Abstract
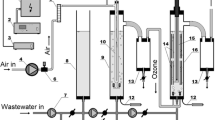
The present work reports the use of a flotation cell as a prospective reactor for ozonation and the intensification of ozonation (catalytic ozonation and photocatalytic ozonation). The effect of the pH, ozone concentration and loading catalyst was investigated. The performance of the flotation cell was compared with that of conventional reactors used in ozonation through the ozone utilized index (OUI), which was proposed in this work and relates the amount of ozone supplied to the system per milligram of degraded pollutant. The flotation cell has the lowest OUI, which indicates that the ozone supplied is highly consumed. It was found that the modified flotation cell is an efficient reactor for ozonation, catalytic ozonation and photocatalytic ozonation processes because total diclofenac degradation was achieved in a short time, mass transfer limitations were not found (Ha = 7.26), and it presented a relatively low energy consumption (1.15 kW h m−3).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. M. Monteagudo, A. Durán and I. San Martín, Mineralization of wastewater from the pharmaceutical industry containing chloride ions by UV photolysis of H2O2/Fe(ii) and ultrasonic irradiation, J. Environ. Manage., 2014, 141, 61–69.
Z. Wang, J. Xu, W. Cai, B. Zhou, Z. He, C. Cai and X. Hong, J. Environ. Sci., 2005, 17, 76–80.
C. G. Daughton, Emerging pollutants, and communicating the science of environmental chemistry and mass spectrometry: Pharmaceuticals in the environment, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2001, 12, 1067–1076.
N. Zhang, J. M. Li, G. G. Liu, X. L. Chen and K. Jiang, Photodegradation of diclofenac in seawater by simulated sunlight irradiation: The comprehensive effect of nitrate, Fe(iii) and chloride, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2017, 117, 386–391.
M. Fathinia and A. Khataee, Photocatalytic ozonation of phenazopyridine using TiO2nanoparticles coated on ceramic plates: Mechanistic studies, degradation intermediates and ecotoxicological assessments, Appl. Catal., A, 2015, 491, 136–154.
F. Parrino, G. Camera-Roda, V. Loddo, G. Palmisano and V. Augugliaro, Combination of ozonation and photocatalysis for purification of aqueous effluents containing formic acid as probe pollutant and bromide ion, Water Res., 2014, 50, 189–199.
A. R. Krishnan and S. Kanmani, A study on synergistic effect of photocatalysis and ozonation on textile wastewater treatment, Indian J. Environ. Prot., 2008, 28, 979–984.
A. C. Mecha, M. S. Onyango, A. Ochieng, C. J. S. Fourie and M. N. B. Momba, Synergistic effect of UV–vis and solar photocatalytic ozonation on the degradation of phenol in municipal wastewater: A comparative study, J. Catal., 2016, 341, 116–125.
T. Yang, J. Peng, Y. Zheng, X. He, Y. Hou, L. Wu and X. Fu, Enhanced photocatalytic ozonation degradation of organic pollutants by ZnO modified TiO2 nanocomposites, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 221, 223–234.
A. C. Mecha, M. S. Onyango, A. Ochieng and M. N. B. Momba, Ultraviolet and solar photocatalytic ozonation of municipal wastewater: Catalyst reuse, energy requirements and toxicity assessment, Chemosphere, 2017, 186, 669–676.
V. J. P. Vilar, C. C. Amorim, G. Li Puma, S. Malato and D. D. Dionysiou, Intensification of photocatalytic processes for niche applications in the area of water, wastewater and air treatment, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 310, 329–330.
M. S. Lucas, J. A. Peres, B. Y. Lan and G. Li Puma, Ozonation kinetics of winery wastewater in a pilot-scale bubble column reactor, Water Res., 2009, 43, 1523–1532.
B. Y. Lan, R. Nigmatullin and G. Li Puma, Ozonation kinetics of cork-processing water in a bubble column reactor, Water Res., 2008, 42, 2473–2482.
M. S. Lucas, J. A. Peres and G. Li Puma, Treatment of winery wastewater by ozone-based advanced oxidation processes (O3, O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2) in a pilot-scale bubble column reactor and process economics, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2010, 72, 235–241.
F. J. Beltrán, A. Aguinaco and J. F. García-Araya, Kinetic modelling of TOC removal in the photocatalytic ozonation of diclofenac aqueous solutions, Appl. Catal., B, 2010, 100, 289–298.
A. Aguinaco, F. J. Beltrán, J. F. García-Araya and A. Oropesa, Photocatalytic ozonation to remove the pharmaceutical diclofenac from water: Influence of variables, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 189–190, 275–282.
V. Naddeo, V. Belgiorno, D. Ricco and D. Kassinos, Degradation of diclofenac during sonolysis, ozonation and their simultaneous application, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2009, 16, 790–794.
M. S. Lucas, N. M. Reis and G. Li Puma, Intensification of ozonation processes in a novel, compact, multi-orifice oscillatory baffled column, Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 296, 335–339.
A. Dhenain, G. Mercier, J. F. Blais and M. Chartier, Combined column and cell flotation process for the treatment of PAH contaminated hazardous wastes produced by an aluminium production plant, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 165, 394–407.
J. Yianatos and F. Contreras, Particle entrainment model for industrial flotation cells, Powder Technol., 2010, 197, 260–267.
E. Amini, D. J. Bradshaw, J. A. Finch and M. Brennan, Influence of turbulence kinetic energy on bubble size in different scale flotation cells, Miner. Eng., 2013, 45, 146–150.
J. Meng, W. Xie, E. Tabosa, K. Runge and D. Bradshaw, Turbulence model development for flotation cells based on piezoelectric sensor measurements, Int. J. Miner. Process., 2016, 156, 116–126.
S. Ata and G. J. Jameson, The formation of bubble clusters in flotation cells, Int. J. Miner. Process., 2005, 76, 123–139.
R. R. Solís, F. J. Rivas, A. Martínez-Piernas and A. Agüera, Ozonation, photocatalysis and photocatalytic ozonation of diuron: Intermediates identification, Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 292, 72–81.
C. H. Wu and H. Y. Ng, Degradation of C.I. Reactive Red 2 (RR2) using ozone-based systems: Comparisons of decolorization efficiency and power consumption, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 152, 120–127.
S. P. Ghuge and A. K. Saroha, Catalytic ozonation for the treatment of synthetic and industrial effluents - Application of mesoporous materials: A review, J. Environ. Manage., 2018, 211, 83–102.
H. Yan, W. Chen, G. Liao, X. Li, S. Ma and L. Li, Activity assessment of direct synthesized Fe-SBA-15 for catalytic ozonation of oxalic acid, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2016, 159, 1–6.
O. Oputu, M. Chowdhury, K. Nyamayaro, O. Fatoki and V. Fester, Catalytic activities of ultra-small B-FeOOH nano-rods in ozonation of 4-chlorophenol, J. Environ. Sci., 2015, 35, 83–90.
L. Yuan, J. Shen, Z. Chen and X. Guan, Role of Fe/pumice composition and structure in promoting ozonation reactions, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 180, 707–714.
Y. Ren, Y. Chen, T. Zeng, J. Feng, J. Ma and W. A. Mitch, Influence of Bi-doping on Mn1–xBixFe2O4 catalytic ozonation of di-n-butyl phthalate, Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 283, 622–630.
Q. Dai, J. Wang, J. Yu, J. Chen, J. Wang and J. Chen, Catalytic ozonation for the degradation of acetylsalicylic acid in aqueous solution by magnetic CeO2 nanometer catalyst particles, Appl. Catal., B, 2014, 144, 686–693.
K. H. Hama Aziz, H. Miessner, S. Mueller, D. Kalass, D. Moeller, I. Khorshid and M. A. M. Rashid, Degradation of pharmaceutical diclofenac and ibuprofen in aqueous solution, a direct comparison of ozonation, photocatalysis, and non-thermal plasma, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 313, 1033–1041.
G. Gao, J. Shen, W. Chu, Z. Chen and L. Yuan, Mechanism of enhanced diclofenac mineralization by catalytic ozonation over iron silicate-loaded pumice, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2017, 173, 55–62.
F. J. Beltrán, P. Pocostales, P. Alvarez and A. Oropesa, Diclofenac removal from water with ozone and activated carbon, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 163, 768–776.
N. F. F. Moreira, C. A. Orge, A. R. Ribeiro, J. L. Faria, O. C. Nunes, M. F. R. Pereira and A. M. T. Silva, Fast mineralization and detoxification of amoxicillin and diclofenac by photocatalytic ozonation and application to an urban wastewater, Water Res., 2015, 87, 87–96.
Y. Jung, E. Hong, M. Kwon and J. W. Kang, A kinetic study of ozone decay and bromine formation in saltwater ozonation: Effect of O3dose, salinity, pH, and temperature, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 312, 30–38.
F. J. Beltrán, Ozone Reaction Kinetics for Water and Wastewater Systems, CRC Press, London, 1st edn, 2003.
M. M. Huber, S. Canonica, G. Y. Park and U. Von Gunten, Oxidation of pharmaceuticals during ozonation and advanced oxidation processes, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37, 1016–1024.
M. Saquib Hasnain, P. Rishishwar, S. Rishishwar, S. Ali and A. K. Nayak, Isolation and characterization of Linum usitatisimum polysaccharide to prepare mucoadhesive beads of diclofenac sodium, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 116, 162–172.
G. N. Lucena, R. C. Alves, M. P. Abuçafy, L. A. Chiavacci, I. C. da Silva, F. R. Pavan and R. C. G. Frem, Zn-based porous coordination solid as diclofenac sodium carrier, J. Solid State Chem., 2018, 260, 67–72.
M. D. G. De Luna, Murniati, W. Budianta, K. K. P. Rivera and R. O. Arazo, Removal of sodium diclofenac from aqueous solution by adsorbents derived from cocoa pod husks, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2017, 5, 1465–1474.
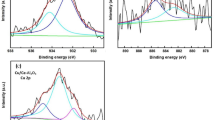
K. S. Finnie, D. J. Cassidy, J. R. Bartlett and J. L. Woolfrey, IR spectroscopy of surface water and hydroxyl species on nanocrystalline TiO2 films, Langmuir, 2001, 17, 816–820.
A. Hassani, A. Khataee, S. Karaca and M. Fathinia, Heterogeneous photocatalytic ozonation of ciprofloxacin using synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles on a montmorillonite support: Parametric studies, mechanistic analysis and intermediates identification, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 87569–87583.
A. Khataee, T. S. Rad and M. Fathinia, The role of clinoptilolite nanosheets in catalytic ozonation process: Insights into the degradation mechanism, kinetics and the toxicity, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2017, 77, 205–215.
J. F. García-Araya, F. J. Beltrán and A. Aguinaco, Diclofenac removal from water by ozone and photolytic TiO2 catalysed processes, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2010, 85, 798–804.
X. Li, W. Chen, Y. Tang and L. Li, Relationship between the structure of Fe-MCM-48 and its activity in catalytic ozonation for diclofenac mineralization, Chemosphere, 2018, 206, 615–621.
K. Hikmat, H. Aziz, H. Miessner, S. Mueller, D. Kalass, D. Moeller, I. Khorshid, M. Amin and M. Rashid, Degradation of pharmaceutical diclofenac and ibuprofen in aqueous solution, a direct comparison of ozonation, photocatalysis, and non-thermal plasma, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 313, 1033–1041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c8pp00308d
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lara-Ramos, J.A., Sánchez-Gómez, K., Valencia-Rincón, D. et al. Intensification of the O3/TiO2/UV advanced oxidation process using a modified flotation cell. Photochem Photobiol Sci 18, 920–928 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8pp00308d
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c8pp00308d