Abstract
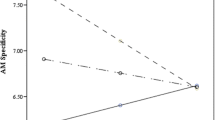
Overgeneral autobiographical memory (OGM) refers to the tendency to retrieve less specific personal memories. According to the functional avoidance hypothesis, OGM might act as a cognitive strategy to avoid emotionally distressing details of negative memories. In the present study, we investigated the effect of an experimentally induced avoidant state on memory specificity. We primed an avoidant state in half of the participants and an approaching state in the other half by means of a Scrambled Sentences Task (SST). Memory specificity was measured before and after priming. Trait cognitive avoidant coping was assessed prior to the experiment. Analyses indicated that higher trait avoidance was significantly associated with lower memory specificity after the SST and stronger reductions in memory specificity from pre- to post-SST, irrespective of the priming condition. The latter suggests that the SST triggered high avoiders’ avoidance schema in both conditions, possibly because it was experienced as a stressor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AGLAN, A., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., PICKLES, A., & HILL, J. (2010). Overgeneral autobiographical memory in women: Association with childhood abuse and history of depression in a community sample. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 49, 359–372. Avoidance and Memory Specificity Following SST doi: 10.1348/014466509X467413
BREWIN, C. R., WATSON, M., MCCARTHY, S., HYMAN, P., & DAYSON, D. (1998). Intrusive memories and depression in cancer patients. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 36, 1131–1142. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(98)00084-9
CACIOPPO, J. T., PRIESTER, J. R., & BERNTSON, G. G. (1993). Rudimentary determinants of attitudes. II: Arm flexion and extension have differential effects on attitudes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 65, 5–17. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.65.1.5
COHEN, J., COHEN, P., WEST, S., & AIKEN, L. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
CONWAY, M. A., & PLEYDELL-PEARCE, C. W. (2000). The construction of autobiographical memories in the self-memory system. Psychological Review, 107, 261–288. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.107.2.261
DALGLEISH, T., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., GOLDEN, A. J., PERKINS, N., BARRETT, L. F., BARNARD, P. J., … WATKINS, E. (2007). Reduced specificity of autobiographical memory and depression: The role of executive control. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 136, 23–42. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.136.1.23
DEBEER, E., RAES, F., CLAES, S., VRIEZE, E., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., & HERMANS, D. (2012). Relationship between cognitive avoidant coping and changes in overgeneral autobiographical memory retrieval following an acute stressor. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 43, S37-S42. doi: 10.1016/j. jbtep.2011.04.002
DEBEER, E., RAES, F., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., & HERMANS, D. (2011). Context-dependent activation of reduced autobiographical memory specificity as an avoidant coping style. Emotion, 11, 1500–1506. doi: 10.1037/a0024535
DEFRANC, A., RAES, F., & HERMANS, D. (2004). The approach/avoidance scrambled sentences task. Unpublished instrument, Department of Psychology, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
FÖRSTER, J. (2003). The influence of approach and avoidance motor actions on food intake. European Journal of Social Psychology, 33, 339–350. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.150
FRAZIER, P. A., TIX, A. P., & BARRON, K. E. (2004). Testing moderator and mediator effects in counseling psychology research. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 51, 115–134. doi: 10.1037/0022-0167.51.1.115
GOSSELIN, P., LANGLOIS, F., FREESTON, M. H., LADOUCEUR, R., DUGAS, M. J., & PELLETIER, O. (2002). Le Questionnaire d’Evitement Cognitif (QEC): Développement et validation auprès d’adultes et d’adolescents [The Cognitive Avoidance Questionnaire (CAQ): Development and validation among adult and adolescent samples]. Journal de Thérapie Comportementale et Cognitive, 12, 24–37. Retrieved from http://www.aftcc.org/jtcc.php
HARVEY, A. G., BRYANT, R. A., & DANG, S. T. (1998). Autobiographical memory in acute stress disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66, 500–506. doi: 0.1037/0022-006X.66.3.500
HAUER, B. J. A., WESSEL, I., ENGELHARD, I. M., PEETERS, L. L., & DALGLEISH, T. (2009). Prepartum autobiographical memory specificity predicts post-traumatic stress symptoms following complicated pregnancy. Memory, 17, 544–556. doi: 10.1080/09658210902953836
HAUER, B. J. A., WESSEL, I., GERAERTS, E., MERCKELBACH, H., & DALGLEISH, T. (2008). Autobiographical memory specificity after manipulating retrieval cues in adults reporting childhood sexual abuse. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 117, 444–453. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.117.2.444
HAUER, B. J. A., WESSEL, I., & MERCKELBACH, H. (2006). Intrusions, avoidance and overgeneral memory in a non-clinical sample. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, 13, 264–268. doi: 10.1002/cpp.495
HERMANS, D., DE DECKER, A., DE PEUTER, S., RAES, F., EELEN, P., & WILLIAMS, J. M. G. (2008). Autobiographical memory specificity and affect regulation: Coping with a negative life event. Depression and Anxiety, 25, 787–792. doi: 10.1002/da.20326
HERMANS, D., DEFRANC, A., RAES, F., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., & EELEN, P. (2005). Reduced autobiographical memory specificity as an avoidant coping style. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 44, 583–589. doi: 10.1348/014466505X53461
HERMANS, D., VAN DEN BROECK, K., BELIS, G., RAES, F., PIETERS, G., & EELEN, P. (2004). Trauma and autobiographical memory specificity in depressed inpatients. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 42, 775–789. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(03)00197-9
HÖPING, W., & DE JONG-MEYER, R. (2003). Differentiating unwanted intrusive thoughts from thought suppression: What does the White Bear Suppression Inventory measure? Personality and Individual Differences, 34, 1049–1055. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(02)00089-2
HOROWITZ, M., WILNER, M., & ALVAREZ, W. (1979). Impact of Event Scale: A measure of subjective stress. Psychosomatic Medicine, 41, 209–218. doi: 0033-3174/79/03020910
KIRSCHBAUM, C., PIRKE, K. M., & HELLHAMMER, D. H. (1993). The ‘Trier Social Stress Test’: A tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology, 28, 76–81. doi: 10.1159/000119004
KUYKEN, W., & BREWIN, C. R. (1995). Autobiographical memory functioning in depression and reports of early abuse. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104, 585–591. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.104.4.585
KUYKEN, W., & MOULDS, M. L. (2009). Remembering as an observer: How is autobiographical memory retrieval vantage perspective linked to depression? Memory, 17, 624–634. doi: 10.1080/09658210902984526
LEMOGNE, C., BERGO UIGNAN, L., PIOLINO, P., JOUVENT, R., ALLILAIRE, J.-F., & FOSSATI, P. (2009). Cognitive avoidance of intrusive memories and autobiographical memory: Specificity, autonoetic consciousness, and self-perspective. Memory, 17, 1–7. doi: 10.1080/09658210802438466
MCNALLY, R. J., LASKO, N. B., MACKLIN, M. L., & PITMAN, R. K. (1995). Autobiographical memory disturbance in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 34, 619–630. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(95)00007-K
MURIS, P., MERCKELBACH, H., & HORSELENBERG, R. (1996). Individual differences in thought suppression. The White Bear Suppression Inventory: Factor structure, reliability, validity, and correlates. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 34, 501–513. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(96)00005-8
OTTENBREIT, N. D., & DOBSON, K. S. (2004). Avoidance and depression: The construction of the Cognitive-Behavioral Avoidance Scale. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 42, 293–313. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(03)00140-2
PALM, K. M., & STRONG, D. R. (2007). Using item response theory to examine the White Bear Suppression Inventory. Personality and Individual Differences, 42, 87–98. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2006.06.023
RAES, F., HERMANS, D., DE DECKER, A., EELEN, P., & WILLIAMS, J. M. G. (2003). Autobiographical memory specificity and affect regulation: An experimental approach. Emotion, 3, 201–206. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.3.2.201
RAES, F., HERMANS, D., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., BRUNFAUT, E., HAMELINCK, L., & EELEN, P. (2006). Reduced autobiographical memory specificity and trauma in major depression: On the importance of post-trauma coping versus mere trauma exposure. In S. M. Sturt (Ed.), New developments in child abuse research (pp. 61–72). New York, NY: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
RAES, F., HERMANS, D., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., & EELEN, P. (2006). Reduced autobiographical memory specificity and affect regulation. Cognition and Emotion, 20, 402–429. doi: 10.1080/02699930500341003
RAES, F., HERMANS, D., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., & EELEN, P. (2007). A sentence completion procedure as an alternative to the Autobiographical Memory Test for assessing overgeneral memory in non-clinical populations. Memory, 15, 495–507. doi: 10.1080/09658210701390982
RAES, F., WATKINS, E. R., WILLIAMS, J. M. G., & HERMANS, D. (2008). Non-ruminative processing reduces overgeneral autobiographical memory retrieval in students. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 46, 748–756. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2008.03.003
RASSIN, E., MURIS, P., SCHMIDT, H., & MERCKELBACH, H. (2000). Relationships between thought-action fusion, thought suppression and obsessive-compulsive symptoms: A structural equation modeling approach. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 38, 889–897. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(99)00104-7
SMEESTERS, D., WARLOP, L., VAN AVERMAET, E., CORNEILLE, O., & YZERBYT, V. (2003). Do not prime hawks with doves: The interplay of construct activation and consistency of social value orientation on cooperative behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84, 972–987. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.84.5.972
SRULL, T. K., & WYER, R. S. (1979). The role of category accessibility in the interpretation of information about persons: Some determinants and implications. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37, 1660–1672. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.37.10.1660
STOKES, D. J., DRITSCHEL, B. H., & BEKERIAN, D. A. (2004). The effect of burn injury on adolescents autobiographical memory. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 42, 1357–1365. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2003.10.003
WEGNER, D. M., & ZANAKOS, S. (1994). Chronic thought suppression. Journal of Personality, 62, 615–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.1994.tb00311.x
WESSEL, I., MERCKELBACH, H., & DEKKERS, T. (2002). Autobiographical memory specificity, intrusive memory, and general memory skills in Dutch-Indonesian survivors of the World War II era. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 15, 227–234. doi: 10.1023/A:1015207428675
WILLIAMS, A. D., & MOULDS, M. L. (2007). Cognitive avoidance of intrusive memories: Recall vantage perspective and associations with depression. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45, 1141–1153. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2006.09.005
WILLIAMS, J. M. G., BARNHOFER, T., CRANE, C., HERMANS, D., RAES, F., WATKINS, E., & DALGLEISH, T. (2007). Autobiographical memory specificity and emotional disorder. Psychological Bulletin, 133, 122–148. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.122
WILLIAMS, J. M. G., & BROADBENT, K. (1986). Autobiographical memory in suicide attempters. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 95, 144–149. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.95.2.144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by a predoctoral grant from the Research Foundation-Flanders (FWOVlaanderen) and by a postdoctoral research grant from the University of Leuven.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debeer, E., Raes, F., Williams, J.M.G. et al. Reduction in Memory Specificity Following an Approach/Avoidance Scrambled Sentences Task Relates to Cognitive Avoidant Coping. Psychol Rec 63, 73–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.11133/j.tpr.2013.63.1.006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.11133/j.tpr.2013.63.1.006