Abstract
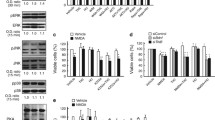
We have recently examined the status of the endocannabinoid transmission in the basal ganglia in Huntington’s disease (HD) using a rat model generated by bilateral intrastriatal injections of 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP). In these previous studies, we focused on the early phase of hyperactivity that occurs 1–2 weeks after the lesion, comparable to early grades of the human disease, while in the present study, we wanted to explore the late akinetic phase observed 3–4 weeks after the lesion (similar to advanced grades). First, we confirmed that 3-NP-lesioned rats exhibited a marked akinesia tested at 4 weeks post-lesion. We observed a marked reduction in ambulatory and exploratory activities and a trend towards a decrease in stereotypies, paralleled by a strong increase in the time spent in inactivity. There was also a profound reduction in GABA contents and glutamic acid decarboxylase activity, particularly in the caudateputamen and the globus pallidus. Dopamine and DOPAC contents, as well as the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase, were also reduced, particularly in the caudate-putamen. mRNA levels for neuronal-specific enolase, proenkephalin and substance P were also dramatically reduced in the caudate-putamen, thus indicating a death of both the direct (striatonigral) and the indirect (striatopallidal) GABA ergic projection pathways, which corresponded with a marked loss of CB1 receptor-mRNA levels observed in both parts, lateral and medial, of the caudate-putamen. However, losses of CB1 receptor binding were confined to the globus pallidus and the caudate-putamen, whereas there were no changes in the substantia nigra and the entopeduncular nucleus. Finally, we failed to reduce the marked akinesia found in these animals by administering SR141716A, a selective antagonist of CB1 receptors, which had exhibited hyperlocomotor effects in previous studies with naive animals. In summary, behavioral and biochemical changes observed in rats intrastriatally lesioned with 3-NP were compatible with a profound degeneration of striatal efferent GABAergic neurons, similar to those occurring in advances stages of the human disease. As expected, a loss of CB1 receptors was evident in the basal ganglia of these rats during the late akinetic stage of the disease. Further studies should demonstrate whether these receptors might be a target for a new therapy in HD, a disease with a poor pharmacological outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexi, T., Hughes, P.E., Faull, R.L.M. and Williams, C.E. (1998) “3-Nitropropionic acid’s lethal triplet: cooperative pathways of neurodegeneration”, Neuroreport 9, 57–64.
Beal, M.F., Brouillet, E., Jenkins, B.G., Ferrante, R.J., Kowall, N.W., Miller, J.M., Storey, E., Srivastava, R., Rosen, B.R. and Hyman, B.T. (1993) “Neurochemical and histologic characterization of striatal excitotoxic lesions produced by the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid”, J. Neurosci. 13, 4181–4192.
Borlongan, C.V., Koutouzis, T.K., Freeman, T.B., Hauser, R.A., Cahill, D.W. and Sanberg, P.R. (1997) “Hyperactivity and hypoactivity in a rat model of Huntington’s disease: the systemic 3-nitropropionic acid model”, Brain Res. Protoc. 1, 253–257.
Brouillet, E., Jenkins, B.G., Hyman, B.T., Ferrante, R.J., Kowall, N.W., Srivastava, R., Roy, D.S., Rosen, B.R. and Beal, M.F. (1993) “Age-dependent vulnerability of the striatum to the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid”, J. Neurochem. 60, 356–359.
Consroe, P. (1998) “Brain cannabinoid systems as targets for the therapy of neurological disorders”, Neurobiol. Dis. 5, 534–551.
Denovan-Wright, E.M. and Robertson, H.A. (2000) “Cannabinoid receptor messenger RNA levels decrease in subset of neurons of the lateral striatum, cortex and hippocampus of transgenic Huntington’s disease mice”, Neuroscience 98, 705–713.
Feigin, A. (1998) “Advances in Huntington’s disease: implications for experimental therapeutics”, Curr. Opin. Neurol. 11, 357–362.
Glass, M., Faull, R.L.M. and Dragunow, M. (1993) “Loss of cannabinoid receptors in the substantia nigra in Huntington’s disease”, Neuroscience 56, 523–527.
Glass, M., Dragunow, M. and Faull, R.L.M. (2000) “The pattern of neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease: a comparative study of cannabinoid, dopamine, adenosine and GABAA receptor alterations in the human basal ganglia in Huntington’s disease”, Neuroscience 97, 505–519.
González, S., Romero, J., de Miguel, R., Lastres, I., Villanúa, M.A., Makriyannis, A., Ramos, J.A. and Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. (1999) “Extrapyramidal and neuroendocrine effects of AM404, an inhibitor of the carrier-mediated transport of anandamide”, Life Sci. 65, 327–336.
Harper, P.S. (1996) Huntington’s Disease (Saunders, London).
Herkenham, M., Lynn, A.B., de Costa, B.R. and Richfield, E.K. (1991a) “Neuronal localization of cannabinoid receptors in the basal ganglia of the rat”, Brain Res. 547, 267–274.
Herkenham, M., Lynn, A.B., Johnson, M.R., Melvin, L.S., de Costa, B.R. and Rice, K.C. (1991b) “Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study”, J. Neurosci. 11, 563–583.
Hersch, S.M. and Ferrante, R.J. (1997) “Neuropathology and pathophysiology of Huntington’s disease”, In: Watts, R.L. and Koller, W.C., eds, Movement Disorders, Neurologic Principals and Practice (McGraw-Hill, New York), pp 503–518.
Hohmann, A.G. and Herkenham, M. (2000) “Localization of cannabinoid CB1 receptor mRNA in neuronal subpopulations of rat striatum: a double-label in situ hybridization study”, Synapse 37, 71–80.
Katagiri, T., Feng, X., Ichikawa, T., Usni, M., Takahashi, Y. and Kumanishi, T. (1993) “Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and non-neuronal enolase (NNE) mRNAs are co-expressed in neurons of the rat cerebellum: in situ hybridization histochemistry”, Mol. Brain Res. 19, 1–8.
Lastres-Backer, I., Fezza, F., Cebeira, M., Bisogno, T., Ramos, J.A., Milone, A., Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. and Di Marzo, V. (2001) “Changes in endocannabinoid transmission in the basal ganglia in a rat model of Huntington’s disease”, Neuroreport 12, 2125–2129.
Lastres-Becker, I., Berrendero, F., Lucas, J.J., Martín-Aparicio, E., Yamamoto, A., Ramos, J.A. and Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. (2002a) “Loss of mRNA levels, binding and activation of GTP-binding proteins for cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the basal ganglia of a transgenic model of Huntington’s disease”, Brain Res. 929, 236–242.
Lastres-Becker, I., Hansen, H.H., Berrendero, F., de Miguel, R., Pérez-Rosado, A., Manzanares, J., Ramos, J.A. and Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. (2002b) “Loss of cannabinoid CB1 receptors and alleviation of motor hyperactivity and neurochemical deficits by endocannabinoid uptake inhibition in a rat model of Huntington’s disease”, Synapse 44, 23–35.
Mailleux, P. and Vanderhaeghen, J.J. (1992) “Distribution of neuronal cannabinoid receptor in the adult brain: a comparative receptor binding radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry”, Neuroscience 48, 655–668.
Nagatsu, T., Oka, K. and Kato, T. (1979) “Highly sensitive assay for tyrosine-hydroxylase activity by high-performance liquid chromatography”, J. Chromatogr. 163, 247–252.
Nawa, H., Kotani, H. and Nakanishi, S. (1984) “Tissue-specific generation of two preprotachykinin mRNAs from one gene by alternative RNA splicing”, Nature 312, 729–734.
Nicoletti, F., Grandison, L. and Meek, J.L. (1985) “Effects of repeated administration of estradiol benzoate on tubero-infundibular GABAergic activity in male rats”, J. Neurochem. 44, 1217–1220.
Page, K.J., Besret, L., Jain, M., Monaghan, E.M., Dunnett, S.B. and Everitt, B.J. (2000) “Effects of systemic 3-nitropropionic acid-induced lesions of the dorsal striatum on cannabinoid and muopioid receptor binding in the basal ganglia”, Exp. Brain Res. 130, 142–150.
Palkovits, M. and Brownstein, J. (1988) Maps and Guide to Microdissection of the Rat Brain (Elsevier, Amsterdam).
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C. (1986) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic Press, London).
Reddy, P.H., Williams, M. and Tagle, D.A. (1999) “Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease”, TINS 22, 248–255.
Reiner, A., Albin, R.L., Anderson, K.D., D’Amato, C.J., Penney, J.B. and Young, A.B. (1988) “Differential loss of striatal projection neurons in Huntington’s disease”, Proc. Natl Acad Sci. USA 85, 5733–5737.
Richfield, E.K. and Herkenham, M. (1994) “Selective vulnerability in Huntington’s disease: preferential loss of cannabinoid receptors in lateral globus pallidus”, Ann. Neurol. 36, 577–584.
Romero, J., de Miguel, R., García-Palomero, E., Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. and Ramos, J.A. (1995) “Time-course of the effects of anandamide, the putative endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, on extrapyramidal function”, Brain Res. 694, 223–232.
Romero, J., Lastres-Becker, I., de Miguel, R., Berrendero, F., Ramos, J.A. and Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. (2002) “The endogenous cannabinoid system and the basal ganglia: biochemical, pharmacological and therapeutic aspects”, Pharmacol. Ther., In press.
Rubino, T., Massi, P., Patrini, G., Venier, I., Giagnoni, G. and Parolaro, D. (1994) “Chronic CP-55,940 alters cannabinoid receptor mRNA in the rat brain: an in situ hybridization study”, Neuroreport 5, 2493–2496.
Shear, D.A., Dong, J., Gundy, C.D., Haik-Creguer, K.L. and Dunbar, G.L. (1998) “Comparison of intrastriatal injections of quinolinic acid and 3-nitropropionic acid for use in animal models of Huntington’s disease”, Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 22, 1217–1240.
Smith, S. and Sharp, T. (1994) “Measurement of GABA in rat brain microdialysates using o-phtaldialdehyde-sulphite derivatization and high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection”, J. Chromatogr. 652, 228–233.
Tsou, K., Brown, S., Sañudo-Peña, M.C., Mackie, K. and Walker, J.M. (1998) “Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system”, Neuroscience 83, 393–411.
Vonsattel, J.P., Myers, R.H., Stevens, T.J., Ferrante, R.J., Bird, E.D. and Richardson, E.P. (1985) “Neuropathological classification of Huntington’s disease”, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 44, 559–577.
Young, W.S., Bonner, T.I. and Brann, M.R. (1986) “Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain”, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 83, 9827–9831.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lastres-Becker, I., Gómez, M., de Miguel, R. et al. Loss of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the basal ganglia in the late akinetic phase of rats with experimental Huntington’s disease. neurotox res 4, 601–608 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/10298420290030514
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10298420290030514