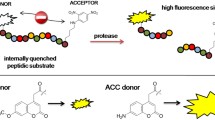
Abstract
Based on the widely applied fluorogenic peptide FS-6 (Mca-Lys-Pro-Leu-Gly-Leu-Dpa-Ala-Arg-NH2; Mca = methoxycoumarin-4-acetyl; Dpa = N-3-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)l-α,β-diaminopropionyl) a caged substrate peptide Ac-Lys-Pro-Leu-Gly-Lys*-Lys-Ala-Arg-NH2 (*, position of the cage group) for matrix metalloproteinases was synthesized and characterized. The synthesis implies the modification of a carbamidated lysine side-chain amine with a photocleavable 2-nitrobenzyl group. Mass spectrometry upon UV irradiation demonstrated the complete photolytic cleavage of the protecting group. Time-resolved laser-flash photolysis at 355 nm in combination with transient absorption spectroscopy determined the biphasic decomposition with τa = 171 ± 3 ms (79%) and τb = 2.9 ± 0.2 ms (21%) at pH 6.0 of the photo induced release of the 2-nitrobenzyl group. The recombinantly expressed catalytic domain of human membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP or MMP-14) was used to determine the hydrolysis efficiency of the caged peptide before and after photolysis. It turned out that the cage group sufficiently shields the peptide from peptidase activity, which can be thus controlled by UV light.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Tatsu, Y. Shigeri, S. Sogabe, N. Yumoto and S. Yoshikawa, Solid-Phase Synthesis of Caged Peptides Using Tyrosine Modified with a Photocleavable Protecting Group: Application to the Synthesis of Caged Neuropeptide Y Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996 227 688–693.
S. R. Adams and R. Y. Tsien, Controlling Cell Chemistry with Caged Compounds Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1993 55 755–784.
A. P. Pelliccioli and J. Wirz, Photoremovable protecting groups: reaction mechanisms and applications Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002 1 441–458.
G. C. R. Ellis-Davies, Caged compounds: photorelease technology for control of cellular chemistry and physiology Nat. Methods 2007 4 619–628.
H. T. Yu, J. B. Li, D. D. Wu, Z. J. Qiu and Y. Zhang, Chemistry and biological applications of photo-labile organic molecules Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010 39 464–473.
S. Abbruzzetti, E. Grandi, C. Viappiani, S. Bologna, B. Campanini, S. Raboni, S. Bettati and A. Mozzarelli, Kinetics of acid-induced spectral changes in the GFPmut2 chromophore J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005 127 626–635.
C. Tallant, A. Marrero, F. X. Gomis-Rüth, Matrix metalloproteinases: Fold and function of their catalytic domains Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010 1803 20–28.
G. Murphy and H. Nagase, Progress in matrix metalloproteinase research Mol. Aspects Med. 2008 29 290–308.
R. Visse and H. Nagase, Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry Circ. Res. 2003 92 827–839.
M. Grossman, B. Born, M. Heyden, D. Tworowski, G. B. Fields, I. Sagi and M. Havenith, Correlated structural kinetics and retarded solvent dynamics at the metalloprotease active site Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011 18 1102–1108.
H. Nagase and G. B. Fields, Human matrix metalloproteinase specificity studies using collagen sequence-based synthetic peptides Biopolymers 1996 40 399–416.
M. Heyden and M. Havenith, Combining THz spectroscopy and MD simulations to study protein-hydration coupling Methods 2010 52 74–83.
S. J. Kim, B. Born, M. Havenith and M. Gruebele, Real-time detection of protein-water dynamics upon protein folding by terahertz absorption spectroscopy Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008 47 6486–6489.
A. Jabaiah and P. S. Daugherty, Directed Evolution of Protease Beacons that Enable Sensitive Detection of Endogenous MT1-MMP Activity in Tumor Cell Lines Chem. Biol. 2011 18 392–401.
H. Nagase, R. Visse and G. Murphy, Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs Cardiovasc. Res. 2006 69 562–573.
V. Pelmenschikov and P. E. M. Siegbahn, Catalytic mechanism of matrix metalloproteinases: Two-layered ONIOM study Inorg. Chem. 2002 41 5659–5666.
H. Ogata, E. Decaneto, M. Grossman, M. Havenith, I. Sagi, W. Lubitz and M. Knipp, Crystalization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the catalytic domain of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase Acta Crystallogr., Sect. F: Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2014 70 232–235.
G. B. Fields, Using Fluorogenic Peptide Substrates to Assay Matrix Metalloproteinases Methods Mol. Biol. 2000 151 495–518.
R. C. Wahl, The calculation of initial velocity from product progress curves when [S]<<Km Anal. Biochem. 1994 383–384.
U. Neumann, H. Kubota, K. Frei, V. Ganu and D. Leppert, Characterization of Mca-Lys-Pro-Leu-Gly-Leu-Dpa-Ala-Arg-NH2, a fluorogenic substrate with increased specificity constants for collagenases and tumor necrosis factor converting enzyme Anal. Biochem. 2004 328 166–173.
S. Abbruzzetti, S. Sottini, C. Viappiani and J. E. T. Corrie, Kinetics of proton release after flash photolysis of 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl sulfate (caged sulfate) in aqueous solution J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005 127 9865–9874.
S. Abbruzzetti, E. Crema, L. Masino, A. Vecli, C. Viappiani, J. R. Small, L. J. Libertini and E. W. Small, Fast events in protein folding: structural volume changes accompanying the early events in the N → I transition of apomyoglobin induced by ultrafast pH jump Biophys. J. 2000 78 405–415.
I. Schechter and A. Berger, On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1967 27 157–162.
C. M. Overall and O. Kleifeld, Towards third generation matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for cancer therapy Br. J. Cancer 2006 94 941–946.
H. Matter and M. Schudok, Recent advances in the design of matrix metalloprotease inhibitors Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Dev. 2004 7 513–535.
J. M. Chen, F. C. Nelson, J. I. Levin, D. Mobilio, F. J. Moy, R. Nilakantan, A. Zask and R. Powers, Structure-Based Design of a Novel, Potent, and Selective Inhibitor for MMP-13 Utilizing NMR Spectroscopy and Computer-Aided Molecular Design J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000 122 9648–9654.
S. P. Gupta, and V. M. Patil, Specificity of Binding with Matrix Metalloproteinases, Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors, Springer, 2012.
C. Fernandez-Catalan, W. Bode, R. Huber, D. Turk, J. J. Calvete, A. Lichte, H. Tschesche and K. Maskos, Crystal structure of the complex formed by the membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase with the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2, the soluble progelatinase A receptor EMBO J. 1998 18 5238–5248.
I. Bertini, I. Calderone, M. Fragai, C. Luchinat, M. Maletta and K. J. Yeo, Snapshots of the Reaction Mechanism of Matrix Metalloproteinases Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2006 45 7952–7955.
J. Berman, M. Green, E. Sugg, R. Anderegg, D. S. Millington, D. L. Norwood, J. Mcgeehan and J. Wiseman, Rapid Optimization of Enzyme Substrates Using Defined Substrate Mixtures J. Biol. Chem. 1992 267 1434–1437.
Y. Tatsu, Y. Shigeri, A. Ishida, K. Isamu, H. Fujisawa and N. Yumoto, Synthesis of caged peptides using caged lysine: Application to the synthesis of caged AIP, a highly specific inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999 9 1093–1096.
Y. Shigeri, Y. Tatsu and N. Yumoto, Synthesis and application of caged peptides and proteins Pharmacol. Ther. 2001 91 85–92.
S. Walbert, W. Pfleiderer and U. E. Steiner, Photolabile Protecting Groups for Nucleosides: Mechanistic Studies of the 2-(2-Nitrophenyl)ethyl Group Helv. Chim. Acta 2001 84 1601–1611.
R. A. McClelland and S. Steenken, Pronounced solvent effect on the absorption spectra of the photochemically produced 2,4-dinitrobenzyl carbanion Can. J. Chem. 1987 65 353–356.
S. J. Atherton and B. B. Craig, Laser photolysis of 2,6-dinitrotoluene in solution Chem. Phys. Lett. 1986 127 7–12.
M. Schwörer and J. Wirz, Photochemical Reaction Mechanisms of 2-Nitrobenzyl Compounds in Solution, I. 2-Nitrotoluene: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Parameters of the aci-Nitro Tautomer Helv. Chim. Acta 2001 84 1441–1458.
M. Gutman and E. Nachliel, The dynamic aspects of proton transfer processes Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990 1015 391–414.
M. Carcelli, P. Pelagatti and C. Viappiani, Determination of the pKa of the Aci-Nitro Intermediate in o-Nitrobenzyl Systems Isr. J. Chem. 1998 38 213–221.
S. Abbruzzetti, M. Carcelli, D. Rogolino and C. Viappiani, Deprotonation yields, pKa, and aci-nitro decay rates in some substituted o-nitrobenzaldehydes Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2003 2 796–800.
A. Barth and J. E. T. Corrie, Characterization of a new caged proton capable of inducing large pH jumps Biophys. J. 2002 83 2864–2871.
J. E. T. Corrie, T. Furuta, R. Givens, A. L. Yousef, and M. Goeldner, Photoremovable Protecting Groups Used for the Caging of Biomolecules, in Dynamic Studies in Biology, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2005, pp. 1–94.
M. Caplow, Kinetics of carbamate formation and breakdown J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968 90 6795–6803.
J. E. Corrie, A. DeSantis, Y. Katayama, K. Khodakhah, J. B. Messenger, D. C. Ogden and D. R. Trentham, Postsynaptic activation at the squid giant synapse by photolytic release of L-glutamate from a ‘caged’ L-glutamate J. Physiol. 1993 465 1–8.
M. Schwörer and J. Wirz, Photochemical reaction mechanism of 2-nitrobenzyl compounds in solution. 1. 2-Nitrotoluene: Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters of the aci-nitro tautomer Helv. Chim. Acta 2001 84 551–606.
Y. V. Il’ichev and J. Wirz, Rearrangements of 2-Nitrobenzyl Compounds. 1. Potential Energy Surface of 2-Nitrotoluene and Its Isomers Explored with ab Initio and Density Functional Theory Methods J. Phys. Chem. A 2000 104 7856–7870.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Decaneto, E., Abbruzzetti, S., Heise, I. et al. A caged substrate peptide for matrix metalloproteinases. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14, 300–307 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4pp00297k
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c4pp00297k