Abstract
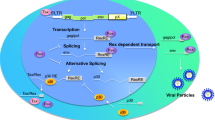
The JC virus early mRNA is alternatively spliced to yield five transcripts that encode large T antigen, small t antigen, T′135, T′136, and T′165. The splicing process is regulated differentially in transformed versus lytically infected cells and temporally during the course of a productive infection. The authors have identified a potential exonic splicing enhancer near the 3′ end of the early viral mRNA that, when mutated, results in altered splice site usage. The authors have only recently begun investigating the function of the three T′ proteins using genetic and biochemical approaches. These studies indicate that the T′ proteins enhance viral DNA replication and bind differentially to the pRB family of cellular tumor suppressor proteins in vitro. Using a G418 selection scheme, the authors have created cell lines that express either T antigen or each of the T’ proteins individually. Preliminary analyses of these lines suggest that T antigen may induce apoptosis in rodent cells, an activity that may be blocked by other JC virus early proteins. Furthermore, examination of protein-protein interactions within the G418-selected cells reveal differences in binding of the viral proteins to the pRB family members relative to that seen in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blencowe BJ (2000). Exonic splicing enhancers: mechanism of action, diversity and role in human genetic diseases. Trends Biochem Sci 25: 106–110.
Bollag B, Prins C, Snyder EL, Frisque RJ (2000). Purified JC virus T and T′ proteins differentially interact with the retinoblastoma family of tumor suppressor proteins. Virology 274: 165–178.
Campbell KS, Mullane KP, Aksoy IA, Stubdal H, Zalvide J, Pipas JM, Silver PA, Roberts TM, Schaffhausen BS, DeCaprio JA (1997). DnaJ/hsp40 chaperone domain of SV40 large T antigen promotes efficient viral DNA replication. Genes Dev 11: 1098–1110.
Elliot DJ (2000). Splicing and the single cell. Histol Histopathol 15: 239–249.
Frisque RJ, Bream GL, Cannella MT (1984). Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J Virol 51: 458–469.
Gjoerup O, Zaveri D, Roberts TM (2001). Induction of p53independent apoptosis by simian virus 40 small t antigen. J Virol 75: 9142–9155.
Kanopka A, Muhlemann O, Petersen-Mahrt S, Estmer C, Ohrmalm C, Akusjarvi G (1998). Regulation of adenovirus alternative RNA splicing by dephosphorylation of SR proteins. Nature 393: 185–187.
Liu HX, Chew SL, Cartegni L, Zhang MQ, Krainer AR (2000). Exonic splicing enhancer motif recognized by human SC35 under splicing conditions. Mol Cell Biol 20: 1063–1071.
Lopez AJ (1998). Alternative splicing of pre-mRNA: developmental consequences and mechanisms of regulation. Annu Rev Genet 32: 279–305.
Molin M, Akusjärvi G (2000). Overexpression of essential splicing factor ASF/SF2 blocks the temporal shift in adenovirus pre-mRNA splicing and reduces virus progeny formation. J Virol 74: 9002–9009.
Prins C, Frisque RJ (2001). JC virus T′ proteins encoded by alternatively spliced early mRNAs enhance T antigenmediated viral DNA replication in human cells. J NeuroVirol 7: 250–264.
Riley MI, Yoo W, Mda NY, Folk WR (1997). Tiny T antigen: An autonomous polyomavirus T antigen aminoterminal domain. J Virol 71: 6068–6074.
Sheng Q, Denis D, Ratnofsky M, Roberts TM, DeCaprio JA, Schaffhausen B (1997). The DnaJ domain of polyomavirus large T is required to regulate RB family tumor suppressor function. J Virol 71: 9410–9416.
Sullivan CS, Cantalupo P, Pipas JM (2000). The molecular chaperone activity of simian virus 40 large T antigen is required to disrupt Rb-E2F family complexes by an ATPdependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 20: 6233–6243.
Sullivan CS, Gilbert SP, Pipas JM (2001). ATP-dependent simian virus 40 T-antigen-Hsc70 complex formation. J Virol 75: 1601–1610.
Swenson JJ, Frisque RJ (1995). Biochemical characterization and localization of JC virus large T antigen phosphorylation domains. Virology 212: 295–308.
Tacke R, Manley JL (1995). The human splicing factors ASF/SF2 and SC35 possess distinct, functionally significant RNA binding specificities. EMBOJ 14: 3540–3551.
Trowbridge PW, Frisque RJ (1993). Analysis of G418selected Rat2 cells containing prototype, variant, mutant, and chimeric JC-virus and SV40 genomes. Virology 196: 458–474.
Trowbridge PW, Frisque RJ (1995). Identification of three new JC virus proteins generated by alternative splicing of the early viral mRNA. J NeuroVirol 1: 195–206.
Xiao SH, Manley JL (1997). Phosphorylation of the ASF/SF2 RS domain affects both protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions and is necessary for splicing. Genes Dev 11: 334–344.
Zerrahn J, Knippschild U, Winkler T, Deppert W (1993). Independent expression of the transforming aminoterminal domain of SV40 large T-antigen from an alternatively spliced third SV40 early messenger RNA. EMBO J 12: 4739–4746.
Zheng ZM, He PJ, Baker CC (1997). Structural, functional, and protein binding analyses of bovine papillomavirus type 1 exonic splicing enhancers. J Virol 71: 9096–9107.
Zuzarte PC, Farrance IK, Simpson PC, Wildeman AG (2000). Tumor cell splice variants of the transcription factor TEF-1 induced by SV40 T-antigen transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1517: 82–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by U.S. Public Health Service grant NS41833 from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, and an Innovative Technology grant from Penn State’s Life Sciences Consortium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frisque, R.J., Bollag, B., Tyagarajan, S.K. et al. T′ proteins influence JC virus biology. Journal of NeuroVirology 9 (Suppl 1), 15–20 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280390195270
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280390195270