Abstract
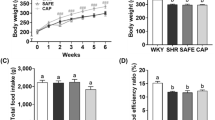
During the fermentation of mackerel to narezushi, the concentration of peptides required to inhibit 50% of the ACE activity in the assay media (IC50), as an index of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity, was remarkably decreased with a rapid increase in peptide contents. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) decreased between 2 and 4 h after the single oral administration of greater than 10 mg peptide/kg narezushi extract, and recovered to the initial level by 8 h thereafter. The SBP decreased at seven successive daily doses of 10 mg/kg of narezushi extract and then recovered to the initial level 5 days after stopping a total of 10 daily administrations. The extract was administered to five-week-old SHR rats for 70 days and SBP decreased 21 days after starting and continued for 28 days after the end of administration. The peptide-rich fraction from narezushi extract had a powerful antihypertensive effect, whereas the other fraction had a similar, but weak effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ondetti MA, Williams NJ, Sabo EF, Plušcec J, Weaver ER, Kocy O. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors from the venom of Bothrops jararaca: isolation, elucidation of structure, and synthesis. Biochemistry 1971; 10: 4033–4039.
Sugiyama K, Takada K, Egawa M, Yamamoto I, Onzuka H, Oba K. Hypotensive effect of fish protein hydrolysate. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 1991; 65: 35–43.
Ukeda H, Matsuda H, Kuroda H, Osajima K, Matsufuji H, Osajima Y. Preparation and separation of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 1991; 65: 1223–1228.
Saito Y, Nakamura K, Kawato K, Imayasu S. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors in sake and its by-products. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 1992; 66: 1081–1087.
Seki E, Osajima K, Matsui T, Osajima Y. Separation and purification of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from heated sardine meat by treatment with alkaline protease. Nippon Shokuh in Kogyo Gakkaishi 1993; 40: 783–791.
Saito Y, Wanezaki K, Kawato A, Imayasu S. Structure and activity of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from sake and sake lees. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994; 58: 1767–1771.
Astawan M, Wahyuni M, Yasuhara T, Yamada K, Tadokoro T, Maekawa A. Effects of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory substances derived from Indonesian driedsalted fish on blood pressure of rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995; 59: 425–429.
Okamoto A, Hanagata H, Matsumoto E, Kawamura Y, Koizumi Y, Yanagida F. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory activities of various fermented foods. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995; 59: 1147–1149.
Teranaka T, Ezawa M, Matsuyama J, Ebine H, Kiyosawa I. Inhibitory effects of extracts from rice-koji miso, barley-koji miso, and soybean-koji miso on the activity of angiotensin I converting enzyme. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 1995; 69: 1163–1169.
Ohta T, Iwashita A, Sasaki S, Kawamura Y. Antihypertensive action of the orally administered protease hydrolysates of chum salmon head and their angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Tokyo 1997; 3: 339–343.
Yoshii H, Tachi N, Sakamura O, Takemiya H, Ohba R, Itani T. Antihypertensive effect of oligo-peptide derived from hen’s eggs. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 1999; 46: 45–50.
Ono S, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K, Takahashi K. Isolation of peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory effect derived from hydrolysate of upstream chum salmon muscle. J. Food Sci. 2003; 68: 1611–1614.
Itou K, Akahane Y. Antihypertensive effect of heshiko, a fermented mackerel product, on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Fish Sci. 2004; 70: 1121–1129.
Kabir Y, Yamaguchi M, Kimura S. Effect of Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) and Maitake (Grifola frondosa) mushrooms on blood pressure and plasma lipids of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1987; 33: 341–346.
Kabir Y, Kimura S. Dietary mushrooms reduce blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1989; 35: 91–94.
Suetsuna K, Osajima K. Blood pressure reduction and vasodilatory effect in vivo of peptides originating from sardine muscle. Nippon Eiyo Shokuryo Gakkaishi 1989; 42: 47–54.
Yamamoto N, Akino A, Takano T. Antihypertensive effects of different kinds of fermented milk in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994; 58: 776–778.
Fujita H, Sasaki R, Yoshikawa M. Potentiation of the antihypertensive activity of orally administered ovokinin, a vasorelaxing peptide derived from ovalbumin, by emulsification in egg phosphatidylcholine. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995; 59: 2344–2345.
Nakamura Y, Masuda O, Takano T. Decrease of tissue angiotensin I-converting enzyme activity upon feeding sour milk in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996; 60: 488–489.
Seki E, Kawasaki T, Yoshida M, Osajima K, Tamaya K, Matsui T, Osajima Y. Antihypertensive effect of sardine peptide and valyl-tyrosine in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nippon Eiyo Shokuryo Gakkaishi 1999; 52: 271–277.
Shimizu E, Hayashi A, Takahashi R, Aoyagi Y, Murakami T, Kimoto K. Effects of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor from ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) on blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1999; 45: 375–383.
Ohtsuru M, Horio H, Masui H, Takeda I. Effect of administration of Grifola frondosa on blood pressure and body weight in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 1999; 46: 806–814.
Wu J, Ding X. Hypotensive and physiological effect of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from soy protein on spontaneously hypertensive rat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001; 49: 501–506.
Itou K, Akahane Y. Changes in proximate composition and extractive components of rice-bran-fermented mackerel Heshiko during processing. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 2000; 66: 1051–1058.
Itou K, Kobayashi S, Ooizumi T, Akahane Y. Changes of proximate composition and extractive components in narezushi, a fermented mackerel product, during processing. Fish Sci. 2006; 72: 1269–1276.
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr A, Randall R. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951; 193: 265–275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itou, K., Nagahashi, R., Saitou, M. et al. Antihypertensive effect of Narezushi, a fermented mackerel product, on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Fish Sci 73, 1344–1352 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01477.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01477.x