Abstract
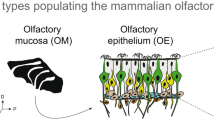
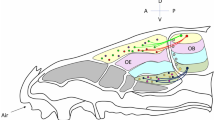
Since the discovery of the superfamily of approximately 1000 odorant receptor genes in rodents, the structural simplicity as well as the complexity of the olfactory system have been revealed. The simple aspects include the one neuron-one receptor rule and the exclusive convergence of projections from receptor neurons expressing the same receptors to one or two glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. Odor decoding in the olfactory cortex or higher cortical areas is likely to be a complicated process that depends on the sequence of signal activation and the relative signal intensities of receptors overlapping for similar but different odors. The aim of the present study was to investigate odor information processing both in receptors and in the olfactory cortex. At the receptor level, the similarity and difference in receptor codes between a pair of chiral odorants were examined using the tissue-printing method for sampling all the epithelial zones. In order to dissect odor-driven signal processing in the olfactory cortex by reducing cross-talk with the non-olfactory activities, such as cyclic respiration or other sensory inputs, an in vitro preparation of isolated whole brain with an attached nose was developed, and the methodologies and resulting hypothesis of receptor-sensitivity-dependent hierarchical odor information coding were reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balu R, Pressler RT, Strowbridge BW (2007) Multiple modes of synaptic excitation of olfactory bulb granule cells. J Neurosci 27, 5621–32.
Bozza TC, Feinstein P, Zheng C, Mombaerts P (2002) Odorant receptor expression defines functional units in the mouse olfactory system. J Neurosci 22, 3033–43.
Bressler SL, Freeman WJ (1980) Frequency analysis of olfactory system EEG in cat, rabbit, and rat. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 50, 19–24.
Buck L, Axel R (1991) A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: A molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell 65, 175–87.
Chabaud P, Ravel N, Wilson DA et al. (2000) Exposure to behaviourally relevant odour reveals differential characteristics in rat central olfactory pathways as studied through oscillatory activities. Chem Senses 25, 561–73.
Chapman CA, Xu Y, Haykin S, Racine RJ (1998) Beta-frequency (15-35 Hz) electroencephalogram activities elicited by toluene and electrical stimulation in the behaving rat. Neuroscience 86, 1307–19.
de Curtis M, Paré D, Llinás R (1991) The electrophysiology of the olfactory hippocampal circuit in the isolated and perfused adult mammalian brain. Hippocampus 1, 341–54.
de Curtis M, Biella G, Forti M, Panzica F (1994) Multifocal spontaneous epileptic activity induced by restricted bicuculline ejection in the piriform cortex of the isolated guinea pig brain. J Neurophysiol 71, 2463–76.
de Curtis M, Biella G, Buccellati C, Folco G (1998) Simultaneous investigation of the neuronal and vascular compartments in the guinea pig brain isolated in vitro. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 3, 221–8.
de Curtis M, Takashima I, Iijima T (1999) Optical recording of cortical activity after in vitro perfusion of cerebral arteries with a voltage-sensitive dye. Brain Res 837, 314–19.
Desmaisons D, Vincent JD, Lledo PM (1999) Control of action potential timing by intrinsic subthreshold oscillations in olfactory bulb output neurons. J Neurosci 19, 10 727–37.
Ekstrand JJ, Domroese ME, Johnson DMG et al. (2001) A new subdivision of anterior piriform cortex and associated deep nucleus with novel features of interest for olfaction and epilepsy. J Comp Neurol 434, 289–307.
Erickson RP (2001) The evolution and implications of population and modular neural coding ideas. In: Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 130: Advances in Neural Population Coding (Nicolelis MAL, ed.). Elsevier, Amsterdam, 9–29.
Fornai F, Bassi L, Gesi M et al. (2000) Similar increases in extracellular lactic acid in the limbic system during epileptic and/or olfactory stimulation. Neuroscience 97, 447–58.
Fox PT, Raichle ME, Mintum MA, Dence C (1988) Nonoxidative glucose consumption during physiologic neural activity. Science 241, 462–4.
Godfrey PA, Malnic B, Buck LB (2004) The mouse olfactory receptor gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 2156–61.
Haberly LB (1969) Single-unit responses to odors in the prepyriform cortex of the rat. Brain Res 12, 481–4.
Haberly LB (2001) Parallel-distributed processing in olfactory cortex: New insights from morphological and physiological analysis of neuronal circuitry. Chem Senses 26, 551–76.
Haberly LB, Price JL (1977) The axonal projection patterns of the mitral and tufted cells of the olfactory bulb in the rat. Brain Res 129, 152–7.
Haberly LB, Price JL (1978) Association and commissural fiber systems of the olfactory cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 178, 711–40.
Hamana H, Hirono J, Kizumi M, Sato T (2003) Sensitivity-dependent hierarchical receptor codes for odors. Chem Senses 28, 87–104.
Hirono J, Sato T, Tonoike M, Takebayashi M (1992) Simultaneous recording of [Ca2+], increases in isolated olfactory receptor neurons retaining their original spatial relationship in intact tissue. J Neurosci Methods 42, 185–94.
Iijima T, Sato T, Kajiwara R, Takashima I (2000) Olfactory information processing lab. Bull Electrotechn Lab 64, 69–71.
Ishikawa T, Sato T, Shimizu A, Tsutsui KI, de Curtis M, Iijima T (2007) Odor-driven activity in the olfactory cortex of an in vitro isolated guinea-pig whole brain with olfactory epithelium. J Neurophysiol 97, 670–9.
Kashiwadani H, Sasaki YF, Uchida N, Mori K (1999) Synchronized oscillatory discharges of mitral/tufted cells with different molecular receptive ranges in the rabbit olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol 82, 1786–92.
Ketchum KL, Haberly LB (1993) Synaptic events that generate fast oscillations in piriform cortex. J Neurosci 13, 3980–5.
Linster C, Johnson BA, Yue E et al. (2001) Perceptual correlates of neural representations evoked by odorant enantiomers. J Neurosci 21, 9837–43.
Llinás R, Yaron Y, Sugimori M (1981) Isolated mammalian brain in vitro: New technique for analysis of electrical activity of neuronal circuit function. Fed Proc 40, 2240–5.
Malnic B, Hirono J, Sato T, Buck L (1999) Combinatorial receptor codes for odors. Cell 96, 713–23.
Matsutani S, Senba E, Tohyama M (1989) Terminal field of cholecystokinin-8-like immunoreactive projection neurons of the rat main olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 285, 73–82.
McCollum J, Larson J, Otto T, Schottler F, Granger R, Lynch G (1991) Short-latency single unit processing in the olfactory cortex. J Cogn Neurosci 3, 293–9.
Mombaerts P, Wang F, Dulac C et al. (1996) Visualizing an olfactory sensory map. Cell 87, 675–86.
Mühlethaler M, de Curtis M, Walton K, Llinás R (1993) The isolated and perfused brain of the guinea-pig in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 5, 915–26.
Nagayama S, Takahashi YK, Yoshihara Y, Mori K (2004) Mitral and tufted cells differ in the decoding manner of odor maps in the rat olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol 91, 2532–40.
Nakashima M, Mori K, Takagi SF (1978) Centrifugal influence on olfactory bulb activity in the rabbit. Brain Res 154, 301–6.
Nemitz JW, Goldberg SJ (1983) Neuronal responses of rat piriform cortex to odor stimulation: An extracellular and intracellular study. J Neurophysiol 49, 188–203.
Ressler KJ, Sullivan SL, Buck L (1994) Information coding in the olfactory system: Evidence for a stereotyped and highly organized epitope map on the olfactory bulb. Cell 79, 1245–55.
Rodriguez R, Haberly LB (1989) Analysis of synaptic events in the opposum piriform cortex with improved current sourcedensity techniques. J Neurophysiol 61, 702–18.
Sato T, Hirono J, Tonoike M, Takebayashi M (1994) Tuning specificities to aliphatic odorants in mouse olfactory receptor neurons and their local distribution. J Neurophysiol 72, 2980–9.
Sato T, Hirono J, Hamana H, Kzumi M (2003) Receptor-sensitivity-dependent hierarchical odor coding in olfaction. Jpn J Taste Smell Res 10, 715–18.
Schurr A, Payne RS, Miller JJ, Rigor BM (1997) Brain lactate, not glucose, fuels the recovery of synaptic function from hypoxia upon reoxygenation: An in vitro study. Brain Res 744, 105–11.
Schurr A, Miller JJ, Payne RS, Rigor BM (1999) An increase in lactate output by brain tissue serves to meet the energy needs of glutamate-activated neurons. J Neurosci 19, 34–9.
Serizawa S, Ishii T, Nakatani H et al. (2000) Mutually exclusive expression of odorant receptor transgenes. Nat Neurosci 3, 687–97.
Serizawa S, Miyamichi K, Nakatani H et al. (2003) Negative feedback regulation ensures the one receptor-one olfactory neuron rule in mouse. Science 302, 2088–94.
Shipley MT, McLean JH, Ennis M (1995) Olfactory system. In: The Rat Nervous System (Paxinos G, ed.), Academic Press, San Diego, 123–76.
Sugai T, Miyazawa T, Fukuda M, Yoshimura H, Onoda N (2005) Odor-concentration coding in the guinea-pig piriform cortex. Neuroscience 130, 769–81.
Takahashi YK, Kurosawa M, Hirono S, Mori K (2004) Topographic representation of odorant molecular features in the rat olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol 92, 2413–27.
Tanabe T, Iino M, Takagi SF (1975) Discrimination of odors in olfactory bulb, pyriform-amygdaloid areas, and orbitofrontal cortex of the monkey. J Neurophysiol 38, 1284–96.
Touhara K, Sengoku S, Inaki K et al. (1999) Functional Identification and reconstitution of an odorant receptor in single olfactory receptor neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 4040–5.
Tsuboi A, Yoshihara S, Yamazaki N et al. (1999) Olfactory neurons expressing closely linked and homologous odorant receptor genes tend to project their axons to neighboring glomeruli on the olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 19, 8409–18.
Uchida N, Zachary FM (2003) Speed and accuracy of olfactory discrimination in the rat. Nat Neurosci 6, 1224–9.
Uchida N, Takahashi UK, Tanifuji M, Mori K (2000) Odor maps in the mammalian olfactory bulb: Domain organization and odorant structural features. Nat Neurosci 3, 1035–43.
Wang F, Nemes A, Mendelsohn M, Axel R (1998) Odorant receptors govern the formation of a precise topographic map. Cell 93, 47–60.
Wilson DA (1998) Habituation of odor responses in the rat anterior piriform cortex. J Neurophysiol 79, 1425–40.
Wilson DA (2000) Comparison of odor receptive field plasticity in the rat olfactory bulb and anterior piriform cortex. J Neurophysiol 84, 3036–42.
Zhang X, Firestein S (2002) The olfactory receptor gene superfamily of the mouse. Nat Neurosci 5, 124–33.
Zou Z, Horowitz LS, Montmayeur JP, Snapper S, Buck LB (2001) Genetic tracing reveals a stereotyped sensory map in the olfactory cortex. Nature 414, 173–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, T., Hirono, J., Hamana, H. et al. Architecture of odor information processing in the olfactory system. Anato Sci Int 83, 195–206 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-073X.2007.00215.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-073X.2007.00215.x