Abstract
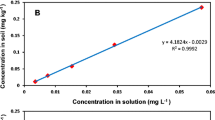
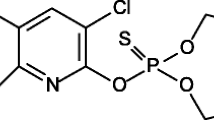
Ecotoxicological impacts of organic pesticides on soil and aquatic ecosystems depend primarily on their behavior in soils. Actual pesticide knowledge is mostly restricted to soils from temperate climates, whereas knowledge of pesticide behavior in tropical soils is scarce. Here, the sorption behavior of two organophosphorous insecticides, parathion and cadusafos, was studied in three agricultural soil samples from central Mexico, Vertisols and Andosols. Using 14C-labeled substances, we assessed sorption and desorption properties in classical batch equilibrium and static soil incubation experiments. Our results show that cadusafos was less sorbed by the various soils (K d values 7.6–12.7 L kg−1) compared with parathion (K d values 38.6–74.9 L kg−1), despite similar log K ow values. Cadusafos exhibited a greater reversibility of sorption than parathion in both soil types. Time-dependent sorption was quantitatively significant, leading to a rapid decrease in the concentration of available insecticide. This finding is partly due to the formation of non-extractable, bound residues. The decrease in the available concentration of both insecticides was greater in the Andosol compared with the Vertisols. Soil organic matter clearly influenced the sorption behavior and availability of parathion. On the other hand, the sorption of cadusafos was more influenced by other soil properties such as clay content and cation exchange capacity. Calculation of residual insecticide levels in the soil solution suggests that both insecticides may have persistent toxic effects in the studied soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AFNOR (2005) Évaluation de la qualité des sols. Volume 1 : Méthodes d’analyse chimique; Volume 2 : Méthodes d’analyses physique et biologique, 946 p.
Agritox: toxicological data base on pesticides, INRA (2005) At: www.inra.fr/agritox/.
Allen-King R.M., Grathwohl P., Ball W.P. (2002) New modeling paradigms for the sorption of hydrophobic organic chemicals to heterogeneous carbonaceous matter in soils, sediments and rocks, Adv. Water Resour. 25, 985–1016.
Barriuso E., Calvet R. (1991) Soil type and herbicide adsorption, Int. J. Environ. An. Ch. 46, 117–128.
Barriuso E., Feller C., Calvet R., Cerri C. (1992) Sorption of atrazine, terbutryn and 2, 4-D herbicides in two Brasilian oxisols, Geoderma 53, 155–167.
Barriuso E., Laird D.A., Koskinen W., Dowdy R.H. (1994) Atrazine desorption from smectites, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 58, 1632–1638.
Bowman B.T., Sans W.W. (1977) Adsorption of parathion, fenitrothion, methyl parathion, aminoparathion and paraoxon by Na+, Ca+, and Fe3+ montmorillonite suspensions, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 41, 514–519.
Calvet R., Barriuso E., Bedos C., Benoit P., Charnay M.P., Coquet Y. (2005) Devenir des pesticides dans les sols, Éditions France Agricole, Paris.
CICOPLAFEST (2004) Comision Intersecretarial para el Control de Proceso y Uso de Plaguicidas, Fertilizantes y Sustancias Tóxicas. Catálogo Oficial de Plaguicidas. SAGARPA, SEDESOL, Méx, D.F. 481.
FOOTPRINT (2006) The FOOTPRINT Pesticide Properties DataBase, University of Hertfordshire as part of the EU-funded FOOTPRINT project (FP6-SSP-022704), http://www.eu-footprint.org/ppdb.html.
Führemann T.W, Lichtenstein E.P. (1978) Release of soil-bound methyl [14C] parathion residues and their uptake by earthworms and oat plants, J. Food. Agr. Chem. 26, 605–610.
Gevao B., Mordaunt C., Semple K.T., Piearce T.G., Jones K.C. (2001) Bioavailability of nonextractable (bound) pesticide residues to earthworms, Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 501–507.
Hamaker J.W., Thompson J.M. (1972) Adsorption of organic chemicals in the soil environment, Vol. 1, in: Goring C.A.I., Hammaker J.W. (Eds.), Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 49–143.
Hassett J.J., Banwart W.L., Griffin R.A. (1983) Correlation of compound properties with sorption characteristics of non polar compounds by soils and sediments: concepts and limitations, in: Francis C.W., Auerbach S.I. (Eds.), Environment and solid wastes, Butterworth, Boston, pp. 161–178.
INEGI (2004) Carta Edafológica y Anuario Estadístico del Estado de Morelos, Institute Nacional de Estadística Geografía e Informática. Edición 2004, Méx, D.F.
Kaiser K., Guggenberger G. (2003) Mineral surfaces and soil organic matter, Eur. J. Soil Sci. 54, 219–236.
Katan J., Fuhremann T.W., Lichtenstein E.P. (1976) Binding of 14C parathion in soil: A reassessment of pesticide persistence, Science 193, 891–894.
Koskinen W.C., Harper S.S. (1990) The retention process: mechanisms, in: Cheng H.H. (Ed.), Pesticides in the Soil Environment: Processes, Impacts and Modelling, SSA Book Series 2, SSSA, Madison, WI, pp. 51–77.
Laabs V., Amelung W. (2005) Sorption and aging of corn and soybean pesticides in tropical soils of Brazil, J. Agr. Food Chem. 53, 7184–7192.
Leenheer J.A., Ahlrichs J.L. (1971) A kinetic and equilibrium study of the adsorption of carbaryl and parathion upon soil organic matter surfaces, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 35, 700–705.
Mamy L., Barriuso E. (2007) Desorption and time-dependent sorption of herbicides in soils, Eur. J. Soil Sci. 58, 174–187.
Oliver D.P., Kookana R.S., Quintana B. (2005) Sorption of pesticides in tropical and temperate soils from Autralia and Philippines, J. Agr. Food Chem. 53, 6420–6425.
Pignatello J.J. (2000) The measurement and interpretation of sorption and desorption rates for organic compounds in soil media, Adv. Agron. 69, 1–73.
Pehkonen S.O., Zhang Q. (2002) The degradation of organophosphorus pesticides in natural waters: a critical review, Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. 32, 17–72.
Pesticide Manual (2003) Incorporating the Agrochemicals Handbook, 13th ed., n. Crop Protection Publication, British Crop Protection Council, The Royal Society of Chemisty, London, 1344 p.
Racket K.D. (2003) What do we know about the fate of pesticides in tropical ecosystems? in: Coast J.R, Yamamoto H. (Eds.), Environmental fate and effects of pesticides, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC., pp. 96–123.
Saffih-Hdaddi K., Bruckler L., Barriuso E. (2003) Modeling of sorption and biodegradation of parathion and its metabolite paraoxon in soil, J. Environ. Qual. 32, 2207–2215.
Saltzmann S., Kliger L., Yaron B. (1972) Adsorption-desorption of parathion as affected by soil organic matter, J. Agr. Food Chem. 16, 21–23.
Sanchez Martin M.J., Sanchez Camazano M. (1991) Relationship between the structure of organophosphorus pesticides and adsorption by soil components, Soil Sci. 152, 283–288.
Wauchope R.D., Yeh S., Linders J.B.H.J., Kloskowski R., Tanaka K., Rubin B., Katayama A., Kordel W., Gerstl Z., Lane M., Unsworth J.B. (2002) Pesticide soil sorption parameters: theory, measurement, uses, limitations and reliability, Pest Manag. Sci. 58, 419–445.
Weber J.B., Best J.A., Gonese J.U. (1993) Bioavailability and bioactivity of sorbed organic chemicals, in: Linn D.M. (Ed.), Sorption and degradation of pesticides and organic chemicals in soil, SSSA special publication No. 32, Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 153–193.
Weber J.B., Wilkerson G.G., Reinhardt F.C. (2004) Calculating pesticides sorption coefficients (Kd) using selected soil properties, Chemosphere 55, 157–166.
Worrall F., Parker A., Rae J.E., Johnson A.C. (1996) Equilibrium adsorption of isoproturon on soil and pure clays, Eur. J. Soil Sci. 47, 265–272.
WRB (1998) World Reference base for Soil Resources. FAO, ISRIC and ISSS©, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Yaron B., Saltzmann S. (1978) Soil-parathion surface interactions, Res. Rev. 69, 1–34.
Zheng S.Q., Cooper J.F. (1996) Adsorption, desorption, and degradation of three pesticides in different soils, Arch. Environ. Con. Tox. 30, 15–20.
Zheng S.Q., Cooper J.F., Palcy L., Coste C.M., Marnotte P. (1994) Mobility and dissipation of cadusafos in banana fields in Martinique, Sci. Total Environ. 156, 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Olvera-Velona, A., Benoit, P., Barriuso, E. et al. Sorption and desorption of organophosphate pesticides, parathion and cadusafos, on tropical agricultural soils. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 28, 231–238 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2008009
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2008009