Abstract
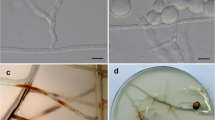
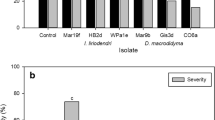
Cylindrocarpon liriodendri was isolated from the roots of diseased own-rooted grapevines (Vitis vinifera cv. Pinot Noir) from the Hunter Valley, New South Wales, Australia. Sequencing of the β-tubulin 2 gene established the identity of the pathogen as C. liriodendri. Soil/root inoculation of potted V. vinifera cv. Chardonnay vines resulted in symptoms typical of black-foot disease. This study has established the pathogenicity of an Australian isolate of C. liriodendri on V. vinifera.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davoren CW, Stephens PM, Wicks T (1999) Incidence and possible influence of soil-borne pathogenic fungi in vineyard nurseries. In ‘Asia-Pacific plant pathology for the New Millennium, 12th biennial conference, 27–30 September 1999’. (Eds Arawang Communication Group, Canberra) p. 285. (Australasian Plant Pathology Society: Canberra)
Edwards J, Pascoe IG (2004) Occurrence of Phaeomoniella chlamydospora and Phaeoacremonium aleophilum associated with Petri disease and esca in Australian grapevines. Australasian Plant Pathology 33, 273–279. doi: 10.1071/AP04016
Fourie PH, Halleen F, Volkmann AS (2000) Fungi associated with grape wood, root and trunk diseases: a summary of the 1999 results from the diagnostic service at Nietvoorbij. In ‘Proceedings of the 2nd International viticulture and enology Congress. November 2000, Cape Town, South Africa’. p. 12. (South African Society of Viticulture and Enology: Stellenbosch)
Grasso S (1984) Infezioni di Fusarium oxysporum e di Cylindrocarpon destructans associate a una moria di giovani piante di vite in Sicilia. Informatore Fitopatologico 1, 59–63.
Grasso S, Magnano Di San Lio G (1975) Infezioni di Cylindrocarpon obtusisporium su piante di vite in Sicilia. Vitis 14, 36–39.
Gubler WD, Baumgartner K, Browne GT, Eskalen A, Rooney Latham S, Petit E, Bayramian LA (2004) Root diseases of grapevines in California and their control. Australasian Plant Pathology 33, 157–165. doi: 10.1071/AP04019
Halleen F, Schroers H, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2004a) Fungi associated with black foot disease in South African vineyards and nurseries. In ‘Abstracts 4th international workshop on grapevine trunk diseases — esca and grapevine declines — January 2005’. p. 42. (International Council on Grapevine Trunk Diseases; South African Society for Plant Pathology; South African Society for Enology and Viticulture: Stellenbosch)
Halleen F, Schroers H, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2004b) Novel species of Cylindrocarpon (Neonectria) and Campylocarpon gen. nov. associated with black foot disease of grapevines (Vitis spp.). Studies in Mycology 50, 431–455.
Halleen F, Schroers H, Groenewald JZ, Rego C, Oliveira H, Crous PW (2006) Neonectria liriodendri sp. nov. the main causal agent of black foot disease of grapevines. Studies in Mycology 55, 227–234.
Kornerup A, Wanscher JH (1989) ‘Methuen handbook of colour.’ 3rd edn. (Methuen: London)
Maluta DR, Larignon P (1991) Pied-noir: Mieux vaut prevenir. Viticulture 11, 71–72.
O’Donnell K, Cigelnik E (1997) Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Molecular Phylogenetic Evolution 7, 103–116. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1996.0376
Petit E, Gubler WD (2005) Characterization of Cylindrocarpon species, the cause of black foot disease of grapevine in California. Plant Disease 89, 1051–1059.
Rego C, Oliviera H, Carvalho A, Phillips A (2000) Involvement of Phaeoacremonium spp. and Cylindrocarpon destructans with grapevine decline in Portugal. Phytopathologia Mediterranea 39, 76–79.
Scheck HJ, Vasquez SJ, Gubler WD (1998) First report of black-foot disease, caused by Cylindrocarpon obtusisporum, of grapevine in California. Plant Disease 82, 448.
Sweetingham M (1983) Studies on the nature and pathogenicity of soil-borne Cylindrocarpon spp. PhD Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart.
Whitelaw-Weckert MA, Curtin S, Huang R, Steel CC, Blanchard CL, Roffey PE (2007) Phylogenetic relationships and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum acutatum isolates from grape in subtropical Australia. Plant Pathology 56, 448–463.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitelaw-Weckert, M.A., Nair, N.G., Lamont, R. et al. Root infection of Vitis vinifera by Cylindrocarpon liriodendri in Australia. Australasian Plant Pathology 36, 403–406 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1071/AP07041
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/AP07041