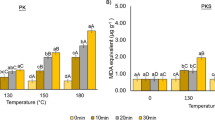
Abstract
Most of the studies on royal jelly (RJ) composition or properties as well as quality standards of commercially available royal jelly are based on RJ harvested three days (72 h) after grafting. In China, some beekeepers produce RJ harvested one (24 h) or two (48 h) days after grafting. There is a lack of knowledge about the quality of the royal jelly harvested earlier than 72 h. This study compared 32 colonies for their chemical compositions of RJ harvested at 24, 48 and 72 h after grafting, according to the proportion of moisture, protein, 10-HDA, total sugar and the value of acidity and superoxide dismutase activity. The analysis of RJ samples revealed that the composition varied significantly (for both fresh and dehydrated samples) and on some occasions above and below the range of present Chinese and Swiss standards. The results suggest that harvesting time should be considered when defining new quality standards of RJ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloodworth B.C., Harn C.S., Hock C.T., Boon Y.O. (1995) Liquid chromatographic determination of trans-10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid content of commercial products containing Royal Jelly, J. AOAC Int. 78, 1019–1023.
Blum M., Novak A., Taber S. (1959) 10-Hydroxy-Δ2-DecenoicA cid, an Antibiotic Found in Royal Jelly, Science 130, 452–453.
Brouwers E. (1984) Glucose/fructose ratio in the food of honeybee larvae during caste differentiation, J. Apic. Res. 23, 94–101.
Brouwers E., Ebert R., Beetsma J. (1987) Behavioural and physiological aspects of nurse bees in relation to the composition of larval food during caste differentiation in the honeybee, J. Apic. Res. 26, 11–23.
Chen C., Chen S. (1995) Changes in protein components and storage stability of royal jelly under various conditions, Food Chem. 54, 195–200.
Chen S., Liu F., Han S., Liu F. (1992) The relationship between the age of larvae grafted and the production of royal jelly, Apic. China 43, 2–6.
Chen S.L., Su S.K., Lin X.Z. (2002) An introduction to high-yielding royal jelly production methods in China, Bee World 83, 69–77.
Fontana R., Mendes M.A., de Souza B.M., Konno K., César L.M.M., Malaspina O., Palma M.S. (2004) Jelleines: a family of antimicrobial peptides from the Royal Jelly of honeybees (Apis mellifera), Peptides 25, 919–928.
Fujii A., Kobayashi S., Kuboyama N., Furukawa Y., Kaneko Y., Ishihara S., Yamamoto H., Tamura T. (1990) Augmentation of wound healing by royal jelly in streptozotocin-diabetic rats, Jpn J. Pharmacol. 53, 331–337.
General Administation of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (2002) The quality standard of royal jelly.
Guo H., Kouzuma Y., Yonekura M. (2009) Structures and properties of antioxidative peptides derived from royal jelly protein, Food Chem. 113, 238–245.
Howe S.R., Dimick P.S., Benton A.W. (1985) Composition of freshly harvested and commercial royal jelly, J. Apic. Res. 24, 52–61.
Kamakura M., Mitani N., Fukuda T., Fukushima M. (2001) Antifatigue effect of fresh royal Jelly in mice, J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 47, 394–401.
Kataoka M., Arai N., Taniguchi Y., Kohno K., Iwaki K., Ikeda M., Kurimoto M. (2001) Analysis of anti-allergic function of royal jelly, Nat. Med. 55, 174–180.
Kimura Y., Washino N., Yonekura M. (1995) N-linked sugar chains of 350-kDa royal jelly glycoprotein, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 59, 507–509.
Kucharski R., Maleszka J., Maleszka R. (2008) Nutritional control of reproductive status in honeybees via DNA methylation, Science 319, 1827–1830.
Lercker G., Caboni M., Vecchi M., Sabatini A., Nanetti A., Piana L. (1985) Composizione della frazione glucidica della gelatina reale e della gelatina delle api operaie in relazione all’età larvale, Apicoltura 8, 27–37.
Lercker G., Capella P., Conte L.S., Ruini F., Giordani G. (1981) Components of royal jelly. I. Identification of organic acids, Lipids 16, 912–919.
Lercker G., Capella P., Conte L.S., Ruini F., Giordani G. (1982) Components of royal jelly: II. The lipid fraction, hydrocarbons and sterolds, J. Apic. Res. 21, 178–184.
Lercker G., Vecchi M.A., Piana L., Sabatini A.G., Nanetti A. (1984) Composition de la fraction lipidique de la gelée de larves d’abeilles reines et ouvrières (Apis mellifera ligustica Spinola) en fonction de l’age des larves, Apidologie 15, 303–314.
Liu J.R., Yang Y.C., Shi L.S., Peng C.C. (2008) Antioxidant properties of royal jelly associated with larval age and time of harvest, J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 11447–11452.
Matsui T., Yukiyoshi A., Doi S., Sugimoto H., Yamada H., Matsumoto K. (2002) Gastrointestinal enzyme production of bioactive peptides from royal jelly protein and their antihypertensive ability in SHR, J. Nutr. Biochem. 13, 80–86.
Messia M., Caboni M., Marconi E. (2005) Storage stability assessment of freeze-dried royal jelly by furosine determination, J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 4440–4443.
Min L., Li J., Liu K., Jiang Y., Liu X., Liu X. (2004) Isolation, purification and characterization of superoxide dismutase from royal jelly of the Italian worker bee, Apis mellifera, Acta Entomol. Sinica 47, 171–177.
Mitsui T., Sagawa T., Sano H. (1964) Studies on rearing honey bee larvae in the laboratory. I. The effect of royal jelly taken from different ages of queen cells on queen differentiation, J. Econ. Entomol. 57, 518–521.
Moritz R., Lattorff H., Neumann P., Kraus F., Radloff S., Hepburn H. (2005) Rare royal families in honeybees, Apis mellifera, Naturwissenschaften 92, 488–491.
Okamoto I., Taniguchi Y., Kunikata T., Kohno K., Iwaki K., Ikeda M., Kurimoto M. (2003) Major royal jelly protein 3 modulates immune responses in vitro and in vivo, Life Sci. 73, 2029–2045.
Sabatini A.G., Marcazzan G., Caboni M.F., Bogdanov S., Almeida-Muradian L.B. (2009) Quality and standardisation of Royal Jelly, J. Apiprod. Apimed. Sci. 1, 1–6.
Schweizerisches Lebensmittelbuch (2003) Methoden für die Untersuchung und Beurteilung von Lebensmitteln und Gebrauchsgegeständen, Gelée Royale, Chap. 23C.
Shen J. (1991) Comparison of the effects of producing royal jelly in various cycle, Apic. China 42, 2–4.
Tang C., Yuan Y. (1999) Effect of temperatue on the activity of Superoxide dismutase in royal jelly, Apic. China 50, 10–11.
Townsend G.F., Morgan J.F., Tolnai S., Hazlett B., Morton H.J., Shuel R.W. (1960) Studies on the in vitro antitumor activity of fatty acids: I. 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid from royal jelly, Cancer Res. 20, 503–510.
Zhang Y., Jiang Y., Niu J. (1996) Determination of Superoxide dismutase activity in royal jelly, J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. 16, 267–268.
Zou G., Gui X., Zhong X., Zhu Y. (1986) Improvements in pyrogallol autoxidation method for the determination of SOD activity, Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 4, 71–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript editor: Stan Schneider
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H.Q., Hu, F.L. & Dietemann, V. Changes in composition of royal jelly harvested at different times: consequences for quality standards. Apidologie 42, 39–47 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1051/apido/2010033
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/apido/2010033