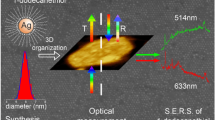
Abstract
Fabrication of dense two-dimensional assemblies consisting of gold(core)—silver(shell) nanoparticles and the resulting peculiar surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) activity are reported. The assemblies were prepared via assembly at air—toluene interfaces by drop-casting toluene solutions containing the nanoparticles protected with octadecylamine molecules onto glass plates. This simple process, which does not require special apparatus or significant fabrication time, leads to uniform assemblies over vast areas (∼34 cm2). In the SERS measurements, the high spatial reproducibility of the SERS signals from p-aminothiophenol adsorbed on the assemblies over vast areas demonstrates that this method is useful for the quantitative investigation of SERS mechanisms. Under 532 nm laser excitation, the difference in the enhancement factors of the SERS signals at the a1 mode between assemblies consisting of gold, silver, and core—shell nanoparticles can be explained by the degree of overlap of the excitation wavelength with their plasmon coupling modes. In contrast, under 785 nm excitation, even though the plasmon band of the core—shell nanoparticle assemblies does not significantly overlap with the excitation wavelength as compared with that of gold nanoparticle assemblies, the enhancement factor from the core—shell nanoparticle assemblies was stronger than those from the gold nanoparticle assemblies. Therefore, we have demonstrated that the gold(core)—silver(shell) nanoparticle assemblies are excellent SERS active materials, which have strong electromagnetic mechanism (EM) as well as chemical mechanism (CM) effects due to the silver shells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes and references
M. Fleischmann, P. J. Hendra, A. J. McQuillan, Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1974, 26, 163–166.
D. A. Stuart, J. M. Yuen, N. Shah, O. Lyandres, C. R. Yonzon, M. R. Glucksberg, J. T. Walsh, R. P. Van Duyne, In vivo glucose measurement by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, Anal. Chem., 2006, 78, 7211–7215.
S. Nie and S. R. Emory, Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering, Science, 1997, 275, 1102–1106.
K. Kneipp, Y. Wang, H. Kneipp, L. T. Perelman, I. Itzkan, R. R. Dasari and M. S. Feld, Single molecule detection using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), Phys. Rev. Lett., 1997, 78, 1667–1670.
A. M. Michaels, J. Jiang and L. Brus, Ag nanocrystal junctions as the site for surface-enhanced Raman scattering of single rhodamine 6G molecules, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, 11965–11971.
L. Brus, Noble metal nanocrystals: plasmon electron transfer photochemistry and single-molecule Raman spectroscopy, Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41, 1742–1749.
A. Campion and P. Kambhampati, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering, Chem. Soc. Rev., 1998, 27, 241–250.
R. Que, M. Shao, S. Zhuo, C. Wen, S. Wang, S.-T. Lee, Highly reproducible surface-enhanced Raman scattering on a capillarity-assisted gold nanoparticle assembly, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011, 21, 3337–3343.
H. Wang, S. Levin and N. J. Halas, Nanosphere arrays with controlled sub-10-nm gaps as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 14992–14993.
W. Lee, S. Y. Lee, R. M. Brider and O. Rabin, Self-assembled SERS substrates with tunable surface plasmon resonances, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011, 21, 3424–3429.
V. Liberman, C. Yilmaz, T. M. Bloomstein, S. Somu, Y. Echegoyen, A. Busnaina, S. G. Cann, K. E. Krohn, M. F. Marchant and M. Rothschild, A nanoparticle convective directed assembly process for the fabrication of periodic surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 4298–4302.
Q. Shao, R. Que, L. Cheng and M. Shao, Fast one-step silicon–hydrogen bond assembly of silver nanoparticles as excellent surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates, RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 1762–1764.
C. A. Smyth, I. Mirza, J. G. Lunney, E. M. McCabe, Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) using Ag nanoparticle films produced by pulsed laser deposition, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 264, 31–35.
X. Ke, B. Lu, J. Hao, J. Zhang, H. Qiao, Z. Zhang, C. Xing, W. Yang, B. Zhang and J. Tang, Facile fabrication of SERS arrays through galvanic replacement of silver onto electrochemically deposited copper micropatterns, ChemPhysChem, 2012, 13, 3786–3789.
J.-C. Bian, Z.-D. Chen, Z. Li, F. Yang, H.-Y. He, J. Wang, J. Z. Y. Tan, J.-L. Zeng, R.-Q. Peng, X.-W. Zhang, G.-R. Han, Electrodeposition of hierarchical Ag nanostructures on ITO glass for reproducible and sensitive SERS application, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, 258, 6632–6636.
G. Haran, Single-molecule Raman spectroscopy: A probe of surface dynamics and plasmonic fields, Acc. Chem. Res., 2010, 43, 1135–1143.
J. P. Camden, J. A. Dieringer, Y. Wang, D. J. Masiello, L. D. Marks, G. C. Schatz, R. P. Van Duyne, Probing the structure of single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman scattering hot spots, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 12616–12617.
G. Braun, I. Pavel, A. R. Morrill, D. S. Seferos, G. C. Bazan, N. O. Reich and M. Moskovits, Chemically patterned microspheres for controlled nanoparticle assembly in the construction of SERS hot spots, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 7760–7761.
A. Chen, A. E. DePrince III, A. Demortiére, A. Joshi-Imre, E. V. Shevchemko, S. K. Gray, U. Welp, V. K. Vlasko-Vlasov, Self-assembled large Au nanoparticle arrays with regular hot spots for SERS, Small, 2011, 7, 2365–2371.
S. Yun, M. K. Oh, S. K. Kim and S. Park, Linker-molecule-free gold nanorod films, Effect of nanorod size on surface enhanced Raman scattering, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 13551–13557.
M. Suzuki, Y. Niidome, N. Terasaki, K. Inoue, Y. Kuwahara and S. Yamada, Surface-enhanced nonresonance Raman scattering of rhodamine 6G molecules adsorbed on gold nanorod films, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 43, L554–L556.
M. A. Mahmoud, C. E. Tabor, M. A. El-Sayed, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering enhancement by aggregated silver nanocube monolayers assembled by the Langmuir–Blodgett technique at different surface pressures, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 5493–5501.
N. Ahamad and A. Ianoul, Using phospholipids to control interparticle distance in SERS-active substrates, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 3587–3594.
A. Sánchez-Iglesias, P. Aldeanueva-Potel, W. Ni, J. Pérez-Juste, I. Pastoriza-Santos, R. A. Alvarez-Puebla, B. N. Mbenkum, L. M. Liz-Marzán, Chemical seeded growth of Ag nanoparticle arrays and their application as reproducible SERS substrates, Nano Today, 2010, 5, 21–27.
T. Arakawa, T. Munaoka, T. Akiyama and S. Yamada, Effects of silver nanoparticles on photoelectrochemical responses of organic dyes, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 11830–11835.
K. Sugawa and Y. Tanoue, Simple fabrication of two-dimensional self-assemblies consisting of gold and silver nanoparticles at an air/toluene interface and their surface-enhanced Raman scattering activity, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2012, 51, 06FG10.
T. P. Bigioni, X.-M. Lin, T. T. Nguyen, E. I. Corwin, T. A. Witten and H. M. Jaeger, Kinetically driven self assembly of highly ordered nanoparticle monolayers, Nat. Mater., 2006, 5, 265–270.
L. Lu, H. Wang, Y. Zhou, S. Xi, H. Zhang, J. Hu and B. Zhao, Seed-mediated growth of large, monodisperse core–shell gold–silver nanoparticles with Ag-like optical properties, Chem. Commun., 2002, 144–145.
N. R. Jana, Silver coated gold nanoparticles as new surface enhanced Raman substrate at low analyte concentration, Analyst, 2003, 128, 954–956.
S. Pande, S. K. Ghosh, S. Praharaj, S. Panigrahi, S. Basu, S. Jana, A. Pal, T. Tsukuda and T. Pal, Synthesis of normal and inverted gold–silver core–shell architectures in β-cyclodextrin and their applications in SERS, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 10806–10813.
S. Pande, J. Chowhury and T. Pal, Understanding the enhancement mechanisms in the surface-enhanced Raman spectra of the 1,10-phenanthroline molecule adsorbed on a Au@Ag bimetallic nanocolloid, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 10497–10509.
M. Mandal, N. R. Jana, S. Kundu, S. K. Ghosh, M. Panigrahi and T. Pal, Synthesis of Aucore–Agshell type bimetallic nanoparticles for single molecule detection in solution by SERS method, J. Nanopart. Res., 2004, 6, 53–61.
J. Turkevich, P. C. Stevenson and J. Hiller, A study of the nucleation on and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold, J. Discuss Faraday Soc., 1951, 11, 55–75.
W. Wang, S. Efrima and O. Regev, Directing oleate stabilized nanosized silver colloids into organic phases, Langmuir, 1998, 14, 602–610.
T. Y. Olson, A. M. Schwartzberg, C. A. Orme, C. E. Talley, B. O’Connell and J. Z. Zhang, Hollow gold-silver double-shell nanospheres: structure, optical absorption, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 6319–6329.
K. Sugawa, Y. Tanoue, D. Tanaka and T. Sakai, Facile phase transfer of gold and Au-core/Ag-shell nanoparticles from aqueous to toluene solution using alkylamine molecules and their assemblies on solid supports, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 50, 04DH14.
L.-B. Zhao, R. Huang, Y.-F. Huang, D.-Y. Wu and B. Ren, Photon-driven charge transfer and Herzberg-Teller vibronic coupling mechanism in surface-enhanced Raman scattering of p-aminothiophenol adsorbed on coinage metal surfaces: a density functional theory study, J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135, 134707.
N. Djaker, R. Hostein, E. Devaux, T. W. Ebbesen, H. Rigneault and J. Wenger, Surface enhanced Raman scattering on a single nanometric aperture, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 16250–16256.
P. M. Jais, D. B. Murray, R. Merlin and A. V. Bragas, Metal nanoparticle ensembles: tunable laser pulses distinguish monomer from dimer vibrations, Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 3685–3689.
P. J. G. Goulet, D. S. dos Santos, R. A. Alvarez-Puebla, O. N. Oliveira and R. F. Aroca, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering on dendrimer/metallic nanoparticle layer-by-layer film substrates, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 5576–5581.
S. Underwood and P. Mulvaney, Effect of the solution refractive index on the color of gold colloids, Langmuir, 1994, 10, 3427–3430.
M. Fan and A. G. Brolo, Silver nanoparticles self assembly as SERS substrates with near single molecule detection limit, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11, 7381–7389.
Y.-F. Huang, D.-Y. Wu, H.-P. Zhu, L.-B. Zhao, G.-K. Liu, B. Ren, Z.-Q. Tian, Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic study of p-aminothiophenol, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 8485–8497.
K. Uetsuki, T. Yano, Y. Saito, T. Ichimura and S. Kawata, Experimental identification of chemical effects in surface enhanced Raman scattering of 4-aminothiophenol, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 7515–7520.
K. Kim and H. S. Lee, Effect of Ag and Au nanoparticles on the SERS of 4-aminobenzenethiol assembled on powdered copper, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 18929–18934.
M. Baia, F. Toderas, L. Baia, J. Popp and S. Astilean, Probing the enhancement mechanisms of SERS with p-aminothiophenol molecules adsorbed on self-assembled gold colloidal nanoparticles, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2006, 422, 127–132.
L. Zhang, Self-assembly Ag nanoparticle monolayer film as SERS substrate for pesticide detection, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 270, 292–294.
W. B. Cai, B. Ren, X. Q. Li, C. X. She, F. M. Liu, X. W. Cai and Z. Q. Tian, Investigation of surface-enhanced Raman scattering from platinum electrodes using a confocal Raman microscope: dependence of surface roughening pretreatment, Surf. Sci., 1998, 406, 9–22.
E. J. Smythe, M. D. Dickey, J. Bao, G. M. Whitesides and F. Capasso, Optical antenna arrays on a fiber facet for in situ surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection, Nano Lett., 2009, 9, 1132–1138.
Y. Wang, X. Zou, W. Ren, W. Wang and E. Wang, Effect of silver nanoplates on Raman spectra of p-aminothiophenol assembled on smooth macroscopic gold and silver surface, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 3259–3265.
M. Osawa, N. Matsuda, K. Yoshii and I. Uchida, Charge transfer resonance Raman process in surface-enhanced Raman scattering from p-aminothiophenol adsorbed on silver: Herzberg-Teller contribution, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, 12702–12707.
Q. Zhou, Y. Chao, Y. Li, W. Xu, Y. Wu and J. Zheng, Contribution of charge-transfer mechanisms to surface-enhanced Raman scattering with near-IR excitation, ChemPhysChem, 2007, 8, 921–925.
K. Kim and J. K. Yoon, Raman scattering of 4-aminobenzenethiol sandwiched between Ag/Au nanoparticle macroscopically smooth Au substrate, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 20731–20736.
W. Ji, Y. Kitahama, X. Xue, B. Zhao and Y. Ozaki, Generation of pronounced resonance profile of charge-transfer contributions to surface-enhanced Raman scattering, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116, 2515–2520.
J. R. Lombardi and R. L. Birke, A unified view of surface-enhanced Raman scattering, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, 734–742.
A. P. Richer, J. R. Lombardi and B. Zhao, Size and wavelength dependence of the charge-transfer contributions to surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy in Ag/PATP/ZnO junctions, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 1610–1614.
J. R. Lombardi and R. L. Birke, A unified approach to surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 5605–5617.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Extinction spectra of colloidal aqueous solution, normalized extinction spectra of colloidal toluene solutions of metal nanoparticles after phase transfer, cross-sectional SEM images of nanoparticle assemblies, and AFM images of the assemblies. See DOI: 10.1039/c3pp50281c
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugawa, K., Tanoue, Y., Ube, T. et al. Fabrication of dense two-dimensional assemblies over vast areas comprising gold(core)—silver(shell) nanoparticles and their surface-enhanced Raman scattering properties. Photochem Photobiol Sci 13, 82–91 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3pp50281c
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c3pp50281c