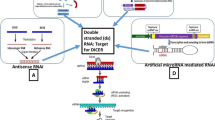
Summary
The notion that the introduction of alien RNA into an organism can cause the silencing of endogenous genes and transgenes came to light in plants during the last decades of the 20th century. It was based on revealing virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) and on the protection against pathogenic viruses by pre-infection with less pathogenic plant viruses or components of such viruses as well as on co-suppression phenomena. The breakthrough in RNA silencing research was the discovery of Mello, Fire and associates that double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) can silence specifically homologous genes in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. The discovery in C. elegans, published in 1998, immediately initiated studies in protozoa, metazoa, fungi, and plants, and similar RNA silencing mechanisms, albeit with some notable differences, were subsequently revealed in almost all eukaryotic organisms in which they were looked for. Investigators dealing with the different organisms were well aware of each others' results and a very active field of study emerged within a few years. Investigators of plant RNA silencing benefited from the findings in other organisms, especially in C. elegans, Drosophila, and mammals, where the protein complexes involved in RNA silencing, such as the Dicer complex and the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), were studied intensively. The study of RNA silencing in plants followed two avenues. In one avenue the process of initiation of endogenous dsRNA was followed, also the fate and the impact of dsRNA that was introduced into plant cells was investigated. It was found how this dsRNA is cut into ∼21 nt fragments and the derived ssRNA of ∼21 nt may guide the RISC to cleave specific mRNA sequences. In the other avenue the formation of ‘hairpin’, or ‘stem loop’ RNA sequences, from transcripts of genomic sequences, was investigated. The ‘maturation’ of these RNA structures into mature microRNA was studied and the possible roles of endogenously formed and introduced microRNAs in the regulation of expression of plant genes were gradually revealed. This review will update the findings in these two avenues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros, V.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D. P.; Burge, C. B.; Carrington, J. C.; Chen, X.; Dreyfuss, G.; Eddy, S. R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Marshall, M.; Matzke, M.; Ruvkun, G.; Tuschl, T. A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 9:277–279; 2003.
Aukerman, M. J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 15:2730–2741; 2003.
Bao, N.; Lye, K.-W.; Barton, M. K. MicroRNA binding sites in Arabidopsis class III HD-ZIP mRNAs are required for methylation of the template chromosome. Dev. Cell 7:653–662; 2004.
Bartel, B.; Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs: at the root of plant development. Plant Physiol. 132:709–717; 2003.
Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297; 2004.
Bass, B. L. Double-stranded RNA as a template for gene silencing. Cell 101:235–238; 2000.
Baulcombe, D. C.; English, J. J. Ectopic pairing of homologous DNA and post-transcriptional gene silencing in transgenic plants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 7:173–180; 1996.
Bonner, J.; Huang, R.-C.; Maheshwari, S. The physical state of newly synthesized RNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 47:1548–1554; 1961.
Byrne, M.; Timmermans, M.; Kidner, C.; Martienssen, R. Development of leaf shape. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4:38–43; 2001.
Chen, X. A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 303:2022–2025; 2004.
Coen, E. S.; Meyerowitz, E. M. The war of the whorls—genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature 353:31–37; 1991.
de Haan, P.; Gielen, J. J. L.; Prins, M.; Wijkamp, I. G.; Vanschepen, A.; Peters, D.; Vangrinsven, M. Q. J. M.; Goldbach, R. Characterization of RNA-mediated resistance to tomato spotted wilt virus in transgenic tobacco plants. Bio-Technology 10:1133–1137; 1992.
Depicker, A.; Van Montagu, M. Post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9:373–382; 1997.
Ding, S. W.; Li, H. W.; Lu, R.; Li, F.; Li, W. X. RNA silencing: a conserved antiviral immunity of plants and animals. Virus Res. 102:109–115; 2004.
Ding, S. W.; Li, W. X.; Symons, R. H. A novel naturally-occurring hybrid gene encoded by a plant RNA virus facilitates long-distance virus movement. EMBO J. 14:5762–5772; 1995.
Emery, J. F.; Floyd, S. K.; Alvarez, J.; Eshed, Y.; Hawker, N. P.; Izhaki, A.; Baum, S. F.; Bowman, J. L. Radial patterning of Arabidopsis shoots by class III HD-ZIP and KANADI Genes. Curr. Biol. 13:1768–1774; 2003.
English, J. J.; Mueller, E.; Baulcombe, D. C. Suppression of virus accumulation in transgenic plants exhibiting silencing of nuclear genes. Plant Cell. 8:179–188; 1996.
Eshed, Y.; Bowman, J. L. MicroRNAs guide asymmetric DNA modifications guiding asymmetric organs. Dev. Cell 7:629–630; 2004.
Fagard, M.; Boutet, S.; Morel, J.-B.; Bellini, C.; Vaucheret, H. AGO1, QDE-2, RDE-1 are related proteins required for post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants, quelling in fungi, and RNA interference in animals. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97:11650–11654; 2000.
Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M. K.; Kostas, S. A.; Driver, S. E.; Mello, C. C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391:806–811; 1998.
Galun, E. Transposable elements—a guide to the perplexed and the novice. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2003.
Galun, E. RNA silencing. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co.; 2005.
Galun, E.; Breiman, A. Transgenic plants. London: Imperial College Press; 1997.
Galun, E.; Galun, E. Manufacture of medical and health products by transgenic plants. London: Imperial College Press; 2001.
Golemboski, D. B.; Lomonossoff, G. P.; Zaitlin, M. Plants transformed with a tobacco mosaic-virus nonstructural gene sequence are resistant to the virus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87:6311–6315; 1990.
Hamilton, A. J.; Baulcombe, D. C. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286:950–952; 1999.
Han, M. H.; Goud, S.; Song, L.; Fedoroff, N. The Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA-binding protein HYL1 plays a role in microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101:1093–1098; 2004.
Helliwell, C.; Waterhouse, P. Constructs and methods for high-throughput gene silencing in plants. Methods 30:289–295; 2003.
Horiguchi, G. RNA silencing in plants: a shortcut to functional analysis. Differentiation 72:65–73; 2004.
Huang, R.-C.; Bonner, J. Histone, a suppressor of chromosomal RNA synthesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 48:1216–1222; 1962.
Jack, T. Molecular and genetic mechanisms of floral control. Plant Cell 16:S1-S17; 2004.
Jacob, F.; Monod, J. Genes de structure et gene de regulation dans la biosynthese de proteins. C.R. Biol. 249:1282–1284; 1959.
Jones-Rhoades, M. W.; Bartel, D. P. Computational identification of plant MicroRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol. Cell 14:787–799; 2004.
Jorgensen, R. A. Sense cosuppression in plants: past, present and future. In: Hannon, G. J., ed. RNAi—a guide to gene silencing. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2003:5–21.
Kusaba, M.; Miyahara, K.; Lida, S.; Fukuoka, H.; Takano, T.; Sassa, H.; Nishimura, M. Low glutelin content1: a dominant mutation that suppresses the glutelin multigene family via RNA silencing in rice. Plant Cell 15:1455–1467; 2003.
Lindbo, J. A.; Silva-Rosales, L.; Proebsting, W. M.; Dougherty, W. G. Induction of a highly specific antiviral state in transgenic plants: implications for regulation of gene expression and virus resistance. Plant Cell 5:1749–1759; 1993.
Lippman, Z.; Martienssen, R. The role of RNA interference in heterochromatic silencing. Nature 431:364–370; 2004.
Liu, Q.; Singh, S. P.; Green, A. G. High-stearic and high-oleic cottonseed oils produced by hairpin RNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing. Plant Physiol. 129:1732–1743; 2002.
Llave, C.; Kasschau, K.; Rector, M. A.; Carrington, J. C. Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14:1605–1619; 2002a.
Llave, C.; Xie, Z.; Kasschau, K. D.; Carrington, J. Cleavage of scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. Science 297:2053–2056; 2002b.
Longstaff, M.; Brigneti, G.; Boccard, F.; Chapman, S.; Baulcombe, D. Extreme resistance to potato virus-X infection in plants expressing a modified component of the putative viral replicase. EMBO J. 12:379–386; 1993.
Mallory, A.; Dugas, D. V.; Bartel, D. P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNA regulation of NAC-domain targets is required for proper formation and separation of adjacent embryonic, vegetative, and floral organs. Curr. Biol. 14:1035–1046; 2004.
Matzke, M. A.; Primig, M.; Trnovsky, J.; Matzke, A. J. M. Reversible methylation and inactivation of marker genes in sequentially transformed tobacco plants. EMBO J. 8:643–649; 1989.
McConnell, J. R.; Emery, J.; Eshed, Y.; Bao, N.; Bowman, J.; Barton, M. K. Role of PHABULOSA and PHAVOLUTA in determining radial patterning in shoots. Nature 411:709–713; 2001.
Meister, G.; Tuschl, T. Mechanism of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature 431:343–349; 2004.
Mette, M. F.; Van der Winden, J.; Matzke, M. A.; Matzke, A. J. M. Short RNAs can identify new candidate transposable element families in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 130:6–9; 2002.
Metzlaff, M.; O'Dell, M.; Cluster, P. D.; Flavell, R. B. RNA-mediated RNA degradation and chalcone synthase A silencing in Petunia. Cell 88:845–854; 1997.
Mueller, E.; Gilbert, J.; Davenport, G.; Brigneti, G.; Baulcombe, D. C. Homology-dependent resistance—transgenic virus-resistance in plants related to homology-dependent gene silencing. Plant J. 7:1001–1013; 1995.
Napoli, C.; Lemieux, C.; Jorgensen, R. Introduction of a chimeric chalcone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible co-suppression of homologous genes in trans. Plant Cell 2:279–289; 1990.
Ogita, S.; Uefuji, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Koizumi, N.; Sano, H. RNA interference—producing decaffeinated coffee plants. Nature 423:823; 2003.
Palauqui, J.-C.; Elmayan, T.; Pollien, J.-M.; Vaucheret, H. Systemic acquired silencing: transgene-specific post-transcriptional silencing is transmitted by grafting from silenced stocks to non-silenced scions. EMBO J. 16:4738–4745; 1997.
Park, W.; Li, J.; Song, R.; Messing, J.; Chen, X. CARPEL FACTORY, a dicer homolog and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 12:1481–1495; 2002.
Reinhart, B. J.; Weinstein, E. G.; Rhoades, M. W.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev. 16:1616–1626; 2002.
Roth, B. M.; Pruss, G. J.; Vance, V. B. Plant viral suppressors of RNA silencing. Virus Res. 102:97–108; 2004.
Ruiz, M. T.; Voinnet, O.; Baulcombe, D. C. Initiation and maintenance of virus-induced gene silencing. Plant Cell 10:937–946; 1998.
Schwarz-Sommer, Z.; Huijser, P.; Nacken, W.; Saedler, H.; Sommer, H. Genetic-control of flower development by homeotic genes in Antirrhinum majus. Science 250:931–936; 1990.
Schweizer, P.; Pokorny, J.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Dudler, R. Double-stranded RNA interferes with gene function at the single-cell level in cereals. Plant J. 24:895–903; 2000.
Segal, G.; Song, R. T.; Messing, J. A new opaque variant of maize by a single dominant RNA-interference-inducing transgene. Genetics 165:387–397; 2003.
Smith, H. A.; Swaney, S. L.; Park, T. D.; Wernsman, E. A.; Dougherty, W. G. Transgenic plant-virus resistance mediated by untranslatable sense RNAs—expression, regulation, and fate of nonessential RNAs. Plant Cell 6:1441–1453; 1994.
Smith, N. A.; Singh, S. P.; Wang, M.-B.; Stoutjesdijk, P. A.; Green, A. G.; Waterhouse, P. M. Total silencing by intron-spliced hairpin RNAs. Nature 407:319–320; 2000.
Snow, M.; Snow, R. The dorsoventrality of leaf primordia. New Phytol. 58:188–207; 1959.
Stoutjesdijk, P. A.; Singh, S. P.; Liu, Q.; Hurlstone, C. J.; Waterhouse, P. A.; Green, A. G. hpRNA-mediated targeting of the Arabidopsis FAD2 gene gives highly efficient and stable silencing. Plant Physiol. 129:1723–1731; 2002.
Sussex, I. M. Experiments on the cause of dorsoventrality in leaves. Nature 174:351–352; 1954.
Tang, G.; Galili, G. Using RNAi to improve plant nutritional value: from mechanism to application. Trends Biotechnol. 22:463–469; 2004.
Tang, G.; Reinhart, B. J.; Bartel, D. P.; Zamore, P. D. A biochemical framework for RNA silencing in plants. Genes Dev. 17:49–63; 2003.
van der Krol, A.; Mur, L. A.; Beld, M.; Mol, J. N. M.; Stuitje, A. R. Flavonoid genes in petunia: addition of a limited number of gene copies may lead to a suppression of gene expression. Plant Cell 2:291–299; 1990.
Vance, V. B. Replication of potato virus-X RNA is altered in coinfections with potato virus-Y. Virology 182:486–494; 1991.
Vance, V. B.; Berger, P. H.; Carrington, J. C.; Hunt, A. G.; Shi, X. M. 5′-proximal potyviral sequences mediate potato-virus-X potyviral synergistic disease in transgenic tobacco. Virology 206:583–590; 1995.
Vargason, J. M.; Szittya, G.; Burgyan, J.; Hall, T. M. T. Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor. Cell 115:799–811; 2003.
Voinnet, O.; Baulcombe, D. C. Systemic signalling in gene silencing. Nature 389:553; 1997.
Wassenegger, M.; Heimes, S.; Riederl, L.; Sanger, H. L. RNA-directed de-novo methylation of genomic sequences in plants. Cell 76:567–576; 1994.
Waterhouse, P. M.; Graham, M. W.; Wang, M.-B. Virus resistance and gene silencing in plants can be induced by simultaneous expression of sense and antisense RNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95:13959–13964; 1998.
Wesley, S. V.; Helliwell, C. A.; Smith, N. A.; Wang, M.; Rouse, D. T.; Liu, Q.; Gooding, P. S.; Singh, S. P.; Abbott, D.; Stoutjesdijk, P. A.; Robinson, S. P.; Gleave, A. P.; Green, A. G.; Waterhouse, P. M. Construct design for efficient, effective and high-throughput gene silencing in plants. Plant J. 27:581–590; 2001.
Ye, M. K.; Malinina, L.; Patel, D. J. Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing. Nature 426:874–878; 2003.
Zamore, P. D. Plant RNAi: How a viral silencing suppressor inactivates siRNA. Curr. Biol. 14:R198-R200; 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galun, E. RNA silencing in plants. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 41, 113–123 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2004619
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2004619