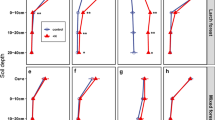
To examine the relative importance of nutrient resorption in increasing the nutrient-use efficiency of Pinus thunbergii Parl., we investigated the nitrogen contents of green and senescent needles of P. thunbergii trees growing at five positions along a slope (LS, lower slope; TR, transitional site; MS, middle slope; US, upper slope; RG, ridge) and found that soil nitrogen availability tended to decrease upslope. Nitrogen concentration in green and senescent needles decreased upslope. Nitrogen resorption efficiencies (percentage change in nitrogen content between green and senescent needles) increased upslope from 43 to 77% with decreasing soil nitrogen availability. Nitrogen resorption efficiency was related to green needle dry mass per unit length, but there was no clear correlation between nitrogen resorption efficiency and nitrogen content in green needles. We concluded that the increase in nitrogen resorption efficiency of P. thunbergii enhanced the nitrogen-use efficiency as a response to the low nitrogen availability.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aerts, R. & De Caluwe, H. (1989) Aboveground productivity and nutrient turnover of Molinia caerulea along an experimental gradient of nutrient availability. Oikos 54: 320--324.
Binkley, D. & Valentine, D. (1991) Fifty-year biogeochemical effects of green ash, white pine, and Norway spruce in a replicated experiment. Forest Ecology and Management 40: 13--25.
Birk, E. M. & Vitousek, P. M. (1986) Nitrogen availability and nitrogen use efficiency in loblolly pine stands. Ecology 67: 69--79.
Boerner, R. E. J. (1984) Foliar nutrient dynamics and nutrient use efficiency of four deciduous tree species in relation to site fertility. Journal of Applied Ecology 21: 1029--1040.
Chapin, F. S. (1980) The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 11: 233--260.
Chapin, F. S. & Kedrowski, R. A. (1983) Seasonal changes in nitrogen and phosphorus fractions and autumn retranslocation in evergreen and deciduous Taiga trees. Ecology 64: 376--391.
Chapin, F. S. & Moilanen, L. (1991) Nutritional controls over nitrogen and phosphorus resorption from Alaskan birch leaves. Ecology 72: 709--715.
Dalla-Tea, F. & Jokela, E. J. (1994) Needlefall returns and resorption rates of nutrients in young intensively managed slash and loblolly pine stands. Forest Science 40: 650--662.
Enoki, T., Kawaguchi, H. & Iwatsubo, G. (1996) Topographic variations of soil properties and stand structure in a Pinus thunbergii plantation. Ecological Research 11: 299--309.
Enoki, T., Kawaguchi, H. & Iwatsubo, G. (1997) Nutrient-uptake and nutrient-use efficiency of Pinus thunbergii Parl. along a topographical gradient of soil nutrient availability. Ecological Research 12: 191--199.
Flanagan, P. W. & Van Cleve, K. (1983) Nutrient cycling in relation to decomposition and organic-matter quality in taiga ecosystems. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 13: 795--817.
Gholz, H. L., Fisher, R. F. & Pritchett, W. L. (1985) Nutrient dynamics in slash pine plantation ecosystems. Ecology 66: 647--659.
Gosz, J. R., Likens, G. E. & Bormann, F. H. (1976) Organic matter and nutrient dynamics of the forest and forest floor in the Hubbard Brook Forest. Oecologia 22: 305--320.
Helmisaari, H. (1992) Nutrient retranslocation within the foliage of Pinus sylvestris. Tree Physiology 10: 45--58.
Hobbie, S. H. (1992) Effects of plant species on nutrient cycling. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 7: 336--339.
Iwatsubo, G., Hirabayashi, Y. & Tsutsumi, T. (1982) On the spraying of sewage water in a forest. (II) Effects of the spraying on the run-off water chemicals and the nutrient budgets of the forest watershed. Journal of the Japanese Forestry Society 64: 419--428.
Killingbeck, K. T. (1996) Nutrients in senesced leaves: Keys to the search for potential resorption and resorption proficiency. Ecology 77: 1716--1727.
Lajtha, K. (1987) Nutrient reabsorption efficiency and the response to phosphorus fertilization in the desert shrub Larrea tridentata (DC.) Cov. Biogeochemistry 4: 265--276.
Lajtha, K. & Klein, M. (1988) The effect of varying nitrogen and phosphorus availability on nutrient use by Larrea tridentata, a desert evergreen shrub. Oecologia 75: 348--353.
Matson, P. (1990) Plant--soil interactions in primary succession at Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. Oecologia 85: 241--246.
Melillo, J. M., Aber, J. D. & Muratore, J. F. (1982) Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 63: 621--626.
Nambiar, E. K. S. & Fife, D. N. (1987) Growth and nutrient retranslocation in needles of radiata pine in relation to nitrogen supply. Annals of Botany 60: 147--156.
Nambiar, E. K. S. & Fife, D. N. (1991) Nutrient retranslocation in temperate conifers. Tree Physiology 9: 185--207.
Parker, G. C. (1983) Throughfall and stemflow in the forest nutrient cycle. Advances in Ecological Research 13: 57--133.
Pastor, J., Aber, J. D., McClaugerty, C. A. & Melillo, J. M. (1984) Aboveground production and N and P cycling along a nitrogen mineralization gradient on Blackhawk Island, Wisconsin. Ecology 65: 256--268.
Pugnaire, F. I. & Chapin, F. S. (1993) Controls over nutrient resorption from leaves of evergreen mediterranean species. Ecology 74: 124--129.
Reich, P. B., Walters, M. B. & Ellsworth, D. S. (1991) Leaf life-span as a determinant of leaf structure and function among 23 amazonian tree species. Oecologia 86: 16--24.
Reich, P. B., Walters, M. B. & Ellsworth, D. S. (1992) Leaf life-span in relation to leaf, plant, and stand characteristics among diverse ecosystems. Ecological Monographs 62: 365--392.
Schlesinger, W. H., Delucia, E. H. & Billings, W. D. (1989) Nutrient-use efficiency of woody plants on contrasting soils in the western Great Basin, Nevada. Ecology 70: 105--113.
Shaver, G. R. & Melillo, J. M. (1984) Nutrient budgets of marsh plants: Efficiency concepts and relation to availability. Ecology 65: 1491--1510.
Small, E. (1972) Photosynthetic rates in relation to nitrogen recycling as an adaptation to nutrient deficiency in peat bog plants. Canadian Journal of Botany 50: 2227--2233.
Systat (1992) Statistics, Version 5.2 Edn. SYSTAT, Inc., Evanston, IL.
Tateno, M. & Chapin, F. S. (1997) Logic of carbon and nitrogen interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. American Naturalist 149: 723--744.
Vitousek, P. M. (1982) Nutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency. American Naturalist 119: 553--572.
Vitousek, P. M. (1984) Litterfall, nutrient cycling, and nutrient limitation in tropical forests. Ecology 65: 285--298.
Vitousek, P. M., Walker, L. R., Whiteaker, L. D., Mueller-Dombois, D. & Matson, P. A. (1987) Biological invasion by Myrica faya alters ecosystem development in Hawaii. Science 238: 802--804.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Enoki, T., Kawaguchi, H. Nitrogen resorption from needles of Pinus thunbergii Parl. growing along a topographic gradient of soil nutrient availability. Ecol Res 14, 1–8 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1703.1999.141280.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1703.1999.141280.x