Abstract
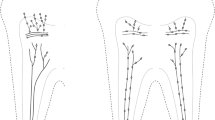
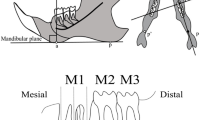
Developmental changes in pulpal innervation of rat incisors and molars were examined using the fluorescent styryl dye AM1-43, which labels sensory cells and nerves in vivo. From 2 to 40 days after birth, the animals were injected once with a small amount of AM1-43 solution (2 µg/g bodyweight). One day after the injection, the animals were killed and examined. In 3-day-old rats, neither incisors nor molars were innervated. In 7-dayold rats, the pulp of incisors and molars was innervated as indicated by fine intensely stained varicose sensory fibers and thicker intensely stained fibers running mostly along the blood vessels. In 15-, 27-, and 41-day-old rats, sensory nerve fibers neither passed through the odontoblast layer nor penetrated into the dentin in incisors, whereas the sensory nerve fibers penetrated into the coronal dentin through the odontoblast layers in molars. These results suggest that innervation of dental pulp is composed of two phases: (i) linear penetration of nerve fibers along blood vessels into the pulp space; and (ii) sprouting and extension of nerve fibers into coronal dentin. Innervation of the incisor pulp may stop at the first phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byers MR (1984) Dental sensory receptors. Int Rev Neurobiol 25, 39–94.
Byers MR, Närhi MVO (1999) Dental injury models: Experimental tools for understanding neuroinflammatory interactions and polymodal nociceptor functions. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 10, 4–39.
Fried K, Nosrat C, Lillesaar C, Hildebrand C (2000) Molecular signaling and pulpal nerve development. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 11, 318–32.
Fristad I, Heyraas KJ, Kvinnsland I (1994) Nerve fibers and cells immunoreactive to neurochemical markers in developing rat molars and supportive tissues. Arch Oral Biol 39, 633–46.
Gale JE, Marcotti W, Kennedy HJ, Kros CJ, Richardson GP (2001) FM1-43 dye behaves as a permanent blocker of the hair-cell mechanotransducer channel. J Neurosci 21, 7013–25.
Gunji T (1982) Morphological research on the sensitivity of dentin. Arch Histol Jpn 45, 45–67.
Hand AR (1970) Nerve-acinar cell relationships in the rat parotid gland. J Cell Biol 47, 540–43.
Headley DB, Suhan NM, Horn JP (2007) Different subcellular distributions of the vesicular monoamine transporter, VMAT2, in subclasses of sympathetic neurons. Brain Res 1129, 156–60.
Kvinnsland IH, Luuko K, Fristad I et al. (2004) Glial cell linederived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) from adult rat tooth serves a distinct population of large-sized trigeminal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 19, 2089–98.
Luukko K, Suvanto P, Saarma M, Thesleff I (1997) Expression of GDNF and its receptors in developing tooth is developmentally regulated and suggests multiple roles in innervation and organogenesis. Dev Dyn 210, 463–71.
Maeda T, Byers MR (1996) Different localizations of growthassociated protein (GAP-43) in mechanoreceptors and free nerve endings of adult rat periodontal ligament, dental pulp and skin. Arch Histol Cytol 59, 291–304.
Matsuo S, Ichikawa H, Henderson TA et al. (2001) trkA modulation of developing somatosensory neurons in oro-facial tissues: Tooth pulp fibers are absent in trkA knockout mice. Neuroscience 105, 747–60.
Meyers JR, MacDonald RB, Duggan A et al. (2003) Lighting up the senses: FM1-43 loading of sensory cells through nonselective ion channels. J Neurosci 23, 4054–65.
Mohamed SS, Atkinson ME (1983) A histological study of the innervation of developing mouse teeth. J Anat 136, 735–49.
Nishikawa S (2006) Systemic labeling and visualization of dental sensory nerves by the novel fluorescent marker AM143. Anat Sci Int 81, 181–6.
Nishikawa S, Sasaki F (1996) Internalization of styryl dye FM143 in the hair cells of lateral line organs in Xenopus larvae. J Histochem Cytochem 44, 733–41.
Nosrat CA, Fried K, Lindskog S, Olsen L (1997) Cellular expression of neurotrophin mRNAs during tooth development. Cell Tissue Res 290, 569–80.
Ringstedt T, Ibáñez CF, Nosrat CA (1999) Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in target invasion in the gustatory system. J Neurosci 19, 3507–18.
Tsuzuki H, Kitamura H (1991) Immunohistochemical analysis of pulpal innervation in developing rat molars. Arch Oral Biol 36, 139–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishikawa, S. Developmental changes in pulpal sensory innervation of rat incisors and molars shown on a single injection of the fluorescent dye AM1-43. Anato Sci Int 82, 227–232 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-073X.2007.00190.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-073X.2007.00190.x