Abstract
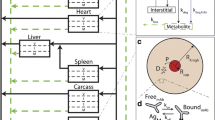
We present improved computational models for investigating monoclonal antibody-based protocols for diagnostic imaging and therapy of solid tumors. Our earlier models used a boundary condition (Dirichlet) that specified concentrations of diffusing molecular species at the interface between a prevascular tumor nodule and surrounding normal tissue. Here we introduce a concentration-dependent flux boundary condition with finite rates of diffusion in the normal tissue. We then study the effects of this new condition on the tumor's temporal uptake and spatial distribution of radiolabeled targeting agents. We compare these results to ones obtained with the Dirichlet boundary condition and also conduct parameter sensitivity analyses. Introducing finite diffusivity for any molecular species in normal tissue retards its delivery to and removal from the tumor nodule. Effects are protocol- and dose regimen-dependent; generally, however, mean radionuclide concentration and tumor-to-blood ratio declined, whereas relative exposure and mean residence time increased. Finite diffusivity exacerbates the negative effects of antigen internalization. Also, the sensitivity analyses show that mean concentration and tumor-to-blood ratio are quite sensitive to transcapillary permeability and lymphatic efflux values, yet relatively insensitive to precise values of diffusion coefficients. Our analysis underscores that knowledge of antigen internalization rates and doses required to saturate antigen in the tumor will be important for exploiting antibody-based imaging and treatment approaches. © 2001 Biomedical Engineering Society.
PAC01: 8758-b, 8710+e, 8753-j
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berk, D. A., F. Yuan, M. Leunig, and R. K. Jain. Direct in vivo measurement of targeted binding in a human tumor xenograft. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.94:1785–1790, 1997.
Chary, S. R., and R. K. Jain. Direct measurement of interstitial convection and diffusion of albumin in normal and neoplastic tissues by fluorescence photobleaching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.86:5385–5389, 1989.
Clauss, M. A., and R. K. Jain. Interstitial transport of rabbit and sheep antibodies in normal and neoplastic tissues. Cancer Res.50:3487–3492, 1990.
Crone, C., and D. G. Levitt. Capillary permeability to small solutes. In: The Cardiovascular System, edited by E. M. Renkin, C. C. Michel, and S. R. Geiger. Bethesda, MD: American Physiological Society, 1984, pp. 411–466.
Fujimori, K., D. R. Fisher, and J. N. Weinstein. Integrated microscopic-macroscopic pharmacology of monoclonal antibody radioconjugates: The radiation dose distribution. Cancer Res.51:4821–4827, 1991.
Fujimori, K., D. G. Covell, J. E. Fletcher, and J. N. Weinstein. Modeling analysis of the global and microscopic distribution of immunoglobulin G, F(ab′)2, and Fab in tumors. Cancer Res.49:5656–5663, 1989.
Fujimori, K., D. G. Covell, J. E. Fletcher, and J. N. Weinstein. A modeling analysis of monoclonal antibody percolation through tumors: A binding-site barrier. J. Nucl. Med.31:1191–1198, 1990.
Goodwin, D. A., C. F. Meares, M. J. McCall, M. McTigue, and W. Chaovapong. Pretargeted immunoscintigraphy of murine tumors with indium-111-labeled bifunctional haptens. J. Nucl. Med.29:226–234, 1988.
Hnatowich, D. J., F. Virzi, and M. Rusckowki. Investigations of avidin and biotin for imaging applications. J. Nucl. Med.28:1294–1302, 1987.
Juweid, M., R. Neumann, C. Paik, M. J. Perez-Bacete, J. Sato, W. van Osdol, and J. N. Weinstein. Micropharmacology of monoclonal antibodies in solid tumors: direct experimental evidence for a binding site barrier. Cancer Res.52:5144–5153, 1992.
Khawli, L. A., M. M. Alauddin, G. K. Miller, and A. L. Epstein. Improved immunotargeting of tumors with biotinylated monoclonal antibodies and radiolabeled streptavidin. Antibody, Immunoconjugates, Radiopharm.6:13–27, 1993.
LeDoussal, J. M., M. Martin, M. Delaage, and J. Barbet. In vitro and in vivo targeting of radiolabeled monovalent and divalent haptens with dual specificity monoclonal antibody conjugates: Enhanced divalent hapten affinity for cell bound antibody conjugate. J. Nucl. Med.30:1358–1366, 1989.
Nakamoto, Y., T. Saga, H. Sakahara, Z. Yao, M. Zhang, N. Sato, S. Zhao, H. Nakada, I. Yamashina, and J. Konishi. Three-step tumor imaging with biotinylated monoclonal antibody, streptavidin and 111In-DTPA-biotin. Nucl. Med. Biol.25:95–99, 1998.
Nicholson, C., and L. Tao. Hindered diffusion of high molecular weight compounds in brain extracellular microenvironment measured with integrative optical imaging. Biophys. J.65:2277–2290, 1993.
Nugent, L. J., and R. K. Jain. Extravascular diffusion in normal and neoplastic tissue. Cancer Res.44:238–244, 1984.
Oehr, P., J. Westermann, and H. J. Biersack. Streptavidin and biotin as potential tumor imaging agents [letter]. J. Nucl. Med.29:728–729, 1988.
Paganelli, G.et al.Three-step monoclonal antibody tumor targeting in carcinoembryonic antigen-positive patients. Cancer Res.51:5960–5966, 1991.
Paganelli, G.et al.Radioimmunoguided surgery using iodine-125-labeled biotinylated monoclonal antibodies and cold avidin. J. Nucl. Med.35:1970–1975, 1994.
Pimm, M. V., H. F. Fells, A. C. Perkins, and R. W. Baldwin. Iodine-131 and indium-111 labeled avidin and streptavidin for pretargeted immunoscintigraphy with biotinylated and anti-tumor monoclonal antibody. Nucl. Med. Comm.9:931–941, 1988.
Renkin, E. M.Multiple pathways of capillary permeability. Circ. Res.41:735–743, 1977.
Rippe, B., and B. Haraldsson. Fluid and protein fluxes across small and large pores in the microvasculature. Application of two-pore equations. Acta Physiol. Scand.131:411–428, 1987.
Saga, T., R. D. Neumann, T. Heya, J. Sato, S. Kinuya, N. Le, C. H. Paik, and J. N. Weinstein. Targeting cancer micrometastases with monoclonal antibodies: A binding-site barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.92:8999–9003, 1995.
Sharkey, R. M., H. Karacay, G. L. Griffiths, T. M. Behr, R. D. Blumenthal, M. J. Mattes, H. J. Hansen, and D. M. Goldenberg. Development of a streptavidin-anti-carcinoembryonic antigen antibody, radiolabeled biotin pretargeting method for radioimmunotherapy of colorectal cancer. Studies in a human colon cancer xenograft model. Bioconjug. Chem.8:595–604, 1997.
Siccardi, A. G., G. Paganelli, A. E. Pontiroli, M. Pelagi, P. Magnani, G. Viale, G. Faglia, and F. Fazio. In vivo imaging of chromogranin A-positive endocrine tumours by three-step monoclonal antibody targeting. Eur. J. Nucl. Med.23:1455–1459, 1996.
Stickney, D. R., L. D. Anderson, J. B. Slater, C. N. Ahlem, G. A. Kirk, S. A. Schweighardt, and J. M. Frincke. Bifunctional antibody: A binary radiopharmaceutical delivery system for imaging colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res.51:6650–6655, 1991.
Sung, C., and W. W. van Osdol. Pharmacokinetic comparison of direct antibody targeting with pretargeting protocols based on streptavidin-biotin binding [see comments]. J. Nucl. Med.36:867–876, 1995.
Sung, C., W. W. van Osdol, T. Saga, R. D. Neumann, R. L. Dedrick, and J. N. Weinstein. Streptavidin distribution in metastatic tumors pretargeted with a biotinylated monoclonal antibody: Theoretical and experimental pharmacokinetics. Cancer Res.54:2166–2175, 1994.
van Osdol, W., K. Fujimori, and J. N. Weinstein. An analysis of monoclonal antibody distribution in microscopic tumor nodules: Consequences of a “binding site barrier.” Cancer Res.51:4776–4784, 1991.
van Osdol, W. W., C. Sung, R. L. Dedrick, and J. N. Weinstein. A distributed pharmacokinetic model of two-step imaging and treatment protocols: Application to streptavidin-conjugated monoclonal antibodies and radiolabeled biotin. J. Nucl. Med.34:1552–1564, 1993.
Weinstein, J. N., R. R. Eger, D. G. Covell, C. D. Black, J. Mulshine, J. A. Carrasquillo, S. M. Larson, and A. M. Keenan. The pharmacology of monoclonal antibodies. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.507:199–210, 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Praxmarer, M., Sung, C., Bungay, P.M. et al. Computational Models of Antibody-Based Tumor Imaging and Treatment Protocols. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 29, 340–358 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1359453
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1359453