Abstract
Aim
Endometrial tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) appear to play an essential role during early implantation by modulating the invasiveness of the trophoblast. The expression of TIMP-1, TIMP-2 and TIMP-3 in human endometrial stromal cells (ESC) was investigated during decidualization in vitro.
Methods
Endometrial stromal cells were isolated from hysterectomy specimens from premenopausal women undergoing surgery for benign reasons. Decidualization in vitro was induced by the application of 1 μmol/L progesterone and 30 nmol/L 17β-estradiol over 9 days. The expression of TIMP-1, TIMP-2 and TIMP-3 in ESC was measured by semiquantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay over intervals of 3 days.
Results
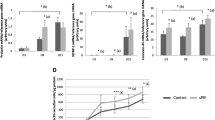
Decidualization in vitro was confirmed by a significant increase in prolactin expression. TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA and secreted protein showed no significant changes over the time-course of decidualization. In contrast, TIMP-3 was upregulated during the first 3 days of decidualization. An eightfold upregulation was observed until day 6, and the effect was less pronounced by day 9.
Conclusion
These results suggest a regulatory role of the TIMP system for endometrial differentiation in the second half of the menstrual cycle and in early implantation. The expression pattern of endometrial TIMP-3 might be important for the regulation of trophoblast invasion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aplin JD. Implantation, trophoblast differentiation and haemochorial placentation: mechanistic evidence in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Sci 1991; 99: 681–692.
Bischof P, Meisser A, Campana A. Biochemistry and molecular biology of trophoblast invasion. Ann NY Acad Sci 2001; 943: 157–162.
Dunn CL, Kelly RW, Critchley HO. Decidualization of the human endometrial stromal cell: an enigmatic transformation. Reprod Biomed Online 2003; 7: 151–161.
Strowitzki T, Germeyer A, Popovici R, von Wolff M. The human endometrium as a fertility-determining factor. Hum Reprod Update 2006; 12: 617–630.
Wilcox AJ, Baird DD, Weinberg CR. Time of implantation of the conceptus and loss of pregnancy. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 1796–1799.
Irwin IC, Utian WH, Eckert RL. Sex steroids and growth factors differentially regulate the growth and differentiation of cultured human endometrial stromal cells. Endocrinology 1991; 129: 2385–2392.
Pijnenborg R, Dixon G, Robertson WB, Brosens I. Trophoblastic invasion of human decidua from 8 to 18 weeks of pregnancy. Placenta 1980; 1: 3–19.
Bischof P, Campana A. Molecular mediators of implantation. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2000; 14: 801–814.
Curry TE Jr, Osteen KG. The matrix metalloproteinase system: changes, regulation, and impact throughout the ovarian and uterine reproductive cycle. Endocr Rev 2003; 24: 428–465.
Bischof P, Martelli M, Campana A, Itoh Y, Ogata Y, Nagase H. Importance of matrix metalloproteinases in human trophoblast invasion. Early Pregnancy 1995; 1: 263–269.
Librach CL, Werb Z, Fitzgerald ML et al. 92-kD type IV collagenase mediates invasion of human cytotrophoblasts. J Cell Biol 1991; 113: 437–449.
Shimonovitz S, Hurwitz A, Dushnik M, Anteby E, Geva-Eldar T, Yagel S. Developmental regulation of the expression of 72 and 92 kd type IV collagenases in human trophoblasts: a possible mechanism for control of trophoblast invasion. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994; 171: 832–838.
Hulboy DL, Rudolph LA, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases as mediators of reproductive function. Mol Hum Reprod 1997; 3: 27–45.
Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Yoshiji H, Thorgeirsson UP. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur J Cell Biol 1997; 74: 111–122.
Birkedal-Hansen H, Moore WG, Bodden MK et al. Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Medical 1993; 4: 197–250.
Zhang I, Salamonsen LA. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-l,-2 and-3 in human endometrium during the menstrual cycle. Mol Hum Reprod 1997; 3: 735–741.
Jokimaa V, Oksjoki S, Kujari H, Vuorio E, Anttila L. Altered expression of genes involved in the production and degradation of endometrial extracellular matrix in patients with unexplained infertility and recurrent miscarriages. Mol Hum Reprod 2002; 8: 1111–1116.
Higuchi T, Kanzaki H, Nakayama H et al. Induction of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 gene expression during in vitro decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells. Endocrinology 1995; 136: 4973–4981.
Goffin F, Munaut C, Frankenne F et al. Expression pattern of metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrixmetalloproteinases in cycling human endometrium. Biol Reprod 2003; 69: 976–984.
Henriet P, Cornet PB, Lemoine P et al. Circulating ovarian steroids and endometrial matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Ann NY Acad Sci 2002; 955: 119–138.
Vassilev V, Pretto CM, Cornet PB et al. Response of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases messenger ribonucleic acids to ovarian steroids in human endometrial expiants mimics their gene- and phase-specific differential control in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 5848–5857.
von Wolff M, Stieger S, Lumpp K, Bucking I, Strowitzki T, Thaler CI. Endometrial interleukin-6 in vitro is not regulated directly by female steroid hormones, but by pro-inflammatory cytokines and hypoxia. Mol Hum Reprod 2002; 8: 1096–1102.
Fluhr H, Krenzer S, Deperschmidt M, Zwirner M, Wallwiener D, Licht P. Human chorionic gonadotropin inhibits insulin-like growth-factor-binding protein-1 and prolactin in decidualized human endometrial stromal cells. Fertil Steril 2006; 86: 236–238.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods 2001; 25: 402–408.
Bischof P, Meisser A, Campana A. Paracrine and autocrine regulators of trophoblast invasion — a review. Placenta 2000; 21: S55-S60.
Bischof P, Campana A. A model for implantation of the human blastocyst and early placentation. Hum Reprod Update 1996; 2: 262–270.
Chegini N, Rhoton-Vlasak A, Williams RS. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-26 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and-4 in endometrium throughout the normal menstrual cycle and alteration in users of levonorgestrel implants who experience irregular uterine bleeding. Fertil Steril 2003; 80: 564–570.
Lockwood CJ, Krikun G, Hausknecht VA, Papp C, Schatz F. Matrix metalloproteinase and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor expression in endometrial stromal cells during progestin-initiated decidualization and menstruation-related progestin withdrawal. Endocrinology 1998; 139: 4607–4613.
Salamonsen LA, Butt AR, Hammond FR, Garcia S, Zhang J. Production of endometrial matrix metalloproteinases, but not their tissue inhibitors, is modulated by progesterone withdrawal in an in vitro model for menstruation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 1409–1415.
Raga F, Casan EM, Wen Y, Huang HY, Bonilla-Musoles F, Polan ML. Independent regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), and TIMP-3 in human endometrial stromal cells by gonadotropin-releasing hormone: implications in early human implantation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 636–642.
Pavloff N, Staskus PW, Kishnani NS, Hawkes SP. A new inhibitor of metalloproteinases from chicken: ChIMP-3. A third member of the TIMP family. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 17 321–17 326.
Pijnenborg R, Robertson WB, Brosens I, Dixon G. Review article. Trophoblast invasion and the establishment of haemochorial placentation in man and laboratory animals. Placenta 1981; 2: 71–91.
Bass KE, Li H, Hawkes SP et al. Tissue inhibitor of metallo-proteinase-3 expression is upregulated during human cytotrophoblast invasion in vitro. Dev Genet 1997; 21: 61–67.
Baker AH, Zaltsman AB, George SJ, Newby AC. Divergent effects of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1,-2, or-3 overexpression on rat vascular smooth muscle cell invasion, proliferation, and death in vitro. TIMP-3 promotes apoptosis. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1478–1487.
Baker AH, George SJ, Zaltsman AB, Murphy G, Newby AC. Inhibition of invasion and induction of apoptotic cell death of cancer cell lines by overexpression of TIMP-3. Br J Cancer 1999; 79: 1347–1355.
Bond M, Murphy G, Bennett MR, Newby AC, Baker AH. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 induces a Fas-associated death domain-dependent type II apoptotic pathway. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 13 787–13 795.
Lim MS, Guedez L, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Stetler-Stevenson M. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 induces apoptosis in human T lymphocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci 1999; 878: 522–523.
Boulday G, Fitau J, Coupel S, Soulillou JP, Charreau B. Exogenous tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 promotes endothelial cell survival through activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Ann NY Acad Sci 2004; 1030: 28–36.
Chromek M, Tullus K, Lundahl J, Brauner A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 activates normal human granulocytes, protects them from apoptosis, and blocks their transmigration during inflammation. Infect Immun 2004; 72: 82–88.
Liu XW, Taube ME, Jung KK et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 protects human breast epithelial cells from extrinsic cell death: a potential oncogenic activity of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 898–906.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fluhr, H., Krenzer, S. & Zygmunt, M. Different regulation of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-1, -2 and -3 in human endometrial stromal cells during decidualization in vitro . Reprod Med Biol 7, 169–175 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0578.2008.00213.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0578.2008.00213.x