Abstract
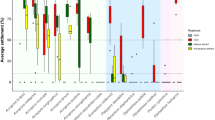
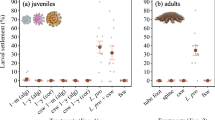
The settlement of larval top shell Turbo (Batillus) cornutus in response to seven macroalgal and three benthic diatom species was examined in the laboratory. The percentages of larval settlement different significantly among algal species, and were significantly higher on two red algal species (Marginisporum crassissima, an articulated coralline alga, and Gelidium elegans, an agarophyte) than on the green algae, brown algae and benthic diatoms tested. Marginisporum crassissima induced larval settlement most strongly throughout the experiments. The percentage of larval settlement on a crustose coralline alga (unidentified species), which is known as a suitable substratum for abalone larvae, was much lower than on M. crassissima and G. elegans, which have morphologically complex growth forms. The percentage of settled individuals on ethanol-killed M. crassissima was much lower than on intact M. crassissima. The results indicate that physical structure is unlikely to be the main inducer of settlement; therefore, settlement of top shell larvae seems to be strongly induced by chemicals from the two red algal species. The specific distribution of juvenile top shell in the field may be at least partly determined by the strong induction of larval settlement by articulated coralline and gelidiacean algae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshiya M, Tuji S, Douke A, Uchino K, Funada H. Fluctuations of topshell resources in the coastal area of Kanmurijima. Bull. Kyoto Inst. Ocean. Fish. Sci. 1990; 13: 21–28.
Uchiba S, Nishima K, Yamamoto T, Kishimoto G. Research about inhabitation and ecology of top shell I; the factors affecting habitats of top shell juvenile. Bull. Fukuoka Pref. Fish. Exp. Stn. 1982: 157–165 (in Japanese).
Yamazaki A, Ishiwata N. Population ecology of the spiny turban shell Batillus cornutus II. Habitat of juvenile shell. La mer 1987; 25: 184–189.
Fujita D, Okada H, Sakata K. The importance of some marine red algae inhabiting fishing-port waterbreak vertical surface as natural food for juvenile horned turban Turbo (Batillus) cornutus. Bull. Toyama Pref. Fish. Exp. Stn. 1990; 2: 41–51.
Sasaki T. Settlement process and mortality at early stages of top shell, Turbo (Batillus) cornutus, at the eastern waters in Shimane prefecture. Bull. Shimane Pref. Fish. Exp. Stn. 2003; 11: 15–22.
Roberts RD. A review of settlement cues for larval abalone (Haliotis spp.). J. Shellfish Res. 2001; 20: 571–587.
McShane PE, Naylor JR. Depth can affect post-settlement survival of Haliotis iris (Mollusca: Gastropoda). J. Exper. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995; 187: 1–12.
Day L, Branch GM. Relationships between recruits of the abalone Haliotis midae, encrusting corallines and the sea urchin Parechinus angulosus. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2000; 22: 137–144.
Roberts RD, Kasper HF, Barker RJ. Settlement of abalone (Haliotis iris) larvae in response to five species of coralline algae. J. Shellfish Res. 2004; 23: 975–987.
Kawamura T, Roberts RD, Takami H. A review of the feeding and growth of postlarval abalone. J. Shellfish Res. 1998; 17: 615–625.
Roberts RD, Kawamura T, Nicholson CM. Growth and survival of postlarval abalone (Haliotis iris) in relation to development and diatom diet. J. Shellfish Res. 1999; 18: 243–250.
Kawamura T, Kikuchi H. Effects of benthic diatoms on settlement and metamorphosis of abalone. Suisanzoshoku 1992; 40: 403–409.
Slattery M. Larval settlement and juvenile survival in the red abalone (Haliotis rufescens): an examination of inductive cues and substrata selection. Aquaculture 1992; 102: 143–153.
Daume S, Brand S, Woelkerling WJ. Preferential settlement of abalone larvae: diatom films vs. non-geniculate coralline red algae. Aquaculture 1999; 174: 243–254.
J//orgensen EG. Antibiotic substances from cells and solution of unicellular algae with special reference to some chlorophyll derivatives. Physiol. Plant. 1962; 15: 530–545.
Morse ANC, Morse DE. Recruitment and metamorphosis of Haliotis larvae induced by molecules uniquely available at the surfaces of crustose red algae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1984; 75: 191–215.
Johonson CR, Sutton DC. Bacteria on the surface of crustose coralline algae induce metamorphosis of the crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci. Mar. Biol. 1994; 120: 305–310.
Bryan PJ, Qian PY. Induction of larval and metamorphosis in the abalone Haliotis diversicolor (Reeve). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998; 223: 39–51.
Daume S, Brand S, Woelkerling WJ. Settlement of abalone larvae (Haliotis laevigata Donovan) in response to nongeniculate coralline red algae (Corallinales, Rhodophyta). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999; 234: 125–143.
Morse DE, Hooker N, Morse ANC, Jensen RA. Control of larval metamorphosis and recruitment in sympatric agariciid corals. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1988; 116: 193–217.
Roberts RD, Nicholson CM. Variable response from abalone larvae (Haliotis iris, H. virginea) to a range of settlement cues. Moll. Res. 1997; 18: 131–142.
Yoshiya M, Kuwahara A, Hamanaka Y, Wada Y. Food and feeding habits of a topshell Batillus cornutus, in the coastal area of Aoshima, Kyoto, Japan. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1987; 53: 1359–1366.
Fujii A, Yotsui T, Ogawa S. Alga preference of young topshell, Batillus cornutus. Bull. Nagasaki Pref. Inst. Fish, 1988; 14: 19–25.
Naylor JR, McShane PE. Predation by polychaete worms on larval and post-settlement abalone Haliotis iris (Mollusca: Gastropoda). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997; 214: 283–290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayakawa, J., Kawamura, T., Horii, T. et al. Settlement of larval top shell Turbo (Batillus) cornutus in response to several marine algae. Fish Sci 73, 371–377 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01344.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01344.x