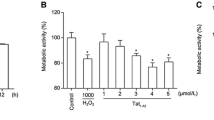
Abstract
In a substantial number of cases, Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection causes neuronal cell loss and leads to the development of AIDS associated dementia. Several studies have suggested that both host and viral factors contribute to neuronal loss. Here we studied the effect of HIV-1 Tat in primary rat neuronal cells as a model to understand mechanism of neuronal cell death. At nano molar concentration, recombinant Tat induced cell death in primary rat mixed cortical neurons. Tat could also induce uptake of calcium in primary rat cultures. When cells were incubated with NMDA receptor antagonists, MK-801 and D-CPP, cell death and 45Ca uptake were inhibited. Under similar conditions non-NMDA antagonists, NBQX, DNQX and CNQX, and sodium channel antagonist, TTX, did not inhibit Tat induced neuronal cell death. In a similar way HIV associated products from in vitro HIV-1 infected cells induced neuronal cell death which was inhibited by NMDA receptor antagonist. Results presented in this paper suggest that activation of NMDA receptors by HIV-1 Tat is responsible for neuronal cell death in primary rat cortical neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DC, Wildemann B, Sasaki M, Glass JD, McArthur JC, Christov VI, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (1996). Immunologic NO synthase: Elevation in severe AIDS dementia and induction by HIV-1 gp41. Science 274: 1917–1921.
Albini A, Benelli R, Giunciuglio D, Cai T, Mariani G, Ferrini S, Noonan D (1998). Identification of a novel domain of HIV Tat involved in monocyte chemotaxis. J Biol Chem 273: 15895–15900.
Albini A, Ferrini S, Benelli R, Sforzini S, Giunciuglio D, Grazia Aluigi M, Proudfoot A, Alouani S, Wells T, Mariani G, Rabin R, Farber J, Noonan D (1998). HIV-1 Tat protein mimicry of chemokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 13153–13158.
Birrell GJ, Gordon MP, Marcoux FW (1993). (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid attenuates N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal cell death in cortical cultures via a reduction in delayed Ca2+ accumulation. Neuropharmacol 32: 1351–1358.
Bloom G, Rausch D (1997). HIV in the brain: pathology and neurobehavioral consequences. J Neuro Virol 3: 102–109.
Buonaguro L, Barillari G, Chang H, Bohan C, Kao V, Morgan R, Gallo R, Ensoli B (1992). Effects of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein on the expression of inflammatory cytokines. J Virol 66: 7159–7167.
Chen P, Mayne M, Power C, Nath A (1997). The Tat protein of HIV-1 induces tumor necrosis factor-α production: implications for HIV-1-associated neurological diseases. J Biol Chem 272: 22385–22388.
Conant K, Garzino-Demo A, Nath A, McArthur J, Halliday W, Power C, Gallo R, Major E (1998). Induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in HIV-1 Tat-stimulated astrocytes and elevation in AIDS dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3117–3121.
Corasaniti M, Navarra M, Catani M, Melino G, Nistico G, Finazzi-Agro A (1996). NMDA and HIV-1 coat protein, gp120, produce necrotic but not apoptotic cell death in human CHP100 neuroblastoma cultures via a mechanism involving calpain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 229: 299–304.
Diop A, Lesort M, Esclaire F, Sindou P, Couratier P, Hugon J (1994). Tetrodotoxin blocks HIV coat protein (gp120) toxicity in primary neuronal cultures. Neurosci Lett 165: 187–190.
Dreyer E, Lipton S (1997). The coat protein gp120 of HIV-1 inhibits astrocyte uptake of excitatory amino acids via macrophage arachidonic acid. Eur J Neurosci 7: 2502–2507.
Epstein L, Gendelman H (1993). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of the nervous system: pathogenic mechanism. Ann Neurol 33: 429–436.
Ferrarese C, Riva R, Dolara A, DeMicheli A, Frattola L (1997). Elevated glutamate in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV dementia. JAMA 277: 630–633.
Fine SM, Angel RA, Perry SW, Epstein LG, Rothstein JD, Dewhursts S, Gelbard HA (1996). Tumor necrosis Factor α inhibits Glutamate uptake by primary Human Astrocytes. J Biol Chem 271: 15303–15306.
Fontana G, Valenti L, Raiteri M (1997). Gp120 can revert antagonism at the glycine site of NMDA receptors mediating GABA release from cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res 49: 732–738.
Frankel A, Bredt D, Pabo C (1988). Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science 240: 70–73.
Frankel A, Pabo C (1988). Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell 55: 1189–1193.
Haughey NJ, Nath A, Geiger JD (1999). Involvement of Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-regulated stores of intracellular calcium in calcium dysregulation and neuron cell death caused by HIV-1 protein Tat. J Neurochemistry 73: 1363–1374.
Hajimohammadreza I, Probert AW, Coughenour LL, Borosky SA, Marcoux FW, Boxer PA, Wang KW (1995). A specific Inhibitor of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-II provides Neuroprotection against NMDA- and Hypoxia/Hypoglycemia-induced cell death. J Neuroscience 15: 4093–4101.
Hayman M, Arbuthnott G, Harkiss G, Brace H, Filippi P, Philippon V, Thomson D, Vigne R, Wright A (1993). Neurotoxicity of peptide analogues of the transactivating protein tat from maedi-visna virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Neuroscience 53: 1–6.
He J, Chen Y, Farzan M, Choe H, Ohagen A, Gartner S, Buscigilio J, Yang X, Hofmann W, Newman W, Mackay CR, Sodroski J, Gabuzda D (1997). CCR3 and CCR5 are co-receptors for HIV-l infection of microglia. Nature (London) 385: 645–649.
Honore T, Davies S, Drejer J, Fletcher E, Jacobsen P, Lodge D, Fe N (1988). Quinoxalinediones: Potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor agonists. Science 241: 701–703.
Ito M, Ishida T, He L, Tanabe F, Rongge Y, Miyakawa Y, Terunuma H (1998). HIV type 1 Tat protein inhibits interleukin 12 production by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 14: 845–849.
Johnson RT (1995). The pathogenesis of HIV infections of the brain. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 202: 3–10.
Katsikis P, Garcia-Ojeda M, Torres-Roca J, Greenwald D, Herzenberg L, Herzenberg L (1997). HIV type 1 Tat protein enhances activation-but not fas (CD95)-induced peripheral blood T cell apoptosis in healthy individuals. Int Immunol 9: 835–841.
Kimpton J, Emerman M (1992). Detection of replication-competent and pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus with a sensitive cell line on the basis of activation of an integrated beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol 66: 2232–2239.
Kirsch T, Boehm M, Schuckert O, Metzger AU, Willbold D, Frank RW, Rosch P (1996). Cloning, High-Yield Expression in Escherichia coli, and purification of biologically active HIV-1 tat protein. Protein Expression and Purification 8: 75–84.
Kruman II, Nath A, Mattson MP (1998). HIV-1 protein Tat induces apoptosis of hippocampal neurons by a mechanism involving caspase activation, calcium overload, and oxidative stress. Exp Neurol 154: 276–288.
Lafrenie R, Wahl L, Epstein J, Hewlett I, Yamada K, Dhawan S (1996). HIV-1-Tat protein promotes chemotaxis and invasive behavior by monocytes. J Immunol 157: 974–977.
Lafrenie R, Wahl L, Epstein J, Yamada K, Dhawan S (1997). Activation of monocytes by HIV-1 Tat treatment is mediated by cytokine expression. J Immunol 159: 4077–4083.
Lavi E, Kolson D, Ulrich A, Fu L, Gonzalez-Scarano F (1998). Chemokine receptors in the human brain and their relationship to HIV infection. J Neuro Virol 4: 301–311.
Li C, Friedman D, Wang C, Metelev V, Pardee A (1995). Induction of apoptosis in uninfected lymphocytes by HIV-1 Tat protein. Science 268, 429–431.
Lipton S (1998). Neuronal injury associated with HIV-1: approaches to treatment. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 38: 159–177.
Lipton S (1996). Similarity of neuronal cell injury and death in AIDS dementia and focal cerebral ischemia: potential treatment with NMDA open-channel blockers and nitric oxide-related species. Brain Pathol 6: 507–517.
Lipton S, Sucher N, Kaiser P, Dreyer E (1991). Synergistic effects of HIV coat protein and NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Neuron 7: 111–118.
Maccarrone M, Navarra M, Corasaniti M, Nistico G, Finazzi-Agro A (1998). Cytotoxic effect of HIV-1 coat glycoprotein gp120 on human neuroblastoma CHP100 cells involves activation of the arachidonate cascade. Biochem J 333: 45–49.
Magnuson D, Knudsen B, Geiger J, Brownstone R, Nath A (1995). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat activates non-n-methyl-d-aspartate excitatory amino acid receptors and causes neurotoxicity. Ann Neurol 37: 373–380.
Mann D, Frankel A (1991). Endocytosis and targeting of exogenous HIV-1 tat protein. EMBO J 10: 1733–1739.
Nath A, Psooy K, Martin C, Knudsen B, Magnuson D, Haughey N, Geiger J (1996). Identification of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat epitope that is neuroexcitatory and neurotoxic. J Virol 70: 1475–1480.
New D, Ma M, Epstein L, Nath A, Gelbard H (1997). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat protein induces death by apoptosis in primary human neuron cultures. J Neuro Virol 3: 168–173.
New D, Maggirwar S, Epstein L, Dewhurst S, Gelbard H (1998). HIV-1 Tat induces neuronal death via tumor necrosis factor-α and activation of non-n-methyl-d-aspartate receptors by a NFκB-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem 273: 17852–17858.
Nishida K, Markey SP, Kustova Y, Morse III HC, Skolnick P, Basile AS, Sci Y (1996). Increased brain levels of platelet-activating factor in a murine acquired immune deficiency syndrome are NMDA receptor-mediated. J Neurochem 66: 433–435.
Nokta M, Hassan M, Loesch K, Pollard R (1995). HIV-induced TNF-α regulates arachidonic acid and PGE2 release from HIV-infected mononuclear phagocytes. Virology 208: 590–600.
Philippon V, Vellutini C, Gambarelli D, Harkiss G, Arbuthnott G, Metzger D, Filippi P (1994). The basic domain of the lentiviral Tat protein is responsible for damages in mouse brain: involvement of cytokines. Virology 205: 519–529.
Probert A, Borosky S, Marcoux F, Taylor C (1997). Sodium channel modulators prevent oxygen and glucose deprivation injury and glutamate release in rat neocortical cultures. Neuropharmacology 36: 1037–1038.
Raber J, Toggas S, Le S, Bloom F, Epstein C, Mucke L (1996). Central nervous system expression of HIV-1 gp120 activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: evidence for involvement of NMDA receptors and nitric oxide synthase. Virology 226: 362–373.
Sabatier J-M, Vives E, Mabrouk K, Benjouad A, Rochat H, Duval A, Hue B, Bahraqui E (1991). Evidence for neurotoxic activity of Tat from human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol 65: 961–967.
Sanders V, Pittman C, White M, Wang G, Wiley C, Achim C (1998). Chemokines and receptors in HIV encephalitis. AIDS 12: 1021–1026.
Scala G, Ruocco M, Ambrosino C, Mallardo M, Giordano B, Baldassarre F, Dragonetti E, Quinto I, Venuta S (1994). The expression of the interleukin 6 gene is induced by human immunodeficiency virus 1 TAT protein. J Exp Med 179: 961–971.
Selmaj KW, Raine CS (1988). Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol 23: 339–346.
Shi B, Raina J, Lorenzo A, Busciglio J, Gabuzda D (1998). Neuronal apoptosis induced by HIV-1 Tat protein and TNF-α: potentiation of neurotoxicity mediated by oxidative stress and implications for HIV-1 dementia. J Neuro Virol 4: 281–290.
Strijbos P, Zamani M, Rothwell N, Arbuthnott G, Harkis G (1995). Neurotoxic mechanisms of transactivating protein Tat of maedi-visna virus. Neuroscience Lett 197: 215–218.
Toggas S, Masliah E, Mucke L (1996). Prevention of HIV-1 gp120-induced neuronal damage in the central nervous system of transgenic mice by the NMDA receptor antagonist memantine. Brain Res 706: 303–307.
Ushijina H, Nishio O, Klocking R, Perovic S, Muller W (1995). Exposure to gp120 of HVI-1 induces an increased release of arachidonic acid in rat primary neuronal cell culture followed by NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Eur J Neurosci 7: 1353–1359.
Vitkovic L, DaCunha A (1995). Role of astrocytosis in HIV-1-associated dementia. Curr Top Microbiol 202: 105–116.
Wang P, Barks JDE, Silverstein FS (1999). Tat, a human immunodeficiency virus-1-derived protein, augments excitotoxic hippocampal injury in neonatal rats. Neuroscience 88: 585–597.
Westerndorp M, Li W, Frank R, Karmmer P (1994). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat upregulates interleukin-2 secretion in activated cells. J Virol 68: 4177–4185.
Zidovetzki R, Wang J-L, Chen P, Jeyaseelan R, Hofman F (1998). Human immunodeficiency virus Tat protein induces interleukin 6 mRNA expression in human brain endothelial cells via protein kinase C and cAMP dependent protein kinase pathways. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 14: 825–833.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez, A., Probert, A.W., Wang, K.K.W. et al. Evaluation of HIV-1 Tat induced neurotoxicity in rat cortical cell culture. Journal of NeuroVirology 7, 1–10 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1080/135502801300069575
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/135502801300069575