Abstract
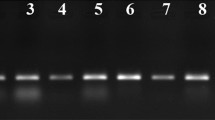
Heteroduplex mobility assay (HMA) was used to determine if genetic variability existed amongst isolates of Australian grapevine yellows (AGY) and the Buckland Valley grapevine yellows (BVGY) phytoplasmas. Genetic variability was detected in two isolates of AGY phytoplasma from the same grapevine when they were compared with an AGY phytoplasma standard using HMA of the elongation factor Tu (tuf) gene. HMA of the tuf gene also showed that an isolate of papaya die back (PDB) phytoplasma, which is closely related to AGY phytoplasma, was different from the AGY phytoplasma standard. The two AGY variant phytoplasmas and PDB phytoplasma were indistinguishable from each other when they were compared using HMA of the tuf gene. No variability was observed amongst isolates of BVGY phytoplasma using HMA of the tuf gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen MY, Beever RE, Forster RLS (2000) Using tuf gene sequences to understand the relationship between Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense diseases. In ‘13th International congress of the International Organization for Mycoplasmology’. 14–19 July 2000 Acros, Fukuoka: program and abstracts Fukuoka. p. 103.
Andersen MT, Beever RE, Sutherland PW, Forster RLS (2001) Association of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense’ with sudden decline of cabbage tree in New Zealand. Plant Disease 85, 462–469.
Andersen MT, Longmore J, Liefting LW, Wood GA, Sutherland PW, Beck DL, Forster RLS (1988) Phormium yellow leaf phytoplasma is associated with strawberry lethal yellows disease in New Zealand. Plant Disease 82, 606–609.
Bowyer J, Verrills N, Gillings M, Holmes AJ (2000) Heteroduplex mobility assay as a tool for predicting phylogenetic affiliation of environmental ribosomal RNA clones. Journal of Microbiological Methods 41, 155–160. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00150-0
Ceranic-Zagorac P, Hiruki C (1996) Comparative molecular studies on aster yellows phytoplasmas. Acta Horticulturae 377, 266–276.
Constable FE, Gibb KS, Symons RH (2003a) Seasonal distribution of phytoplasmas in Australian grapevines. Plant Pathology 52, 267–276. doi:10.1046/J.1365-3059.2003.00849.X
Constable FE, Whiting JR, Gibb KS, Symons RH (2002) A new grapevine yellows phytoplasma from the Buckland Valley of Victoria, Australia. Vitis 41, 147–154.
Constable FE, Whiting JR, Jones J, Gibb KS, Symons RH (2003b) The distribution of grapevine yellows disease associated with the Buckland Valley grapevine yellows phytoplasma. Journal of Phytopathology 151, 65–73. doi: 10.1046/J.1439-0434.2003.00681.X
Cousin MT, Roux J, Boudon-Padieu E, Berges R, Seemüller E, Hiruki C (1998) Use of heteroduplex mobility analysis (HMA) for differentiating phytoplasma isolates causing witches’ broom disease on Populus nigra cv italica and stolbur or big bud symptoms on tomato. Journal of Phytopathology 146, 97–102.
Davis RE, Dally EL, Gundersen DE, Lee I-M, Habili N (1997) Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense”, a new phytoplasma taxon associated with Australian grapevine yellows. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 47, 262–269.
Gibb KS, Constable FE, Moran JR, Padovan AC (1999) Phytoplasmas in Australian grapevines — detection, differentiation and associated diseases. Vitis 38, 107–114.
Green MJ, Thompson DA, MacKenzie DJ (1999) Easy and efficient DNA extraction from woody plants for the detection of phytoplasmas by polymerase chain reaction. Plant Disease 83, 482–485.
Liefting LW, Padovan AC, Gibb KS, Beever RE, Andersen MT, Newcomb RD, Beck DL, Forster RLS (1998) ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma austaliense’ is the phytoplasma associated with Australian grapevine yellows, papaya dieback and Phormium yellow leaf diseases. European Journal of Plant Pathology 104, 619–623. doi: 10.1023/A:1008693904427
Padovan AC, Gibb KS, Daire X, Boudon-Padieu E (1996) A comparison of the phytoplasma associated with Australian grapevine yellows to other phytoplasmas in grapevine. Vitis 35, 189–194.
Padovan A, Gibb K, Persley D (2000) Association of ‘Candidatus phytoplasma australiense’ with green petal and lethal yellows diseasesin strawberry. Plant Pathology 49, 362–369. doi: 10.1046/J.1365-3059.2000.00461.X
Schneider B, Gibb KS, Seemüller E (1997) Sequence and RFLP analysis of the elongation factor Tu gene used in differentiation and classification of phytoplasmas. Microbiology 143, 3381–3389.
Wang K, Hiruki C (2000) Heteroduplex mobility assay detects DNA mutations for differentiation of closely related phytoplasma strains. Journal of Microbiological Methods 41, 59–68. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00137-8
Wang K, Hiruki C (2001) Use of heteroduplex mobility assay for identification and differentiation of phytoplasmas is the aster yellows group and the clover proliferation group. Phytopathology 91, 546–552.
White DT, Blackall LL, Scott PT, Walsh KB (1998) Phylogenetic positions of phytoplasmas associated with dieback, yellow crinkle and mosaic diseases of papaya, and their proposed inclusion in ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense’ and a new taxon, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma australasia’. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 48, 941–951.
Zhong QK, Wang H, Khadhair H, Hiruki C, Cousin M-T (1994) Genetic relatedness of mycoplasmalike organisms investigated by DNA heteroduplex mobility assay. IOM Letters 3, 271.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Constable, F.E., Symons, R.H. Genetic variability amongst isolates of Australian grapevine phytoplasmas. Australasian Plant Pathology 33, 115–119 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1071/AP03096
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/AP03096