Abstract
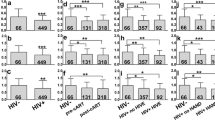
The basal ganglia, structures rich in the neurotransmitter dopamine, are primarily affected during human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The authors measured levels of dopamine and its metabolites, homovanillic acid and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, in brains of uninfected and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected rhesus monkeys during the asymptomatic stage of the infection. Moreover, the authors investigated changes in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB), two factors involved in the signaling pathway of dopamine. The brain regions examined were the nucleus accumbens and the corpus amygdaloideum, which are limbic structures of the basal ganglia that are involved in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse. Dopamine content was reduced in both regions of SIV-infected monkeys compared to uninfected animals. Moreover, dopamine deficits were associated with a decrease in expression of total CREB. Intracellular concentrations of cAMP were decreased in nucleus accumbens and remained unchanged in corpus amygdaloideum of SIV-infected macaques. Changes in dopamine signaling were not related to pathology or viral load of the investigated animals.The results suggest that dopamine defects precede neurologic deficits and implicate dysfunction of the dopaminergic system in the etiopathogenesis of HIV dementia. Therefore, affective complications in HIV subjects should not be interpreted only as reactive psychological changes. The alterations in the mesolimbic dopaminergic system during asymptomatic stage of SIV infection implicate a biological background for psychiatric disorders in HIV infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DC, Wildemann B, Sasaki M, Glass JD, McArthur JC, Christov VI, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (1996). Immunologic NO synthase: elevation in severe AIDS dementia andinduction by HIV-1gp41. Science 274: 1917–1921.
Aloisi F, De Simone R, Columba-Cabezas S, Levi G (1999). Opposite effects of interferon-gamma and prostaglandin E2 on tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-10 production in microglia: a regulatory loop controlling microglia pro- and anti-inflammatory activities. J Neurosci Res 56: 571–580.
Arendt G, Hefter H, Elsing C, Strohmeyer G, Freund HJ (1990). Motor dysfunction in HIV-infected patients without clinically detectable central-nervous deficit. J Neurol 237: 362–368.
Aylward EH, Henderer JD, McArthur JC, Brettschneider PD, Harris GJ, Barta PE, Pearlson GD (1993). Reduced basal ganglia volume in HIV-1-associated dementia: results from quantitative neuroimaging. Neurology 43: 2099–2104.
Berger JR, Arendt G (2000). HIV dementia: the role of the basal ganglia and dopaminergic systems. J Psychopharmacol 14: 214–221.
Berger JR, Nath A (1997). HIV dementia and the basal ganglia. Intervirology 40: 122–131.
Biswas DK, Ahlers CM, Dezube BJ, Pardee AB (1994). Pentoxifylline and other protein kinase C inhibitors down-regulate HIV-LTR NF-kappa B induced gene expression. Mol Med 1: 31–43.
Bradford MM (1976). Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254.
Cornford ME, Holden JK, Boyd MC, Berry K, Vinters HV (1992). Neuropathology of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS): report of 39 autopsies from Vancouver, British Columbia. Can J Neurol Sci 19: 442–452.
Czub S, Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Czub M, Stahl-Hennig C, Muller JG, Pedersen V, Gsell W, Heeney JL, Gerlach M, Gosztonyi G, Riederer P, ter Meulen V (2001). Enhancement of central nervous system pathology in early simian immunodeficiency virus infection by dopaminergic drugs. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 101: 85–91.
Dowlatshahi D, MacQueen GM, Wang JF, Young LT (1998). Increased temporal cortex CREB concentrations and antidepressant treatment in major depression. Lancet 352: 1754–1755.
Duman RS, Heninger GR, Nestler EJ (1997). A molecular and cellular theory of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54: 597–606.
Fibiger HC (1984). The neurobiological substrates of depression in Parkinson’s disease: a hypothesis. Can J Neurol Sci 11: 105–107.
Gerlach M, Youdim MB, Riederer P (1994). Is selegiline neuroprotective in Parkinson’s disease? J Neural Transm Suppl 41: 177–188.
Gsell W, Lange K, Pfeuffer L, Heckers S, Heinsen H, Senitz D, Jellinger K, Ransmayr G, Wichart R, Vock R, Beckmann H, Riederer P (1993). How to run a brain bank. A report from the Austro-German brain bank. J Neural Transm (Suppl) 39: 31–70.
Hyman C, Hofer M, Barde YA, Juhasz M, Yancopoulos GD, Squinto SP, Lindsay RM (1991). BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Nature 350: 230–232.
Klimek V, Schenck JE, Han H, Stockmeier CA, Ordway GA (2002). Dopaminergic abnormalities in amygdaloid nuclei in major depression: a postmortem study. Biol Psychiatry 52: 740–748.
Koutsilieri E, Scheller C, Sopper S, Ter Meulen V, Riederer P (2002a). Psychiatric complications in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J NeuroVirol 8 (Suppl 2): 129–133.
Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Scheller C, ter Meulen V, Riederer P (2002b). Involvement of dopamine in the progression of AIDS Dementia Complex. J Neural Transm 109: 399–410.
Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Scheller C, ter Meulen V, Riederer P (2002c). Parkinsonism in HIV dementia. J Neural Transm 109: 767–775.
Kure K, Weidenheim KM, Lyman WD, Dickson DW (1990). Morphology and distribution of HIV-1 gp41-positive microglia in subacute AIDS encephalitis. Pattern of involvement resembling a multisystem degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 80: 393–400.
Lopez OL, Smith G, Meltzer CC, Becker JT (1999). Dopamine systems in human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol 12: 184–192.
Minghetti L, Nicolini A, Polazzi E, Creminon C, Maclouf J, Levi G (1997). Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in activated rat microglial cultures is downregulated by exogenous prostaglandin E2 and by cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Glia 19: 152–160.
Montminy M (1997). Transcriptional regulation by cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem 66: 807–822.
Nath A, Anderson C, Jones M, Maragos W, Booze R, Mactutus C, Bell J, Hauser KF, Mattson M (2000). Neurotoxicity and dysfunction of dopaminergic systems associated with AIDS dementia. J Psychopharmacol 14: 222–227.
Navia B, Cho E, Petito C, et al (1986). The AIDS dementia complex. II. Neuropathology. Annals of Neurology 19: 525–535.
Nestler EJ, Barrot M, DiLeone RJ, Eisch AJ, Gold SJ, Monteggia LM (2002). Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 34: 13–25.
Nuovo G, Alfieri M (1996). AIDS dementia is associated with massive, activated HIV-1 infection and concomittant expression of several cytokines. Mol Med 2: 358–366.
Patrizio M, Colucci M, Levi G (2001). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein decreases cyclic AMP synthesis in rat microglia cultures. J Neurochem 77: 399–407.
Reyes MG, Faraldi F, Senseng CS, Flowers C, Fariello R (1991). Nigral degeneration in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 82: 39–44.
Rottenberg DA, Moeller JR, Strother SC, Sidtis JJ, Navia BA, Dhawan V, Ginos JZ, Price RW (1987). The metabolic pathology of the AIDS dementia complex. Ann Neurol 22: 700–706.
Sardar A, Czudek C, Reynolds G (1996). Dopamine deficits in the brain: the neurochemical basis of parkinsonian symptoms in AIDS. Neuroreport 7: 910–912.
Sauermann U, Krawczak M, Hunsmann G, Stahl-Hennig C (1997). Identification of Mhc-Mamu-DQB1 allele combinations associated with rapid disease progression in rhesus macaques infected with simian immunodeficiency virus. AIDS 11: 1196–1198.
Senogles SE, Amlaiky N, Berger JG, Caron MG (1988). Biochemical properties of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol 235: 33–41.
Sopper S, Koutsilieri E, Scheller C, Czub S, Riederer P, ter Meulen V (2002). Macaque animal model for HIV-induced neurological disease. J Neural Transm 109: 747–766.
Sopper S, Nierwetberg D, Halbach A, Sauer U, Scheller C, Stahl-Hennig C, Matz-Rensing K, Schafer F, Schneider T, ter Meulen V, Muller JG (2003). Impact of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection on lymphocyte numbers and T-cell turnover in different organs of rhesus monkeys. Blood 101: 1213–1219.
Suzumura A, Ito A, Yoshikawa M, Sawada M (1999). Ibudilast suppresses TNFalpha production by glial cells functioning mainly as type III phosphodiesterase inhibitor in the CNS. Brain Res 837: 203–212.
Treisman G, Fishman M, Schwartz J, Hutton H, Lyketsos C (1998). Mood disorders in HIV infection. Depress Anxiety 7: 178–187.
Tyor WR, Glass JD, Griffin JW, Becker PS, McArthur JC, Bezman L, Griffin DE (1992). Cytokine expression in the brain during the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol 31: 349–360.
Yamada S, Yamamoto M, Ozawa H, Riederer P, Saito T (2003). Reduced phosphorylation of cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein in the postmortem orbitofrontal cortex of patients with major depressive disorder. J Neural Transm 110: 671–680.
Yamamoto-Sasaki M, Ozawa H, Saito T, Rosler M, Riederer P (1999). Impaired phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element binding protein in the hippocampus of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Brain Res 824: 300–303.
Zafra F, Lindholm D, Castren E, Hartikka J, Thoenen H (1992). Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci 12: 4793–4799.
Zauli G, Milani D, Mirandola P, Mazzoni M, Secchiero P, Miscia S, Capitani S (2001). HIV-1 Tat protein down-regulates CREB transcription factor expression in PC12 neuronal cells through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/cyclic nucleoside phosphodiesterase pathway. Faseb J 15: 483–491.
Zauli G, Secchiero P, Rodella L, Gibellini D, Mirandola P, Mazzoni M, Milani D, Dowd DR, Capitani S, Vitale M (2000). HIV-1 Tat-mediated inhibition of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in dopaminergic neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 275: 4159–4165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was supported by grants from the Bundesministerium für Bildung, Wissenschaft, Forschung und Technologie, Germany (BMBF 01 KI 9762/5 and 01 KI 0211 Competence Network HIV/AIDS).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenuwein, M., Scheller, C., Neuen-Jacob, E. et al. Dopamine deficits and regulation of the cAMP second messenger system in brains of simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys. Journal of NeuroVirology 10, 163–170 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280490448016
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280490448016