Abstract
Populations of the common nettle aphid, Microlophium carnosum Buckton, inhabiting nettle patches in an agricultural landscape were surveyed for entomophthoralean infection during 1998, 1999 and 2001. Five pathogenic species were identified from the aphid in the course of the survey. Erynia neoaphidis Remaudière & Hennebert, Neozygites fresenii (Nowakowski) Remaudière & Keller, and Neozygites microlophii Keller affected aphid colonies every year. Two minor pathogens, Entomophthora planchoniana Cornu and Conidiobolus obscurus (Hall & Dunn) Remaudière & Keller, were observed only in 2001.
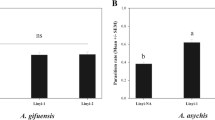
An artificial transmission of the three main fungi was carried out to prove horizontal transmission of infection between the common nettle aphid and different aphid species co-occurring in landscape. N. microlophii, probably monophagous pathogen, did not infect any of the six recipient aphid species in the experiment. Transmissions of E. neoaphidis and N. fresenii conidia were successful with five and four aphid species, respectively. The average mortality of tested aphids after transmission ranged from 0 to 33.33 % for E. neoaphidis and from 0 to 15 % for N. fresenii.
The potential of nettle patches as natural reservoirs for pathogens in the agroecosystem is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barta, M., Cagáň, L. Entomophthoralean fungi associated with the common nettle aphid (Microlophium carnosum Buckton) and the potential role of nettle patches as reservoirs for the pathogens in landscape. Anzeiger für Schädlingskunde/J. Pest Science 76, 6–13 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0280.2003.03004.x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0280.2003.03004.x