Abstract
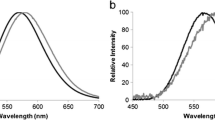
Bioluminescence is widely used in biosensors. Firefly luciferase-based bioluminescent sensors are among the most popular ones. Firefly luciferases are pH-sensitive, displaying a large red shift at acidic pH, a property that has been considered undesirable for most applications. Currently, biosensors that can detect intracellular pH are in demand, and some fluorescent biosensors are available. However, pH sensors using bioluminescence have not been used yet. Thus, we decided to harness a firefly luciferase to measure the intracellular pH in mammalian cells. For this purpose, we engineered the luciferase derived from Macrolampis sp2 firefly to localize it on the cytosol or nucleus, in order to observe pH variation in these compartments during biological activities. We first calibrated the emission ratios (R = Igreen/Ired) at different pH values. As expected, we observed a red shift of light emission under acidic conditions when the cells were subjected to different pH conditions in the presence of the K+/H+ ionophore, nigericin. Based on these results, we concluded that this firefly luciferase can be used as a diagnostic tool for measuring the intracellular pH variation in pathogenic cells or in cells during apoptosis. This is the first example of real time-monitoring of pH change using color tuning luciferase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. W. Hastings, Biological diversity, chemical mechanisms and evolutionary origins of bioluminescent systems, J. Mol. Evol., 1983, 19, 309–321.
T. Wilson and J. W. Hastings, Bioluminescence, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 1998, 14, 197–230.
N. L. Naylor, Reporter gene technology: the future looks bright, Biochem. Pharmacol., 1999, 58, 749–757.
G. B. Sala-Newby, J. M. Kendall, H. E. Jones, K. M. Taylor, M. N. Badminton, D. H. Llewellyn and A. K. Campbell, Bioluminescent and chemiluminescent indicators for molecular signaling and function living cells, in Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity, ed. W. T. Manson, Academic, London, 2nd edn, 1999, pp. 251–271.
V. R. Viviani and Y. Ohmiya, Beetle luciferases: colorful lights on biological processes and diseases, in Photoprotein in Bioanalysis, ed. S. Daunert and S. K. Deo, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006, pp. 49–63.
E. Michelini, L. Cevenini, L. Mezzanote, B. Roda, L. S. Dolci and A. Roda, Bioluminescent reporter proteins for multicolor assays, Minerva Biotecnol., 2009, 21, 87–96.
A. Roda, L. Mezzanotte, R. Aldini, E. Michelini and L. Cevenini, A new gastric-emptying mouse model based on in vivo non-invasive bioluminescence imaging, Neurogastroenterol. Motil., 2010, 22, 1117–e288.
K. V. Wood and M. G. Gruber, Transduction in microbial biosensors using multiplexed bioluminescence, Biosens. Bioelectron., 1996, 11, 207–214.
Y. Nakajima, T. Yamazaki, S. Nishii, T. Noguchi, H. Hoshino, K. Niwa, V. R. Viviani and Y. Ohmiya, Enhanced beetle luciferase for high-resolution bioluminescence imaging, PLoS One, 2010, 5, 100–111.
Y. Nakajima, M. Ikeda, T. Kimura, S. Honma, Y. Ohmiya and K. Honma, Bidirectional role of orphan nuclear receptor RORα in clock gene transcriptions demonstrated by a novel reporter assay system, FEBS Lett., 2004, 565, 122–126.
H. H. Seliger and W. D. McElroy, The colors of firefly bioluminescence: enzyme configuration and species specificity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1964, 52, 75–81.
V. R. Viviani and E. J. H. Bechara, Bioluminescence of Brazilian fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae): spectral distribution and pH-effect on luciferase-elicited colors. Comparison with elaterid and phengodid luciferases, Photochem. Photobiol., 1996, 62, 490–495.
P. Breeuwer, J. Drocourt, F. M. Rombouts and T. Abee, A novel method for continuous determination of the intracellular pH in bacteria with the internally conjugated fluorescent probe 5 (and 6-)-carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, 62, 178–183.
J. Llopis, J. M. McCaffery, A. Miyawaki, M. G. Farquhar and R. Y. Tsien, Measurement of cytosolic, mitochondrial, and Golgi pH in single living cells with green fluorescent proteins, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1988, 95, 6803–6808.
M. Kneen, J. Farinas, Y. Li and A. S. Verkman, Green fluorescent protein as a noninvasive intracellular pH indicator, Biophys. J., 1998, 74, 1591–1599.
D. Cui, X. Qian, F. Liu and R. Zhang, Novel fluorescent pH sensors based on intramolecular hydrogen bonding ability of naphthalimide, Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 2757–2760.
R. Bizzarri, C. Arcangeli, D. Arosio, F. Ricci, P. Faraci, F. Cardarelli and F. Beltram, Development of a novel GFP-based ratiometric excitation and emission pH indicator for intracellular studies, Biophys. J., 2006, 90, 3300–3314.
D. Arosio, F. Ricci, L. Marchetti, R. Gualdani, L. Albertazzi and F. Beltram, Simultaneous intracellular chloride and pH measurements using a GFP-based sensor, Nat. Methods, 2010, 7, 516–520.
M. J. Mahon, pHluorin2: an enhanced, ratiometric, pH-sensitive green florescent protein, Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol., 2011, 2, 132–137.
M. Tantama, Y. P. Hung and G. Yellen, Imaging intracellular pH in live cells with a genetically-encoded red fluorescent protein sensor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 10034–10037.
E. Quatresous, C. Legrand and S. Pouvreau, Mitochondriatargeted cpYFP: pH or superoxide sensor?, J. Gen. Physiol., 2012, 140, 567–570.
J. W. A. van Beilen and S. Brul, Compartment-specific pH monitoring in Bacillus subtilis using fluorescent sensor proteins: a tool to analyze the antibacterial effect of weak organic acids, Front. Microbiol., 2013, 4, 1–11.
S. Pöea-Guyon, H. Pasquier, F. Mérola, N. Morel and M. Erard, The enhanced cyan fluorescent protein: a sensitive pH sensor for fluorescence lifetime imaging, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2013, 405, 3983–3987.
H. Li, H. Dong, M. Yu,C. Liu, Z. Li, L. Wei, L. SunandH. Zhang, Nir ratiometric luminescence detection of pH fluctuation in living cells with hemicyanine derivative-assembled upconversion nanophosphors, Anal. Chem., 2017, 89, 8863–8869.
T. Asai, S. Nishi, Y. Nakajima and Y. Ohmiya, Beetle luciferases in measuring gene expression and imaging cell functions, in Luciferases and Fluorescent Proteins: Principles and Advances in Biotechnology and Bioimaging, ed. V. R. Viviani and Y. Ohmiya, Transworld Research Network, Kerala, 2007, pp. 151–160.
M. Benčina, Illumination of the spatial order of intracellular pH by genetically encoded pH-sensitive sensors, Sensors, 2013, 13, 16736–16758.
M. Hattori, S. Haga, H. Takakura, M. Ozaki and T. Ozawa, Sustained accurate recording of intracellular acidification in living tissues with a photo-controllable bioluminescent protein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, 110, 9332–9337.
V. R. Viviani and E. J. H. Bechara, Biophysical and biochemical aspects of phengodid (railroad-worm) bioluminescence, Photochem. Photobiol., 1993, 58, 615–622.
V. R. Viviani, T. L. Oehlmeyer, F. G. C. Arnoldi and M. R. Brochetto-Braga, A new firefly luciferase with bimodal spectrum: identification of structural determinants in spectral pH-sensitivity firefly luciferases, Photochem. Photobiol., 2005, 81, 843–848.
G. V. M. Gabriel and V. R. Viviani, Novel application of pH-sensitive firefly luciferases as dual reporter genes for simultaneous ratiometric analysis of intracellular pH and gene expression/location, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2014, 13, 1661–1670.
H. Kwon, T. Enomoto, M. Shimogawara, K. Yasuda, Y. Nakajima and Y. Ohmiya, Bioluminescence imaging of dual gene expression at the single-cell level, BioTechniques, 2010, 48, 460–462.
J. A. Thomas, R. N. Buchsbaum, A. Zimniak and E. Racker, Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ, Biochemistry, 1979, 18, 2210–2218.
H. H. Seliger and W. D. McElroy, Spectral emission and quantum yield of firefly bioluminescence, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1960, 88, 136–141.
H. H. Seliger and W. D. McElroy, Chemiluminescence of firefly luciferin without enzyme, Science, 1962, 138, 683–685.
S. H. Cody, P. N. Dubbin, A. D. Beischer, N. D. Duncan, J. S. Hill, A. H. Kaye and D. A. Williams, Intracellular pH mapping with SNARF-1 and confocal microscopy. I: A quantitative technique for living tissues and isolated cells, Micron, 1993, 24, 573–580.
O. Seksek and J. Bolard, Nuclear pH gradient in mammalian cells revealed by laser microspectrofluorimetry, J. Cell Sci., 1996, 109, 257–262.
T. B. Dansen, K. W. A. Wirtz, R. J. A. Wanders and E. H. W. Pap, Peroxisomes in human fibroblasts have a basic pH, Nat. Cell Biol., 2000, 2, 51–53.
C. Balut, M. vandeVen, S. Despa, I. Lambrichts, M. Ameloot, P. Steels and I. Smets, Measurement of cytosolic and mitochondrial pH in living cells during reversible metabolic inhibition, Kidney Int., 2008, 73, 226–232.
X. Zhou, F. Su, H. Lu, P. Senechal-Willis, Y. Tian, R. H. Johnson and D. R. Meldrum, An FRET-based ratiometric chemosensor for in vitro cellular fluorescence analyses of pH, Biomaterials, 2012, 33, 171–180.
Z. Yang, J. Cao, Y. He, J. H. Yang, T. Kim, X. Peng and J. S. Kim, Macro-/micro-environment-sensitive chemosensing and biological imaging, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 4563–4601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Mello Gabriel, G.V., Yasuno, R., Mitani, Y. et al. Novel application of Macrolampis sp2 firefly luciferase for intracellular pH-biosensing in mammalian cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 18, 1212–1217 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8pp00573g
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c8pp00573g