Abstract
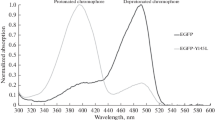
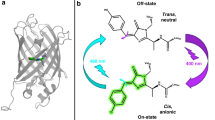
Photochromic (i.e. reversibly photoswitchable) fluorescent proteins increasingly find applications as biomarkers for advanced bioimaging applications. From a mechanistic point of view, photochromicity usually stems from the reversible cis-trans photoisomerization of the chromophore. We demonstrated experimentally that cis-trans photoisomerization constitutes a very efficient deactivation pathway of isolated chromophores upon visible light excitation. Nonetheless, this intrinsic property is seldom displayed by chromophores in the folded protein structure. We found that the E222Q amino acid replacement restores efficient photochromicity in otherwise poorly switchable green fluorescent protein variants of different optical properties. Glutamic acid 222 is known to play a pivotal role in the inner proton wires that involve the GFP chromophore and the surrounding residues. Hence its substitution with an isosteric but non-ionizable residue presumably leads to a extensive rewiring of proton pathways around the chromophore, which has a deep effect also on the photochromic properties. In this work, we review and discuss the main photophysical properties of photochromic E222Q GFP mutants. Additionally we show, by means of flash-photolysis experiments, that chromophore cis to trans photoswitching involves a molecular mechanism where stereochemical isomerization and chromophore protonation occur in a coordinated way. Such a “concerted” mechanism is, in our opinion, at the basis of efficient photochromic behavior and might be activated by the E222Q mutation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes and references
R. M. Wachter, Chromogenic cross-link formation in green fluorescent protein, Acc. Chem. Res., 2007, 40, 120–127.
D. M. Chudakov, S. Lukyanov, K. A. Lukyanov, Fluorescent proteins as a toolkit for in vivo imaging, Trends Biotechnol., 2005, 23, 605–613.
S. Habuchi, P. Dedecker, J. Hotta, C. Flors, R. Ando, H. Mizuno, A. Miyawaki, J. Hofkens, Photo-induced protonation/deprotonation in the GFP-like fluorescent protein Dronpa: mechanism responsible for the reversible photoswitching, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2006, 5, 567–576.
K. A. Lukyanov, D. M. Chudakov, S. Lukyanov, V. V. Verkhusha, Innovation: Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2005, 6, 885–891.
J. Lippincott-Schwartz, G. H. Patterson, Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins for diffraction-limited and super-resolution imaging, Trends Cell Biol., 2009, 19, 555–565.
M. Fernandez-Suarez, A. Y. Ting, Fluorescent probes for super-resolution imaging in living cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2008, 9, 929–943.
R. Ando, H. Mizuno, A. Miyawaki, Regulated fast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling observed by reversible protein highlighting, Science, 2004, 306, 1370–1373.
R. Bizzarri, M. Serresi, F. Cardarelli, S. Abbruzzetti, B. Campanini, C. Viappiani, F. Beltram, Single amino acid replacement makes Aequorea victoria fluorescent proteins reversibly photoswitchable, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 85–95.
E. Betzig, G. H. Patterson, R. Sougrat, O. W. Lindwasser, S. Olenych, J. S. Bonifacino, M. W. Davidson, J. Lippincott-Schwartz, H. F. Hess, Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution, Science, 2006, 313, 1642–1645.
S. T. Hess, T. P. Girirajan, M. D. Mason, Ultra-high resolution imaging by fluorescence photoactivation localization microscopy, Biophys. J., 2006, 91, 4258–4272.
M. Andresen, A. C. Stiel, J. Folling, D. Wenzel, A. Schonle, A. Egner, C. Eggeling, S. W. Hell, S. Jakobs, Photoswitchable fluorescent proteins enable monochromatic multilabel imaging and dual color fluorescence nanoscopy, Nat. Biotechnol., 2008, 26, 1035–1040.
S. Habuchi, R. Ando, P. Dedecker, W. Verheijen, H. Mizuno, A. Miyawaki, J. Hofkens, Reversible single-molecule photoswitching in the GFP-like fluorescent protein Dronpa, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2005, 102, 9511–9516.
M. Andresen, A. C. Stiel, S. Trowitzsch, G. Weber, C. Eggeling, M. C. Wahl, S. W. Hell, S. Jakobs, Structural basis for reversible photoswitching in Dronpa, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2007, 104, 13005–13009.
H. Mizuno, T. K. Mal, M. Walchli, A. Kikuchi, T. Fukano, R. Ando, J. Jeyakanthan, J. Taka, Y. Shiro, M. Ikura, A. Miyawaki, Light-dependent regulation of structural flexibility in a photochromic fluorescent protein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, 105, 9227–9232.
J. N. Henderson, H. W. Ai, R. E. Campbell, S. J. Remington, Structural basis for reversible photobleaching of a green fluorescent protein homologue, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2007, 104, 6672–6677.
M. Andresen, M. C. Wahl, A. C. Stiel, F. Grater, L. V. Schafer, S. Trowitzsch, G. Weber, C. Eggeling, H. Grubmuller, S. W. Hell, S. Jakobs, Structure and mechanism of the reversible photoswitch of a fluorescent protein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2005, 102, 13070–13074.
R. A. G. Cinelli, V. Pellegrini, A. Ferrari, P. Faraci, R. Nifosi, M. Tyagi, M. Giacca, F. Beltram, Green fluorescent proteins as optically controllable elements in bioelectronics, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 79, 3353–3355.
R. Nifosi, A. Ferrari, C. Arcangeli, V. Tozzini, V. Pellegrini, F. Beltram, Photoreversible dark state in a tristable green fluorescent protein variant, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107, 1679–1684.
S. Luin, V. Voliani, G. Lanza, R. Bizzarri, P. Amat, V. Tozzini, M. Serresi, F. Beltram, Raman study of chromophore states in photochromic fluorescent proteins, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 96–103.
N. C. Shaner, P. A. Steinbach, R. Y. Tsien, A guide to choosing fluorescent proteins, Nat. Methods, 2005, 2, 905–909.
A. Miyawaki, Innovations in the imaging of brain functions using fluorescent proteins, Neuron, 2005, 48, 189–199.
W. Cheng, F. Yang, C. L. Takanishi, J. Zheng, Thermosensitive TRPV channel subunits coassemble into heteromeric channels with intermediate conductance and gating properties, J. Gen. Physiol., 2007, 129, 191–207.
S. Abbruzzetti, S. Sottini, C. Viappiani, J. E. Corrie, Kinetics of proton release after flash photolysis of 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl sulfate (caged sulfate) in aqueous solution, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 9865–9874.
S. Abbruzzetti, S. Bruno, S. Faggiano, E. Grandi, A. Mozzarelli, C. Viappiani, Time-resolved methods in Biophysics. 2. Monitoring haem proteins at work with nanosecond laser flash photolysis, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2006, 5, 1109–1120.
A. Banderini, S. Sottini, C. Viappiani, Method for acquiring extended real-time kinetic signals in nanosecond laser flash photolysis experiments, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2004, 75, 2257–2261.
V. Voliani, R. Bizzarri, R. Nifosi, S. Abbruzzetti, E. Grandi, C. Viappiani, F. Beltram, Cis-trans photoisomerization of fluorescent-protein chromophores, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112, 10714–10722.
X. He, A. F. Bell, P. J. Tonge, Ground state isomerization of a model green fluorescent protein chromophore, FEBS Lett., 2003, 549, 35–38.
A. A. Voityuk, M. E. Michel-Beyerle, N. Rosch, Structure and rotation barriers for ground and excited states of the isolated chromophore of the green fluorescent protein, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1998, 296, 269–276.
N. Reuter, H. Lin, W. Thiel, Green fluorescent proteins: Empirical force field for the neutral and deprotonated forms of the chromophore. Molecular dynamics simulation’s of the wild type and S65T mutant, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106, 6310–6321.
J. Dong, F. Abulwerdi, A. Baldridge, J. Kowalik, K. M. Solntsev, L. M. Tolbert, Isomerization in fluorescent protein chromophores involves addition/elimination, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 14096–14098.
J. S. Yang, G. J. Huang, Y. H. Liu, S. M. Peng, Photoisomerization of the green fluorescence protein chromophore and the meta- and para-amino analogues, Chem. Commun., 2008, 1344–1346.
W. Weber, V. Helms, J. A. McCammon, P. W. Langhoff, Shedding light on the dark and weakly fluorescent states of green fluorescent proteins, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1999, 96, 6177–6182.
A. C. Stiel, S. Trowitzsch, G. Weber, M. Andresen, C. Eggeling, S. W. Hell, S. Jakobs, M. C. Wahl, 1.8 A bright-state structure of the reversibly switchable fluorescent protein Dronpa guides the generation of fast switching variants, Biochem. J., 2007, 402, 35–42.
R. Ando, C. Flors, H. Mizuno, J. Hofkens, A. Miyawaki, Highlighted generation of fluorescence signals using simultaneous two-color irradiation on Dronpa mutants, Biophys. J., 2007, 92, L97–L99.
V. Adam, M. Lelimousin, S. Boehme, G. Desfonds, K. Nienhaus, M. J. Field, J. Wiedenmann, S. McSweeney, G. U. Nienhaus, D. Bourgeois, Structural characterization of IrisFP, an optical highlighter undergoing multiple photo-induced transformations, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, 105, 18343–18348.
M. Lelimousin, M. Noirclerc-Savoye, C. Lazareno-Saez, B. Paetzold, S. Le Vot, R. Chazal, P. Macheboeuf, M. J. Field, D. Bourgeois, A. Royant, Intrinsic dynamics in ECFP and Cerulean control fluorescence quantum yield, Biochemistry, 2009, 48, 10038–10046.
R. M. Dickson, A. B. Cubitt, R. Y. Tsien, W. E. Moerner, On/off blinking and switching behaviour of single molecules of green fluorescent protein, Nature, 1997, 388, 355–358.
T. B. McAnaney, W. Zeng, C. F. Doe, N. Bhanji, S. Wakelin, D. S. Pearson, P. Abbyad, X. Shi, S. G. Boxer, C. R. Bagshaw, Protonation, Photobleaching, and Photoactivation of Yellow Fluorescent Protein (YFP 10C): A Unifying Mechanism, Biochemistry, 2005, 44, 5510–5524.
G. Chirico, A. Diaspro, F. Cannone, M. Collini, S. Bologna, V. Pellegrini, F. Beltram, Selective Fluorescence Recovery after Bleaching of Single E2GFP Proteins Induced by Two-Photon Excitation, ChemPhysChem, 2005, 6, 328–335.
G. S. Harms, L. Cognet, P. H. Lommerse, G. A. Blab, T. Schmidt, Autofluorescent proteins in single-molecule research: applications to live cell imaging microscopy, Biophys. J., 2001, 80, 2396–2408.
J. S. Biteen, M. A. Thompson, N. K. Tselentis, G. R. Bowman, L. Shapiro, W. E. Moerner, Super-resolution imaging in live Caulobacter crescentus cells using photoswitchable EYFP, Nat. Methods, 2008, 5, 947–949.
R. Nifosi, V. Tozzini, Cis-trans photolsomerization of the chromophore in the green fluorescent protein variant E(2)GFP: A molecular dynamics study, Chem. Phys., 2006, 323, 358–368.
R. Bizzarri, C. Arcangeli, D. Arosio, F. Ricci, P. Faraci, F. Cardarelli, F. Beltram, Development of a novel GFP-based ratiometric excitation and emission pH indicator for intracellular studies, Biophys. J., 2006, 90, 3300–3314.
R. Bizzarri, R. Nifosi, S. Abbruzzetti, W. Rocchia, S. Guidi, D. Arosio, G. Garau, B. Campanini, E. Grandi, F. Ricci, C. Viappiani, F. Beltram, Green Fluorescent Protein Ground States: The Influence of a Second Protonation Site near the Chromophore(), Biochemistry, 2007, 46, 5494–5504.
M. Serresi, R. Bizzarri, F. Cardarelli, F. Beltram, Real-time measurement of endosomal acidification by a novel genetically encoded biosensor, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2009, 393, 1123–1133.
G. Jung, A. Zumbusch, Improving autofluorescent proteins: comparative studies of the effective brightness of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) mutants, Microsc. Res. Tech., 2006, 69, 175–185.
G. Jung, C. Brauchle, A. Zumbusch, Two-color fluorescence correlation spectroscopy of one chromophore: Application to the E222Q mutant of the green fluorescent protein, J. Chem. Phys., 2001, 114, 3149–3156.
C. Bosisio, V. Quercioli, M. Collini, L. D’Alfonso, G. Baldini, S. Bettati, B. Campanini, S. Raboni, G. Chirico, Protonation and conformational dynamics of GFP mutants by two-photon excitation fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112, 8806–8814.
P. Dedecker, J. Hotta, R. Ando, A. Miyawaki, Y. Engelborghs, J. Hofkens, Fast and reversible photoswitching of the fluorescent protein dronpa as evidenced by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, Biophys. J., 2006, 91, L45–47.
J. J. van Thor, T. Gensch, K. J. Hellingwerf, L. N. Johnson, Phototransformation of green fluorescent protein with UV and visible light leads to decarboxylation of glutamate 222, Nat. Struct. Biol., 2002, 9, 37–41.
G. Jung, J. Wiehler, A. Zumbusch, The photophysics of green fluorescent protein: influence of the key amino acids at positions 65, 203, and 222, Biophys. J., 2005, 88, 1932–1947.
S. Abbruzzetti, E. Grandi, C. Viappiani, S. Bologna, B. Campanini, S. Raboni, S. Bettati, A. Mozzarelli, Kinetics of acid-induced spectral changes in the GFPmut2 chromophore, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 626–635.
S. Violot, P. Carpentier, L. Blanchoin, D. Bourgeois, Reverse pH-dependence of chromophore protonation explains the large Stokes shift of the red fluorescent protein mKeima, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 10356–10357.
S. Pletnev, D. Shcherbo, D. M. Chudakov, N. Pletneva, E. M. Merzlyak, A. Wlodawer, Z. Dauter, V. Pletnev, A crystallographic study of bright far-red fluorescent protein mKate reveals pH-induced cis-trans isomerization of the chromophore, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, 283, 28980–28987.
M. Irie, Diarylethenes for memories and switches, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 1685–1716.
G. H. Patterson, S. M. Knobel, W. D. Sharif, S. R. Kain, D. W. Piston, Use of the green fluorescent protein and its mutants in quantitative fluorescence microscopy, Biophys. J., 1997, 73, 2782–2790.
D. Sinnecker, P. Voigt, N. Hellwig, M. Schaefer, Reversible photobleaching of enhanced green fluorescent proteins, Biochemistry, 2005, 44, 7085–7094.
L. V. Schafer, G. Groenhof, M. Boggio-Pasqua, M. A. Robb, H. Grubmuller, Chromophore protonation state controls photoswitching of the fluoroprotein asFP595, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2008, 4, e1000034.
K. Brejc, T. K. Sixma, P. A. Kitts, S. R. Kain, R. Y. Tsien, M. Ormo, S. J. Remington, Structural basis for dual excitation and photoisomerization of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1997, 94, 2306–2311.
T. Brakemann, G. Weber, M. Andresen, G. Groenhof, A. C. Stiel, S. Trowitzsch, C. Eggeling, H. Grubmuller, S. W. Hell, M. C. Wahl, S. Jakobs, Molecular basis of the light-driven switching of the photochromic fluorescent protein Padron, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, 285, 14603–14609.
S. Olsen, K. Lamothe, T. J. Martinez, Protonic gating of excited-state twisting and charge localization in GFP chromophores: a mechanistic hypothesis for reversible photoswitching, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 1192–1193.
A. R. Faro, V. Adam, P. Carpentier, C. Darnault, D. Bourgeois, E. de Rosny, Low-temperature switching by photoinduced protonation in photochromic fluorescent proteins, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2010, 9, 254–262.
S. L. C. Moors, S. Michielssens, C. Flors, P. Dedecker, J. Hofkens, A. Ceulemans, How is cis-trans isomerization controlled in Dronpa mutants? A replica exchange molecular dynamics study, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2008, 4, 1012–1020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published as part of a themed issue on photofunctional proteins: from understanding to engineering.
‡ Stefania Abbruzzetti and Ranieri Bizzarri contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbruzzetti, S., Bizzarri, R., Luin, S. et al. Photoswitching of E222Q GFP mutants: “concerted” mechanism of chromophore isomerization and protonation. Photochem Photobiol Sci 9, 1307–1319 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0pp00189a
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c0pp00189a