pp. 17–28.
Murtagh, C.E., A Unique Cytogenetics System in Monotremes, Chromosoma, 1977, vol. 65, pp. 37–57.
Watson, J.M., Spencer, J.A., Riggs, A.D., and Graves, J.A.M., The X Chromosome of Monotremes Shares a Highly Conserved Region of the X Chromosomes of Marsupial and Monotreme as Well as Eutherian Mammals, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1990, vol. 87, pp. 7125–7129.
Rens, W., Grtzner, F., O’Brien, P.C.M., et al., Resolution and Evolution of the Duck-Billed Platypus Karyotype with an X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5Y5 Male Sex Chromosome Constitution, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, vol. 101, pp. 16257–16261.
Rens, W., O’Brien, P.C.M., Grtzner, F., et al., The Multiple Sex Chromosomes of Platypus and Echidna Are not Completely Identical and Several Share Homology with the Avian Z, Genome Biol., 2007, vol. 8, p. R23.
Grützner, F., Rens, W., Tsend-Ayush, E., et al., In the Platypus a Meiotic Chain of Ten Sex Chromosomes Shares Genes with the Bird Z and Mammal X Chromosomes, Nature, 2004, vol. 432, pp. 913–917.
Warren, W.C., Hillier, L.W., Marshall, et al., Genome Analysis of the Platypus Reveals Unique Signatures of Evolution, Nature, 2008, vol. 453, pp. 175–183.
Waters, P.D., Delbridge, M.L., Deakin, J.E., et al., Autosomal Location of Genes from the Conserved Mammalian X in the Platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus): Implications for Mammalian Sex Chromosome Evolution, Chromosome Res., 2005, vol. 13, pp. 401–410.
Wallis, M.C., Delbridge, M.L., Pask, A.J., et al., Mapping Platypus SOX Genes: Autosomal Location of SOX9 Excludes It from Sex Determining Role, Cytogenet. Genome Res., 2007, vol. 116, pp. 232–234.
Veyrunes, F., Waters, P.D., Miethke, P., et al., Bird-Like Chromosomes of the Platypus Imply Recent Origin of Mammal Sex Chromosomes, Genome Res., 2008, vol. 18, pp. 965–973.
Wallis, M.C., Waters, P.D., Delbridge, M.L., et al., Sex Determination in Platypus and Echidna: Autosomal Location of SOX3 Confirms the Absence of SRY from Monotremes, Chromosome Res., 2007, vol. 15, pp. 949–959.
Graphodatskaya, D., Rens, W., Wallis, M.C., et al., Search for the Sex Determining Switch in Monotremes: Mapping WT1, SF1, LHX1, LHX2, FGF9, WNT4, RSPO1 and GATA4 in Platypus, Chromosome Res., 2007, vol. 15, pp. 777–785.
Deakin, J.E., Hore, T.A., Koina, E., and Graves, J.A.M., The Status of Dosage Compensation in the Multiple X Chromosomes of the Platypus, PLoS Genet., 2008, vol. 4, p. e1000140.
Edwards, C.A., Rens, W., Clarke, O., et al., The Evolution of Imprinting: Chromosome Mapping of Orthologues of Mammalian Imprinted Domains in Monotremes and Marsupial Mammals, BMC Evol. Biol., 2007, vol. 7, p. 157.
Kortschak, R.D., Tsend-Ayush, E., and Grutzner, F., Analysis of SINE and LINE Repeat Content of Y Chromosomes in the Platypus, Ornithorhyncus anatinus, Reprod. Fertil. Dev., 2009, vol. 21, pp. 964–975.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.A. Ferguson-Smith, W. Rens, 2010, published in Genetika, 2010, Vol. 46, No. 10, pp. 1314–1319.
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferguson-Smith, M.A., Rens, W. The unique sex chromosome system in platypus and echidna. Russ J Genet 46, 1160–1164 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795410100054
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795410100054