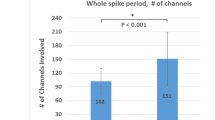
Abstract
Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep is characterized by recurring transient events (Cyclic Alternating Patterns, CAP), some of which consist of increased slow wave activity (A1 subtype). Such transient slow-wave events may play an important role in NREM sleep regulation and are known to facilitate epileptiform activity. In our study we investigated the relationship between interictal spike activity and Cyclic Alternating Patterns in three epileptic patients, using simultaneous scalp electroencephalogram (EEG) recording and intracranial electrocorticography. A significant increase of interictal activity was found during CAP A1 subtypes. A positive correlation between scalp EEG delta power and spike activity was found only in CAP A1 subtypes, but not during other events. These results show that transient (but not subcontinuous) delta activity has a facilitating effect on epileptoform activity, also suggesting a functional dissociation between morphologically similar delta activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pereira AM, Bruni O, Ferri R, Nunes ML. Sleep instability and cognitive status in drug-resistant epilepsies. Sleep Med. 2012; 13: 536–41.
Pereira AM, Bruni O, Ferri R, Palmini A, Nunes ML. The impact of epilepsy on sleep architecture during childhood. Epilepsia 2012; 53: 1519–25.
Foldvary-Schaefer N, Grigg-Damberger M. Sleep and epilepsy: what we know, don’t know, and need to know. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006; 23 (1): 4–20.
Halasz P, Bodizs R. Dynamic Structure of NREM Sleep. Springer: London, 2013.
Terzano MG, Mancia D, Salati MR, Costani G, Decembrino A, Parrino L. The cyclic alternating pattern as a physiologic component of normal NREM sleep. Sleep 1985; 8: 137–45.
Parrino L, Smerieri A, Spaggiari MC, Terzano MG. Cyclic alternating pattern (CAP) and epilepsy during sleep: how a physiological rhythm modulates a pathological event. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000; 111: S39–46.
Ferri R, Bruni O, Miano S, Terzano MG. Topographic mapping of the spectral components of the cyclic alternating pattern (CAP). Sleep Med. 2005; 6 (1): 29–36.
Terzano MG, Parrino L, Smerieri A et al. CAP and arous-als are involved in the homeostatic and ultradian sleep processes. J. Sleep Res. 2005; 14: 359–68.
Parrino L, Ferri R, Bruni O, Terzano MG. Cyclic alternating pattern (CAP): the marker of sleep instability. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012; 16 (1): 27–45.
Ferri R, Rundo F, Bruni O, Terzano MG, Stam CJ. Regional scalp EEG slow-wave synchronization during sleep cyclic alternating pattern A1 subtypes. Neurosci. Lett. 2006; 404: 352–7.
Terzano MG, Parrino L, Fioriti G, Orofiamma B, Depoortere H. Modifications of sleep structure induced by increasing levels of acoustic perturbation in normal subjects. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1990; 76 (1): 29–38.
Halász P. K-complex, a reactive EEG graphoelement of NREM sleep: an old chap in a new garment. Sleep Med. Rev. 2005; 9: 391–412.
Massimini M, Ferrarelli F, Esser SK et al. Triggering sleep slow waves by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007; 104: 8496–501.
Ferri R, Drago V, Arico D et al. The effects of experimental sleep fragmentation on cognitive processing. Sleep Med. 2010; 11: 378–85.
Gigli GL, Calia E, Marciani MG et al. Sleep microstructure and EEG epileptiform activity in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 1992; 33: 799–804.
Halasz P, Terzano MG, Parrino L. Spike-wave discharge and the microstructure of sleep-wake continuum in idi-opathic generalised epilepsy. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2002; 32 (1): 38–53.
Terzano MG, Parrino L, Anelli S, Halasz P, Portera-Sánchez A. Modulation of Generalized spike-and-wave discharges during sleep by cyclic alternating pattern. Epilepsia 1989; 30: 772–81.
Bonakis A, Koutroumanidis M. Epileptic discharges and phasic sleep phenomena in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009; 50: 2434–45.
Terzano MG, Parrino L, Garofalo PG, Durisotti C, Filati-Roso C. Activation of partial seizures with motor signs during cyclic alternating pattern in human sleep. Epilepsy Res. 1991; 10 (2–3): 166–73.
Parrino L, De Paolis F, Milioli G et al. Distinctive polysomnographic traits in nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2012; 53: 1178–84.
Terzano MG, Parrino L, Spaggiari MC, Barusi R, Simeoni S. Discriminatory effect of cyclic alternating pattern in focal lesional and benign rolandic interictal spikes during sleep. Epilepsia 1991; 32: 616–28.
Bruni O, Novelli L, Luchetti A et al. Reduced NREM sleep instability in benign childhood epilepsy with centro-temporal spikes. Clinl Neurophysiol 2010; 121: 665–71.
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson A, Quan S. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specification, 1st edn. American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, IL, 2007.
Terzano MG, Parrino L, Sherieri A et al. Atlas, rules, and recording techniques for the scoring of cyclic alternating pattern (CAP) in human sleep. Sleep Med. 2001; 2: 537–53.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995; 57: 289–300.
Ferri R, Parrino L, Smerieri A et al. Non-linear EEG measures during sleep: effects of the different sleep stages and cyclic alternating pattern. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2002; 43: 273–86.
Ferri R, Rundo F, Bruni O, Terzano MG, Stam CJ. Dynamics of the EEG slow-wave synchronization during sleep. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005; 116: 2783–95.
Ferri R, Bruni O, Miano S, Plazzi G, Terzano MG. All-night EEG power spectral analysis of the cyclic alternating pattern components in young adult subjects. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005; 116: 2429–40.
Borbely AA, Baumann F, Brandeis D, Strauch I, Lehmann D. Sleep deprivation: effect on sleep stages and EEG power density in man. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1981; 51: 483–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ujma, P.P., Simor, P., Ferri, R. et al. Increased interictal spike activity associated with transient slow wave trains during non-rapid eye movement sleep. Sleep Biol. Rhythms 13, 155–162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/sbr.12101
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/sbr.12101